Vacuum casting is the process used to manufacture high-quality plastic parts that are comparable to injection molded parts. Vacuum casting technology has been developed for more than half a century, and it is a processing technology with high cost performance and very low cost and time cost for low-volume manufacturing parts. An-Prototype has more than 15 years of experience in Vacuum casting process, this blog aims to introduce the development history of vacuum casting, advantages and disadvantages, processing process, type and other information, to provide constructive advice for you to choose the right vacuum casting processing service.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Vacuum casting?
Vacuum casting refers to the process of using a two-component polyurethane resin in the manufacturing process to produce high-quality plastic prototypes.Sometimes it is called a silicone mold or a soft mold. The difference between vacuum casting and injection mold is that vacuum casting uses a soft silicone mold, and injection mold is made of steel or aluminum and other materials. Because the process is carried out under vacuum, high-quality castings are produced without bubbles, with light surface texture, fewer defects, and lower cost of construction and time.
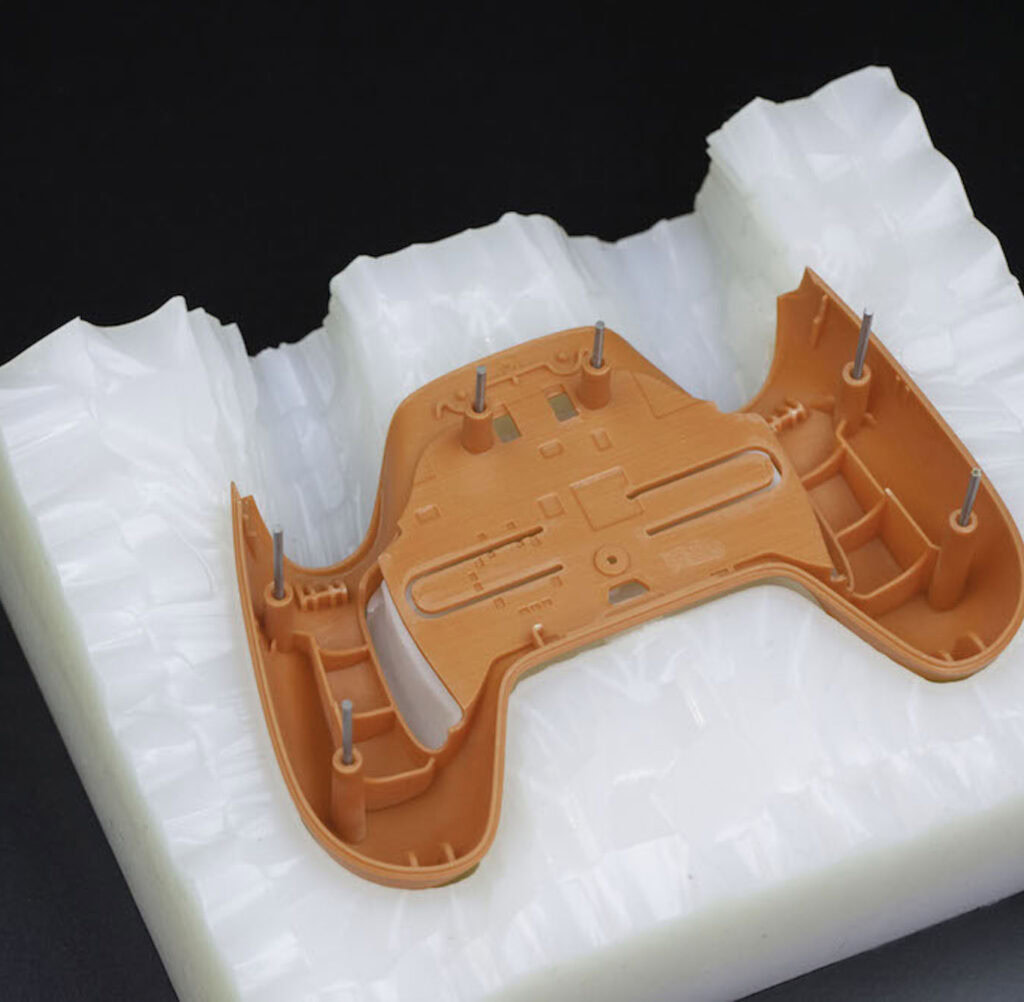

It can be machined and delivered in a few days, and in most cases, dozens of parts can be delivered in a few weeks. Therefore, it is widely used in industrial production, especially for functional test processing, and some prototypes that require small batches and have no special requirements for product materials.
