CNC machining is an essential part of modern manufacturing, revolutionizing the way parts are manufactured across many industries. This technology greatly improves the efficiency and accuracy of machined parts, enabling more complex and precise designs. There are different types of CNC machines with different axis configurations, which are used for specific purposes according to the design and requirements of the part. In this guide, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining and the differences between them.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe difference between 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining
The main difference between 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining is the range of motion. On 3-axis CNC mills, the cutting tool orientation remains constant throughout the cutting path, while on 4- and 5-axis mills, the workpiece can also move. AN-Prototype summarizes the range of motion for 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling machines:
- 3-axis with X, Y, Z axes
- 4-axis with X, Y, Z and A axes
- 5-axis with X, Y, Z, B and C axes
What is an "axis"?
The most basic linear axes of a CNC machine tool are the X, Y, and Z axes. CNC machines use computer software to control the movement of cutting tools around a workpiece. Axes are used to describe motion along a given path. Let’s imagine the following, the X axis will be parallel to the front of your body, moving from left to right and possibly right to left. The Y axis is the direction perpendicular to you (forward and backward), while the Z axis is vertical. On a typical CNC mill, the table moves in the X/Y plane. The spindle, which holds the cutting tool, moves on the Z axis. Note that the cutting tool rotates in the spindle, but this rotational motion is not considered an axis of motion. These ranges of motion define a three-dimensional space in which the