History of vacuum casting?
As early as 1943, the first silicone resins had been developed. However, it was not until the 1960s that vacuum casting technology was developed and presented to the world by the Technical University of Dresden and the Technical University of Cottbus in the German Democratic Republic. Since the Europeans did not systematically learn this processing technology at that time, they sold it to Japan in the 1970s, mainly for the automotive industry. Within a few years, Europe re-introduced the technology and began to pay attention to it, and now almost all large production companies are using the technology in the research and development department, because the technology can reduce production costs and increase production efficiency.
Vacuum casting has long been widely used, and some flexible molds, such as natural rubber and other materials, have also been used by sculptors to make relief or sculpture molds for many years. Vacuum formed plastics were originally developed from vacuum casting and molding techniques in the 1940s and 1950s, and plastics such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) were developed, which is now one of the most commonly used packaging products and the material for plastic water bottles. In the 1980s, thermosetting plastics were developed and used for vacuum casting. Until now, these plastics perfectly mimic the appearance and properties of materials used in mass production, leading to a breakthrough in vacuum replication using silicone molds.
How To Vacuum casting Working?
First of all, vacuum casting will have three steps in processing, which are: first determine the main mold, casting mold and volume production.
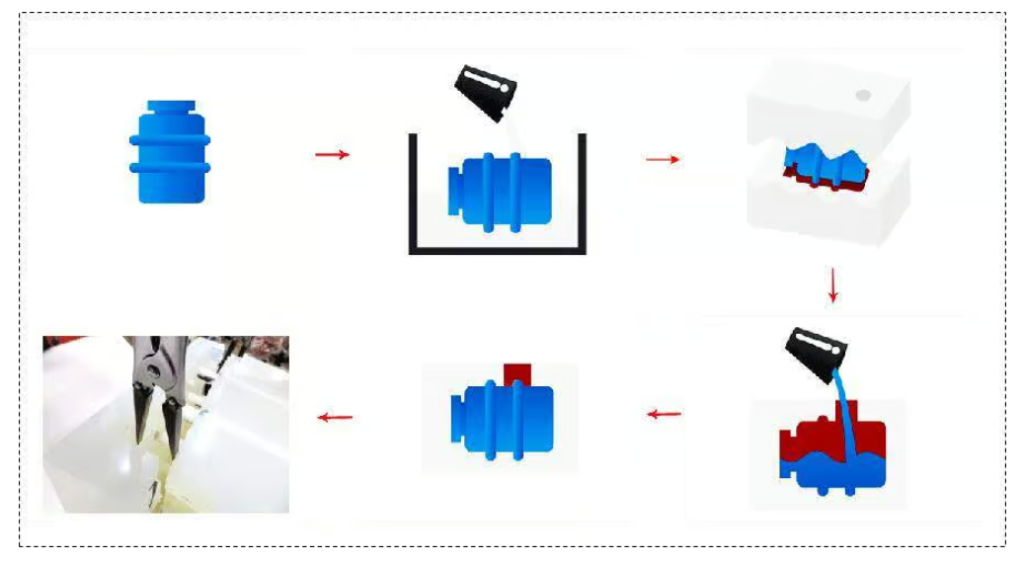
Step 1: First determine the main mold.