CNC cutting tool performs the cutting operation. All CNC machines are built around these basic axes for every hole, cut and feature machined. Today, more advanced CNC machines add a fourth or fifth axis to expand even more machining without resetting the workpiece. In fact, the first step in most CNC projects is to “zero” the axes. This is the process of telling the CNC machine where the material is to get the most accurate end product.
What is 3-axis CNC machining?
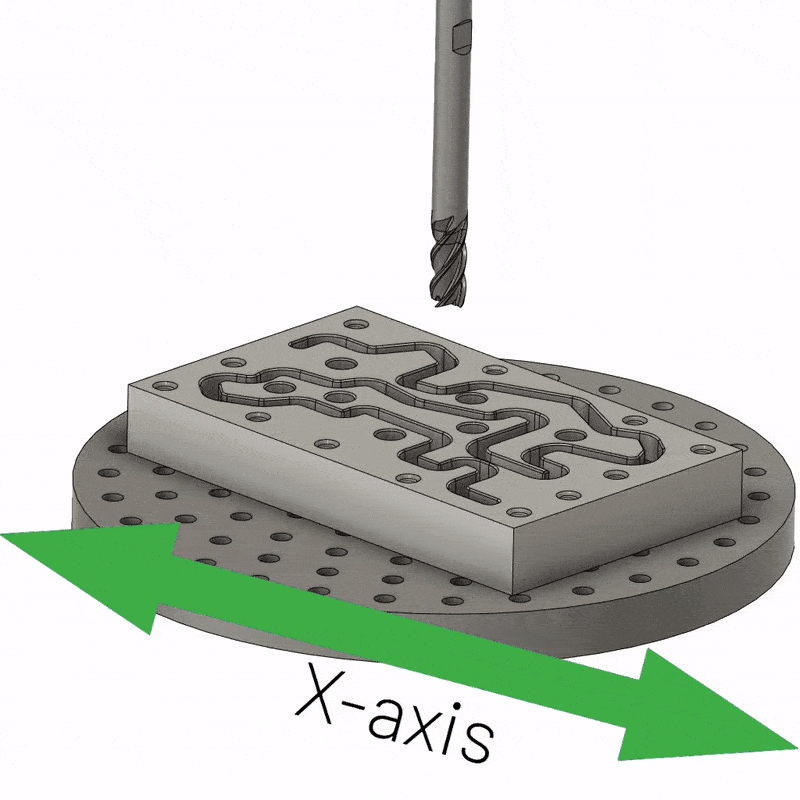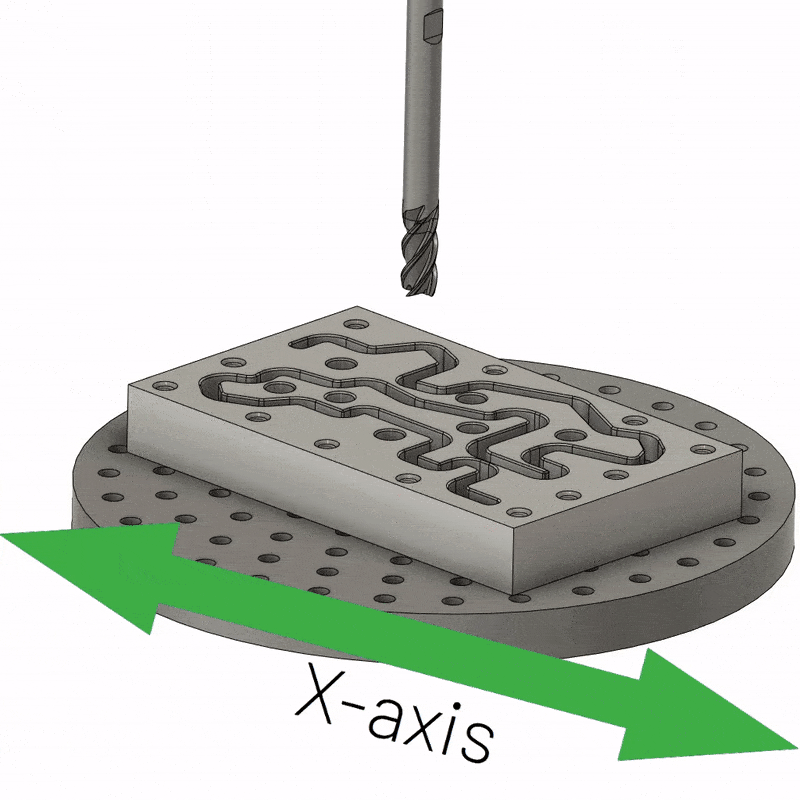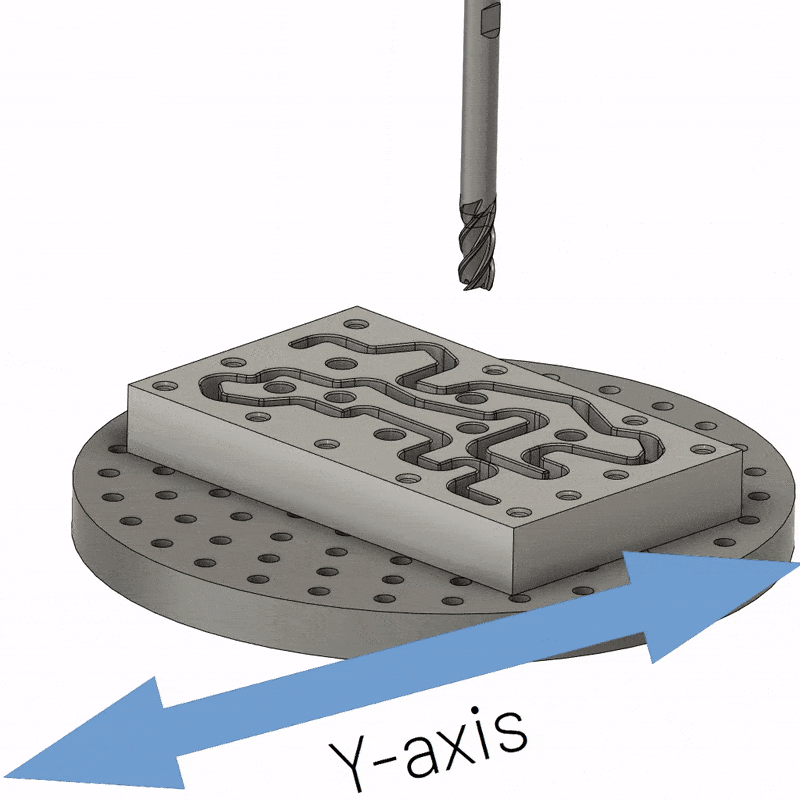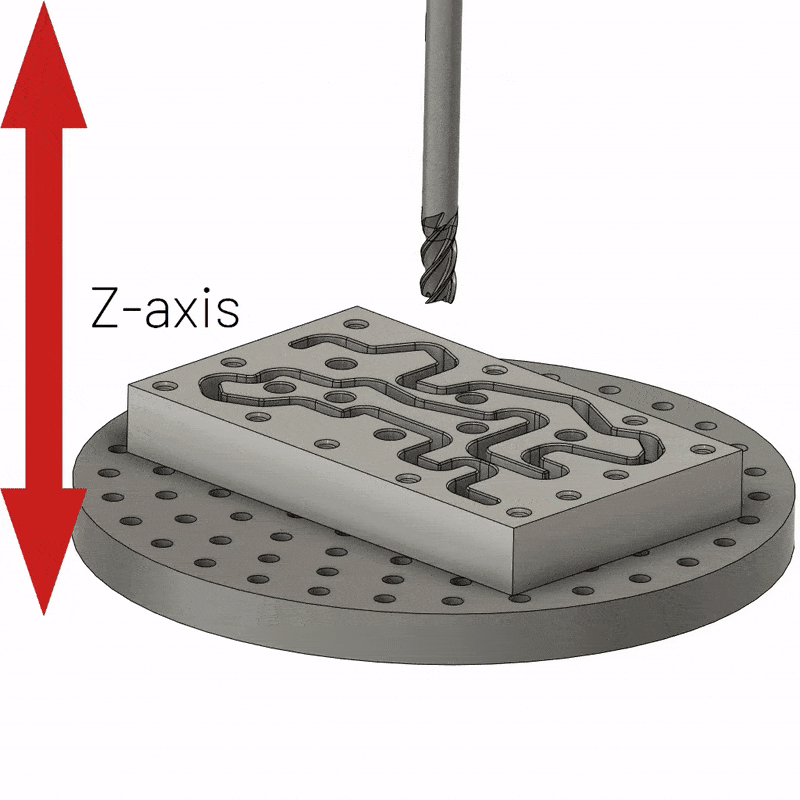
3-axis CNC machining is the simplest type of multi-axis and remains the workhorse of modern manufacturing. It usually has a fixed workpiece and a spindle that moves along three axes (X, Y, and Z). The X axis is parallel to the cutting tool, allowing the milling head to move along the length of the workpiece. The Y-axis maintains