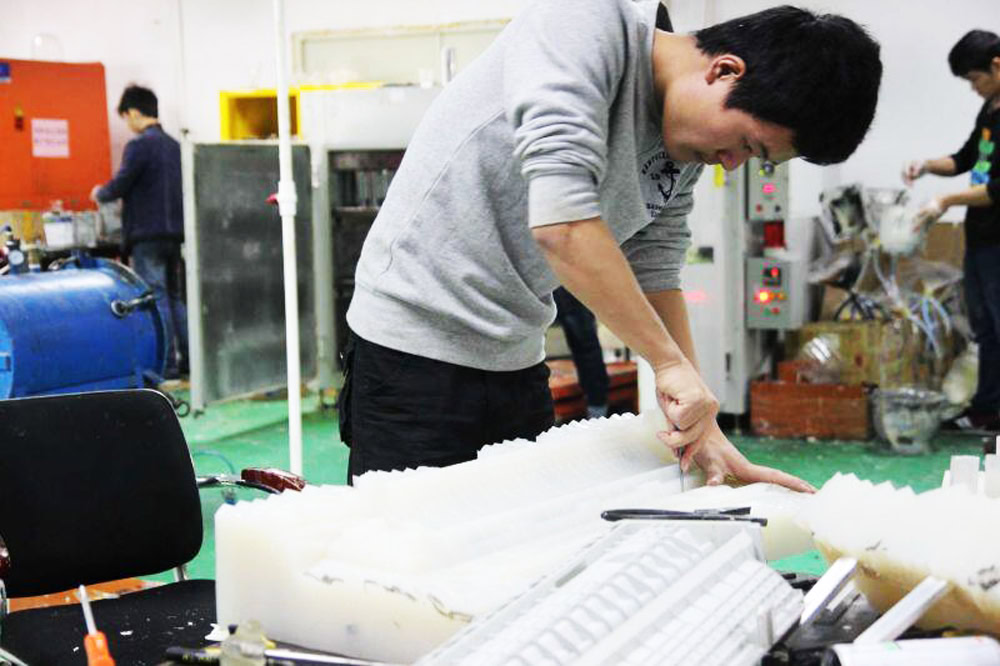
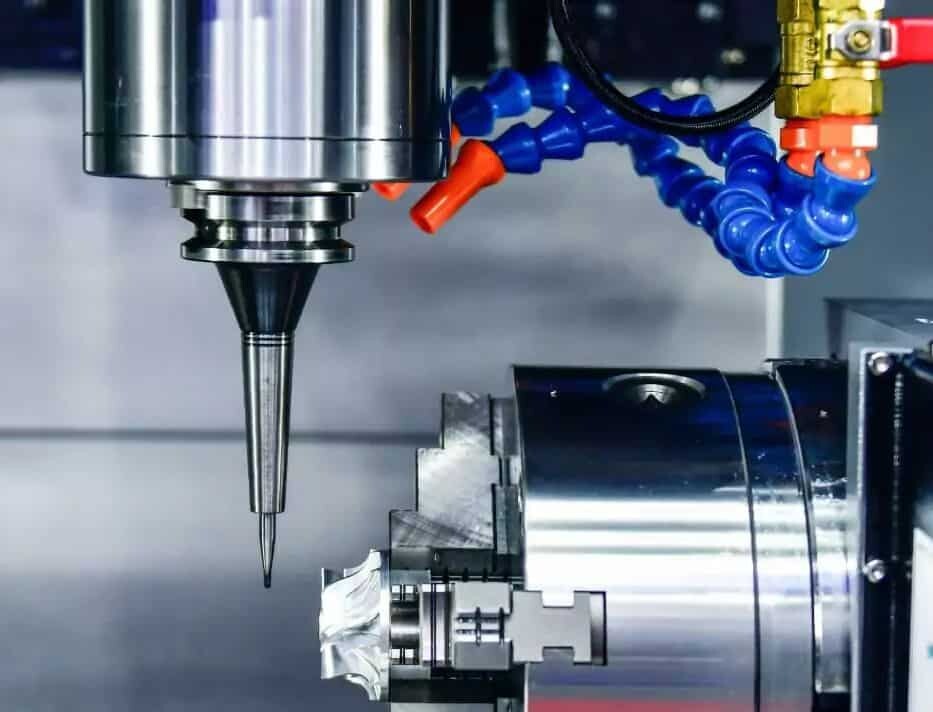
As with most modern manufacturing processes, the first step is to create a 3D model of the shape required when machining the part, and since the master model is used to cast the part, the master model must have the perfect size and appearance, which can be made using CNC machining or through 3D printing machining. The main die is then sanded, painted and primed to achieve the desired surface texture and quality. Because any flaw in the main mold will affect the appearance of the final vacuum cast part, when the appearance requirements of the parts are high, the main mold must be perfect.