a position perpendicular to the cutting tool, allowing the cutting tool to reach each end of the workpiece. Likewise, when adjusting the Z feed, the Z axis is perpendicular to the tool, causing the tool to cut along the surface of the workpiece. 3-axis CNC machining is the easiest option for machining all six sides of a workpiece, but requires a new fixture setup for each side, which can be expensive. With a single fixture setup, only one side of the part can be machined.
3-axis CNC machining is also the cheapest and is mainly used to make parts that don’t require much detail work, for example, you can drill holes, cut sharp edges, tap holes, flatten surfaces and mill slots, etc. So if you’re dealing with smooth 2D to 2.5D parts, choose 3-axis CNC machining. Again, the workpiece should be flat and completely immobile.
What is 4-axis CNC machining?
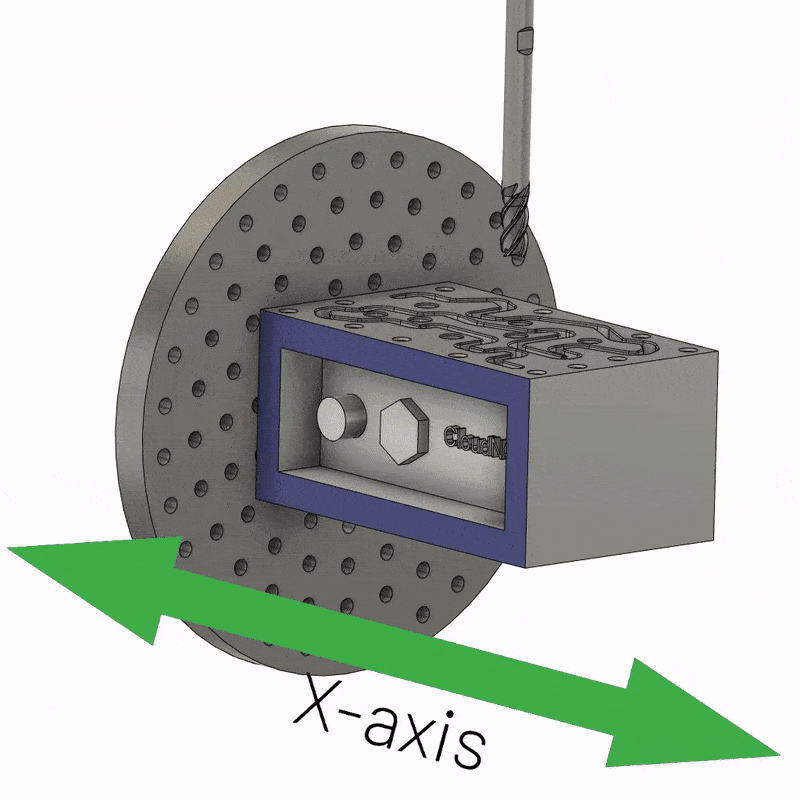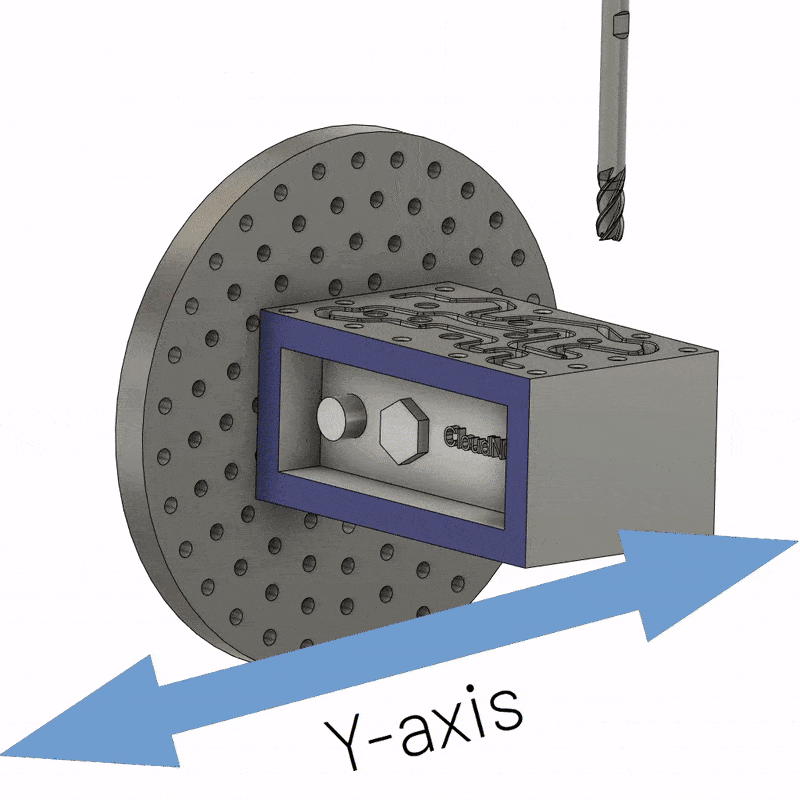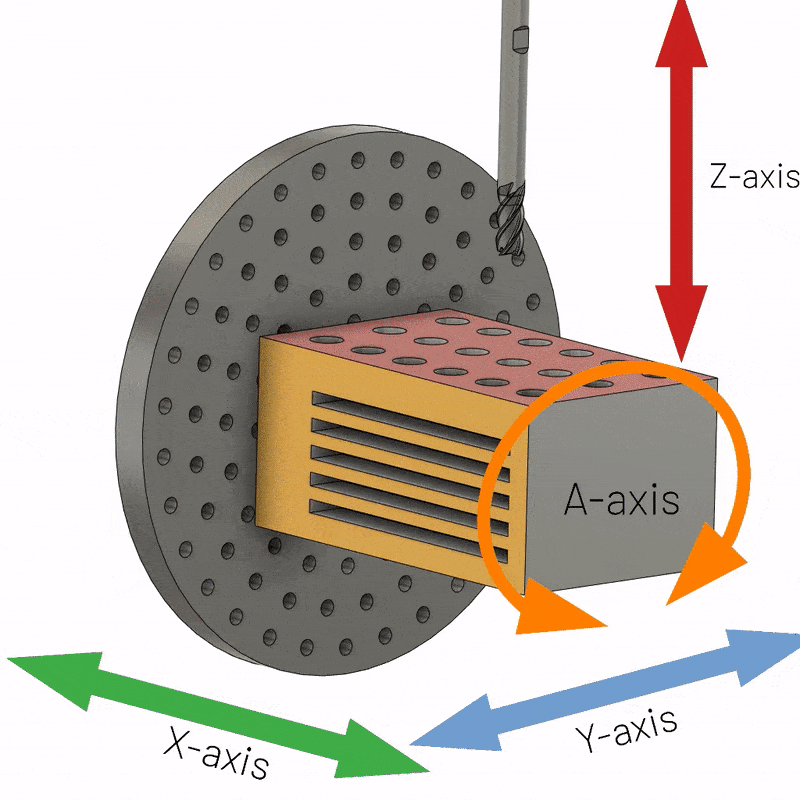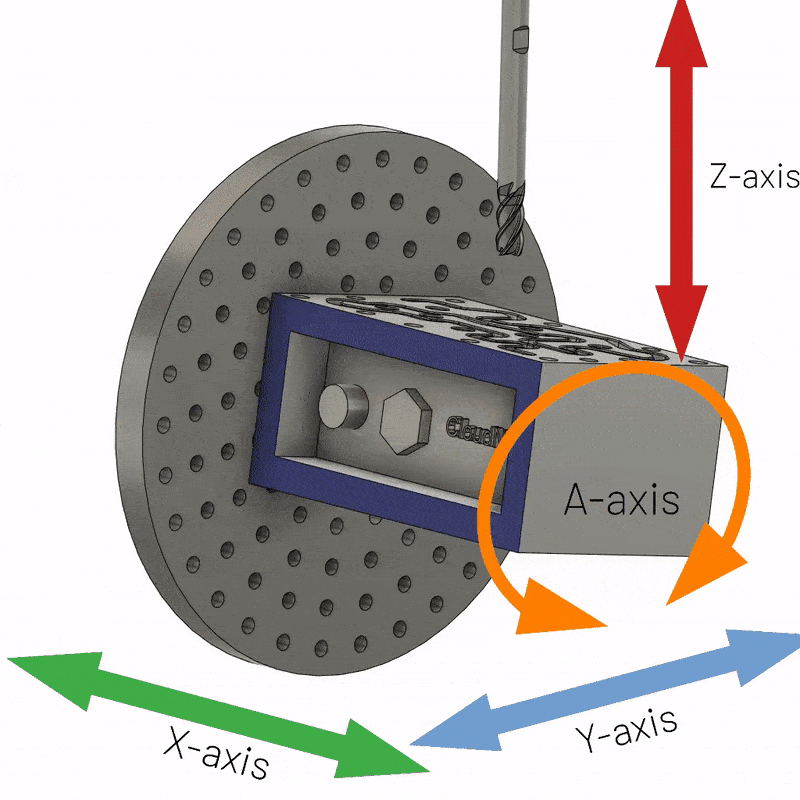
4-axis CNC machining involves using a computer numerically controlled milling machine with four axes to create more complex parts than 3-axis CNC parts. A 4-axis milling machine can move the tool in four directions thanks to the movement of the fourth axis. The addition of a fourth axis of rotation around the X axis, called the A axis, enables many new machining possibilities. It allows movement around a vertical axis, allowing the machine to achieve a 360-degree dynamic range of motion without any special fixtures.
The additional axes on a 4-axis CNC mill make it a more economical choice than a 3-axis CNC mill. Additionally, 4-axis CNC milling provides better overall quality for parts manufactured than 3-axis CNC milling because it can machine four sides at once without repositioning the workpiece. Therefore, the process is also free from possible human errors.
What is 5-axis CNC machining?
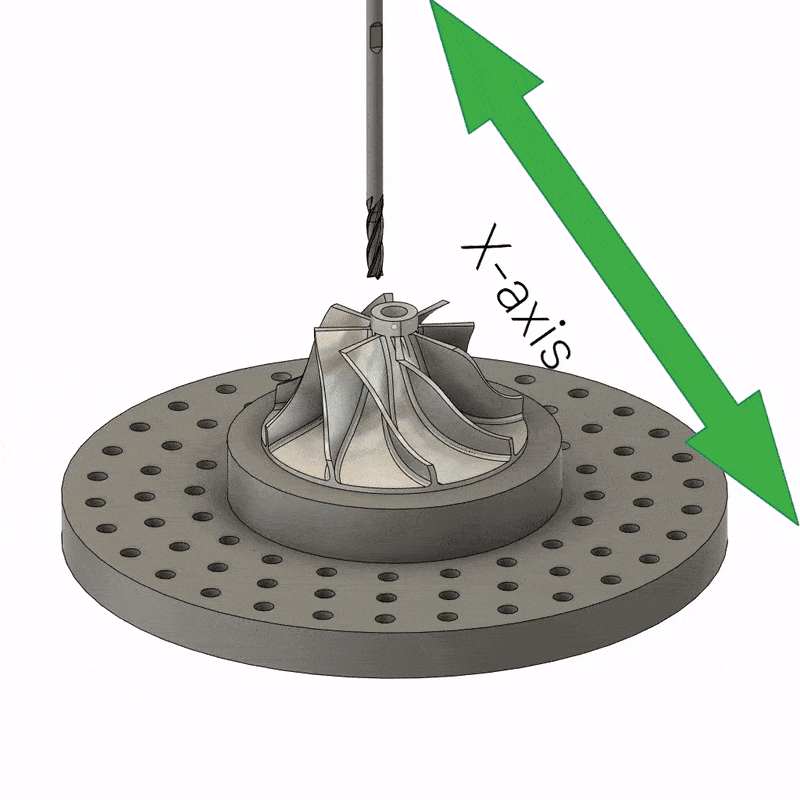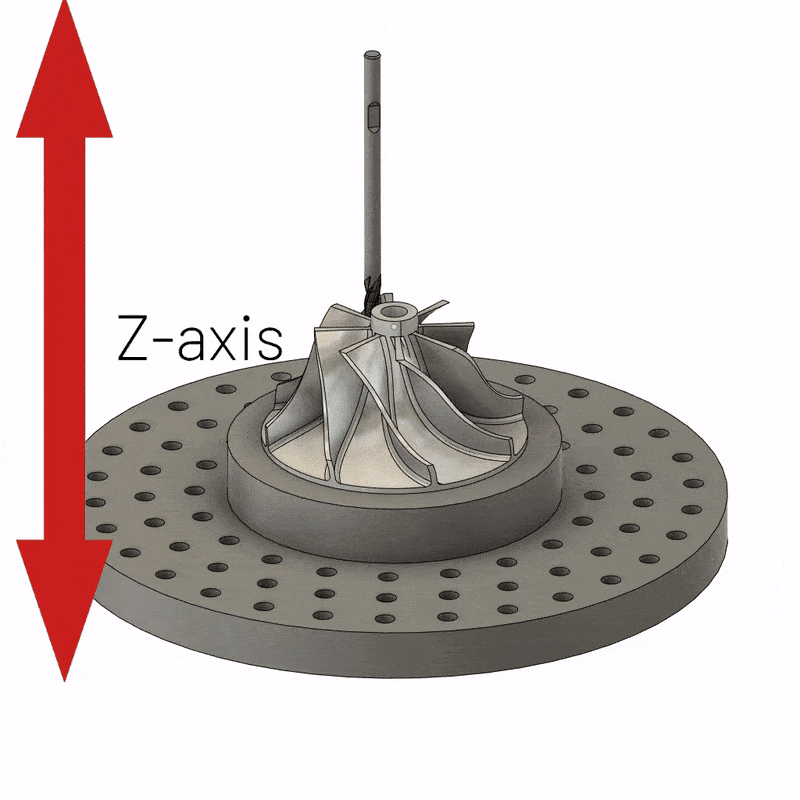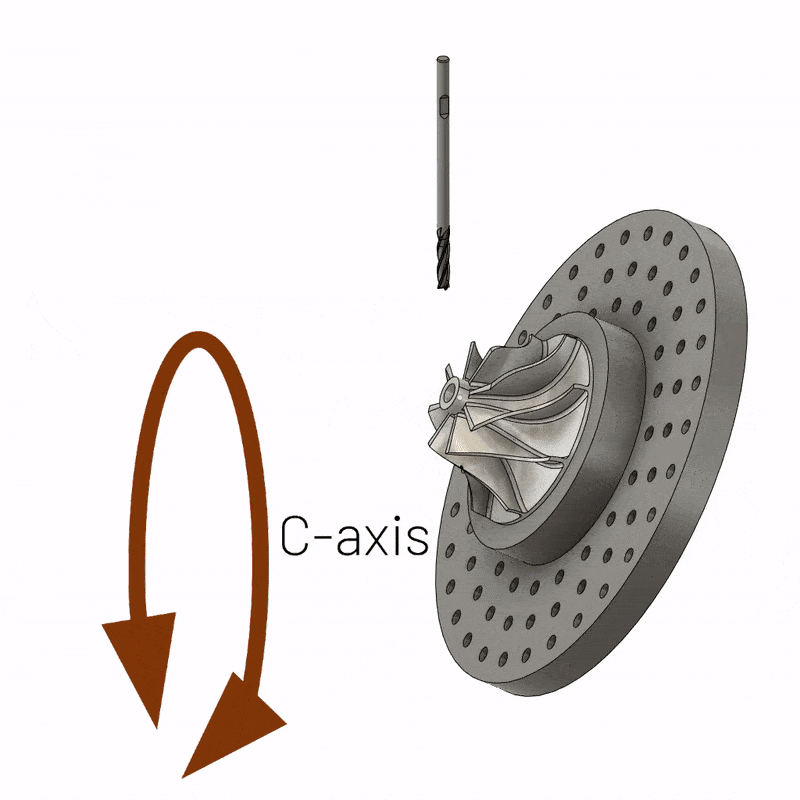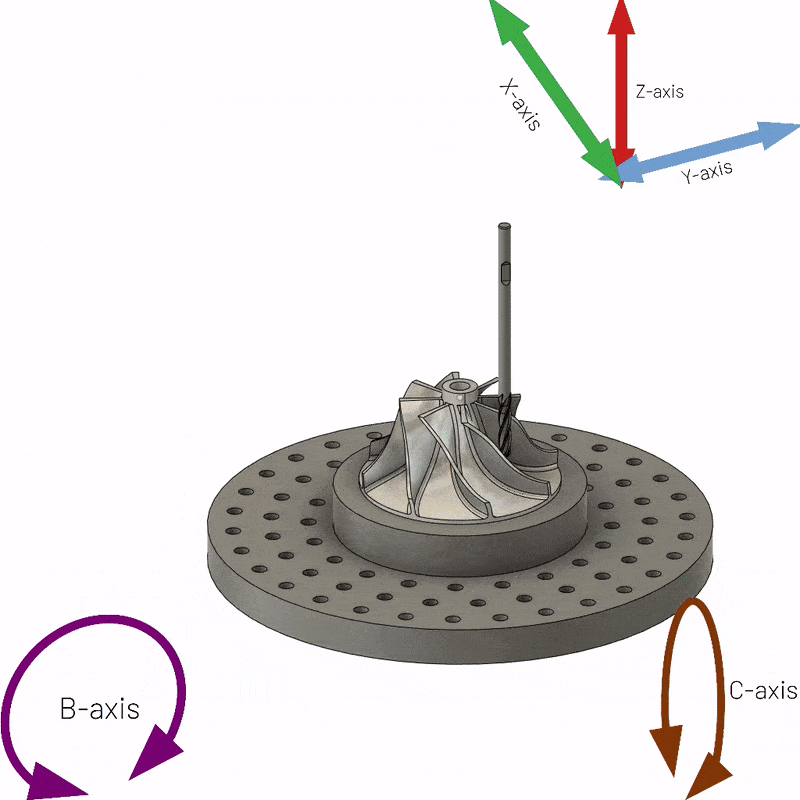
5-axis CNC machining is a versatile and popular method of manufacturing structurally complex parts. It involves cutting the material into the desired shape using a five-axis CNC machine. It is worth noting that the number of axes in a CNC machine usually determines the orientation of the tool and table during machining. However, 5-axis CNC machining offers considerable advantages over 3-axis machining due to the greater number of axes and capabilities of 5-axis CNC machining. 5-axis machines allow rotation in two planes, and the cutting tool is able to move in three directions. What’s more, 5-axis CNC milling machines can handle highly complex tasks without error.
A 5-axis CNC machine uses these three linear axes and two additional axes – A and B. The A-axis represents the axis of rotation along the X-axis, while the B-axis represents rotation/motion around the Y-axis. However, sometimes the mechanics move to the C axis instead of the B axis. The C axis represents rotation along the Z axis.