Step 2: Casting mold.
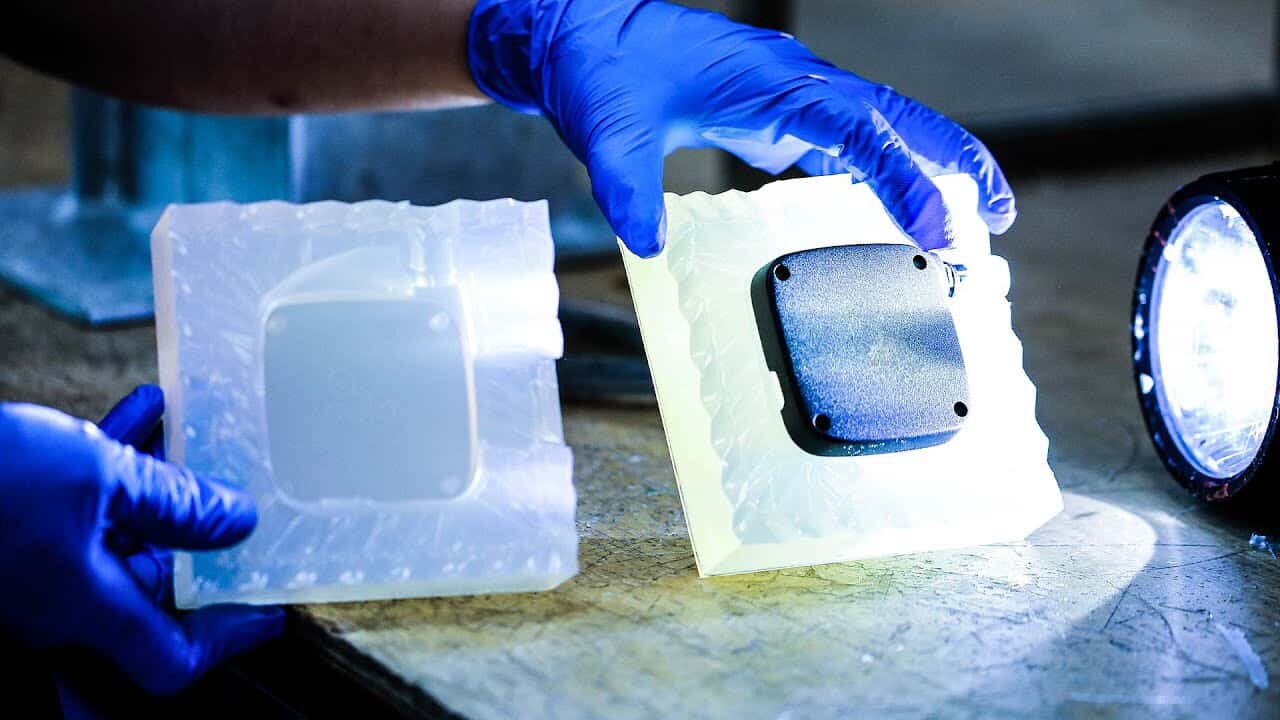
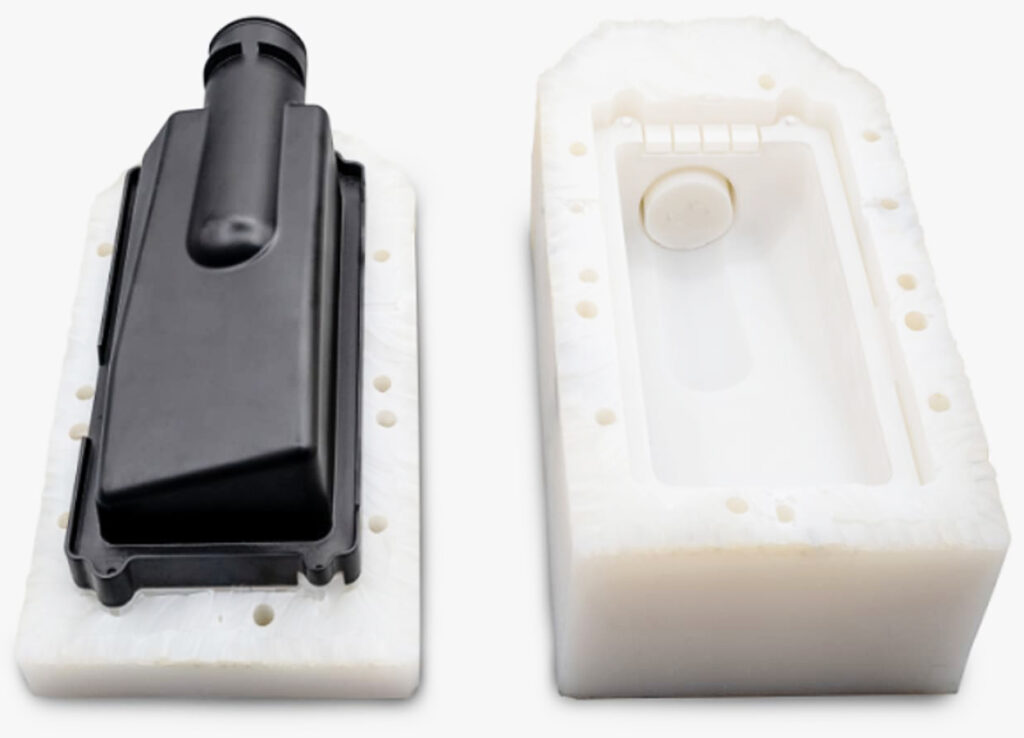
Usually the master models are made of plastic or metal, and the only requirement is that they can withstand temperatures of 40°C and cure for a long time. The master model is positioned and secured into place in a custom sized wooden box, and liquid silicone is poured around it and baked for 8-16 hours to cure. After the silicone dries and solidifies, the box and riser can be removed. Finally, carefully cut the mold with a knife to reveal the negative cavity of the assembly. Any error will usually result in mold damage, and with careful selection and use of release agents, stickiness and surface blemishes can be avoided.
Step 3: volume production
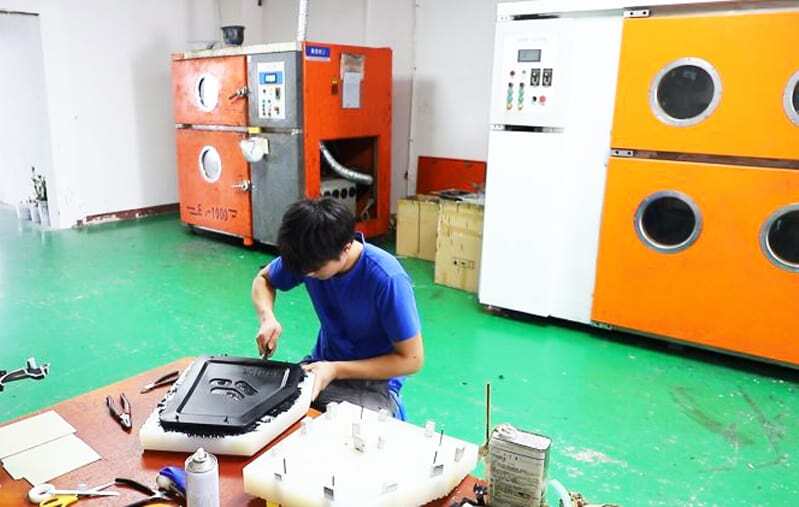
The vacuum casting resin and pigment are mixed and poured into the silicone mold, where they are fully mixed and degassed in vacuum for 50-60 seconds during the automatic pouring process. Next, by eliminating air pockets inside the tool, vacuum technology allows gravity to do all the work of filling the mold. The parts are then transferred to the oven for curing. Curing time also depends on part size. When it hardens, the casting can be removed from the mold. Once the casting is complete, the sprue and risers can be removed, and the final process is to trim the edges of the raw material and apply additional sanding and polishing with 1000 grit sandpaper. The first machined part after completion must be inspected for quality. If the first piece is qualified, production can continue. This process can be repeated 20 to 30 times on average. Exceeding these times will cause the mold to gradually deform and affect the dimensional accuracy.
Considerations for Customization Vacuum casting?
When choosing vacuum casting, the following principles should be considered:
The difference between vacuum casting and injection molding:
If you need a fast, easy and cost-effective way to produce high-quality plastic parts, vacuum casting is an excellent choice. Unlike injection molding, vacuum casting does not require DFM, thus saving project time. When choosing a manufacturing process, it is important to consider yield requirements, tolerance requirements, surface finish requirements, and lead time. Vacuum casting is an excellent choice for low-volume manufacturing, with tight tolerances and a smooth surface finish. Injection molding is most suitable for mass production, tolerances are large, and it is not suitable for the production of parts with higher precision.
Machining accuracy and recommendations: It is recommended that the wall thickness of the machined parts be between 1.5 mm and 4 mm. Use a radius greater than 3 mm. Avoid using 90-degree walls to increase part strength. The best depth for carving is 0.25 mm. The tolerances of the vacuum injection type are required to be machined according to ISO International Standard 2368M.
AN-Prototype uses the following standard tolerances: +/ -0.30mm +0.05mm (per 30mm)
Dimension(mm) | 0–30 | 30–60 | 60–90 | 90–120 | 120–150 |
Tolerance(mm) | +/- 0.3 | +/- 0.35 | +/- 0.4 | +/- 0.45 | +/- 0.5 |


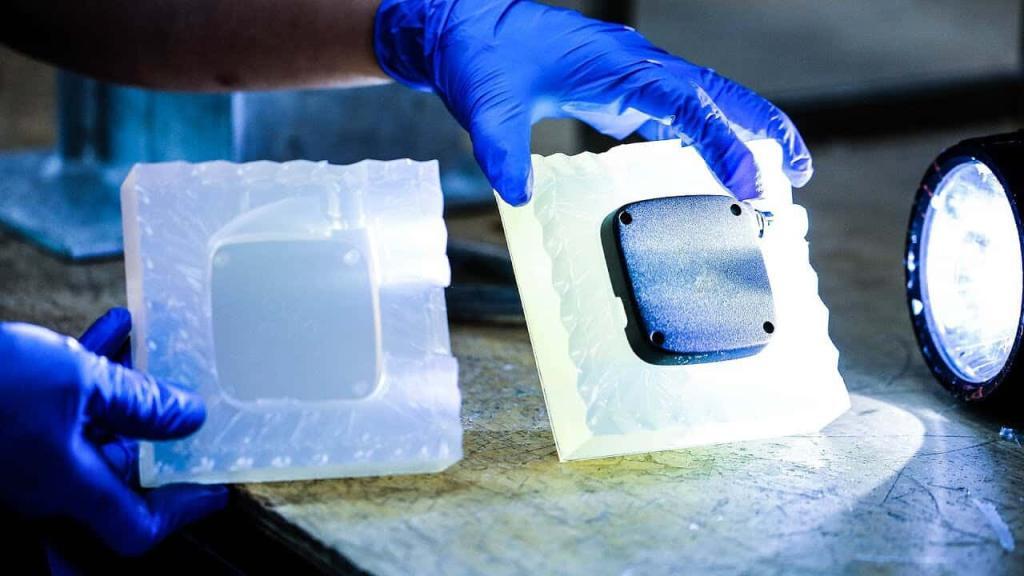
Advantages of Vacuum casting
1. Low cost: Compared with CNC machining and 3D printing, the initial production cost of vacuum casting is much lower.
2. Save production: vacuum forming does not require much time, greatly improving production efficiency, suitable for low-volume manufacturing.