There are two main types of 5-axis CNC machines: 3+2 5-axis CNC and full continuous 5-axis machines.
In 3+2 axis CNC machining, the two axes of rotation operate independently of each other, which means that the workpiece can be rotated to any compound angle relative to the cutting tool to machine the feature. However, simultaneous rotation of both axes during machining is impossible. 3+2 machining can produce highly complex 3D shapes. Full continuous 5-axis machining can rotate two rotary axes simultaneously while machining and the tool moves linearly in XYZ coordinates. 5-axis machining offers designers enormous flexibility to design very complex 3D geometries and can also produce parts with complex curved 3D surfaces.
What is the difference between 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining?
It is imperative to understand the advantages and caveats of the three types of CNC machining. It helps maintain a balance between factors such as cost, product quality and time. When comparing 3-, 4-, and 5-axis machining capabilities, 5-axis CNC machining, while more efficient than 4-axis and 3-axis CNC machining, is not always suitable for all parts. Also, not all parts suitable for 3-axis, 4-axis CNC machining are suitable for 5-axis machining. However, if the parts processed by 3-axis machining are processed by 5-axis CNC, the manufacturing cost will increase astronomically.
1. Accuracy and precision
High precision and high tolerances are some of the main characteristics of CNC machining. While 3-axis CNC machining offers good precision, human errors can occur due to the constant repositioning of the workpiece. However, for most applications, this margin of error is insignificant. Still, the slightest deviation can lead to poor performance in sensitive aerospace applications.
At the same time, 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machines do not require multiple repositionings; therefore, they generally do not suffer from the misalignment errors that 3-axis CNC machining does. These 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machines can add machining capabilities to workpieces in multiple planes/locations using a single fixture. However, consistent repositioning in 3-axis CNC machining is a factor that affects machining deviations.
2. Cost
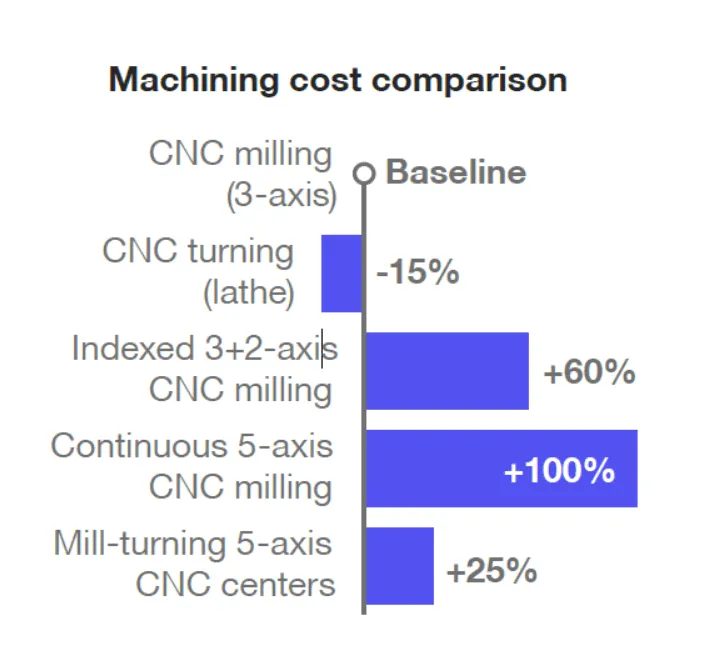
The manufactured part cost is another major parameter that differentiates between 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis machining. In general, 3-axis CNC machines are the most economical option to purchase and maintain, and to manufacture simple parts. However, factors such as machine operator and fixture availability often affect the cost of operating a 3-axis machine on the shop floor.
At the same time, 4- and 5-axis machines are very advanced and feature enhanced, making them relatively expensive. However, their powerful features make them the perfect choice for unique conditions.
3. Application
The requirement or design complexity of the part is what determines which type of CNC machining service to choose. You can create simple aerospace components using a 3-axis CNC machine. However, developing complex components for other fields can be done using 4-axis or 5-axis CNC machining.
Get CNC Machining Services at AN-Prototype
If your CNC project needs to be outsourced, AN-Prototype is the ideal CNC shop for reliable CNC machining services. We have state-of-the-art 3, 4, 5-axis CNC milling machines capable of meeting all your CNC project requirements.