3. Fine details: exquisite workmanship, high reducibility, low scrap rate. If the master mold is 3D printed, complex details can be produced when printing, and these details can be replicated in the final casting.
4. Dimensional accuracy: Parts produced by vacuum casting will fit perfectly together without post-processing steps such as grinding or drilling.
5. Excellent surface finish: Color and surface finish can be easily added, making the process ideal for aesthetically conscious industries.
7. Shorter lead time: Making silicone molds (which takes a few days) is much faster than making steel molds or aluminum molds (which takes weeks).
8. Material flexibility. Vacuum casting resins are available in a variety of colors to meet the needs of different applications.
Disadvantage of Vacuum casting
Production limits: Vacuum casting is inherently suitable for low volume manufacturing, usually in the range of 1-30 parts. The process is not suitable for high temperature applications. At the same time, the main mold will produce shrinkage and round edge phenomenon. As the number exceeds this limit, more master models need to be made.
Dependence on master mold: The vacuum casting process pays great attention to detail. If there is a defect in the main mold at the beginning, it will affect all the parts that are machined later.

Advantages of AN-Prototype Vacuum Casting Service
AN-Prototype can save the production cost of vacuum casting in the following ways:
Materials: There are hundreds of cast polymers available on the market that replicate any imaginable hardness and surface texture. It is also possible to make completely opaque, translucent or completely transparent parts.
Design: Effective mold design can optimize the complexity of the internal emphasis and reduce waste. And take advantage of economies of scale.
Experience: Choosing the right manufacturer to cooperate with can save time and cost, An-prototype has more than 15 years of processing experience in vacuum casting process, and can meet your needs and exceed your expectations in processing and manufacturing.
FAQ
Where can your vacuum casting type be used?
Medical: Vacuum casting is widely used in the medical industry to manufacture complex medical parts.
Automotive industry: Automotive prototypes and parts are mostly made by vacuum casting, because the process can produce very fine parts. For example, the following parts can benefit from the excellent precision and repeatability of silicone vacuum casting: car covers, intake manifalls, upholstery and body panels, among others.
Food industry: This process is commonly used to manufacture complex components in the food industry. It can make food packaging boxes (disposable spoons) and other complex shaped parts required.
Aerospace components: This process can be used to manufacture precision aerospace components. Due to its excellent precision, repeatability and ability to create complex details, vacuum casting can manufacture the following components: air ducts, fuel systems, and more.
Consumer goods: Vacuum casting can manufacture complex consumer goods such as toys and sports equipment, test systems, sensors, textiles, printing, lighting and furniture appliances.
How many days will it take you to finish the processing?
AN-Prototype will be produced according to the complexity of your drawings, and the prototype parts you need will be manufactured in as little as 3 days.Vacuum injection type suitable for what material?
What materials are used in vacuum casting?
Materials used in vacuum casting include thermoplastics, rubber and resins – all of which have specific properties and properties.
Similar to PA: Rugged and durable. It’s light.
Similar to ABS: Good impact resistance and balanced physical characteristics.
PC: Good transparency, good UV resistance.
PP: High impact resistance, good flexibility.
PMMA: Good transparency, good UV resistance.
Soft rubber: Flexible, good shock absorption effect.
Do you have a variety of finishes for vacuum injection molding?
Parts produced by vacuum casting can be tinted directly according to the desired material, or a second paint is applied. Different types of paint can be used, from matte to semi-gloss. Of course, the surface can also be textured or polished.