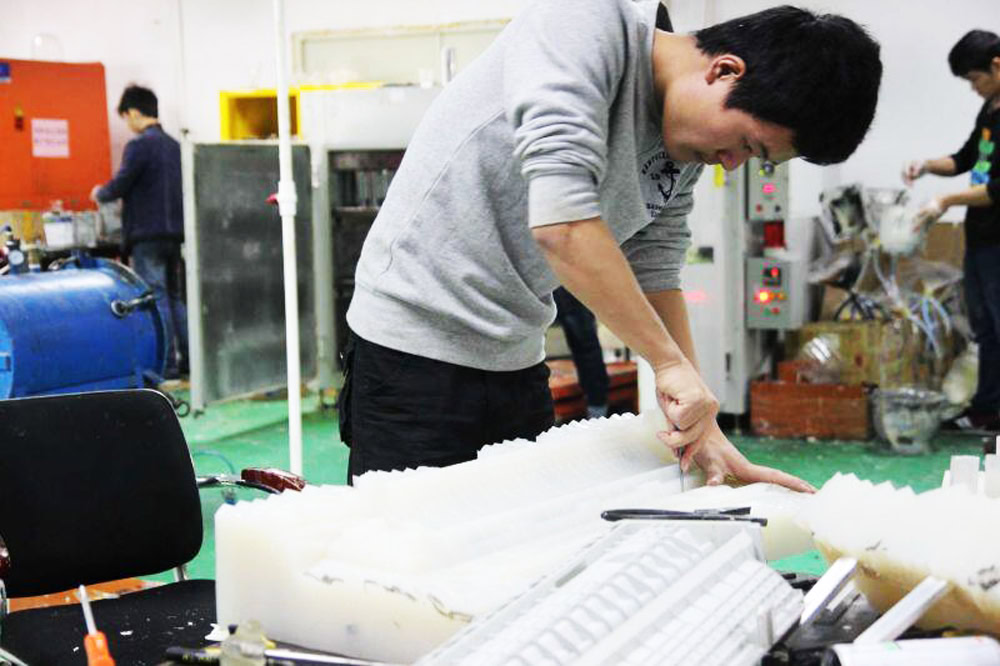
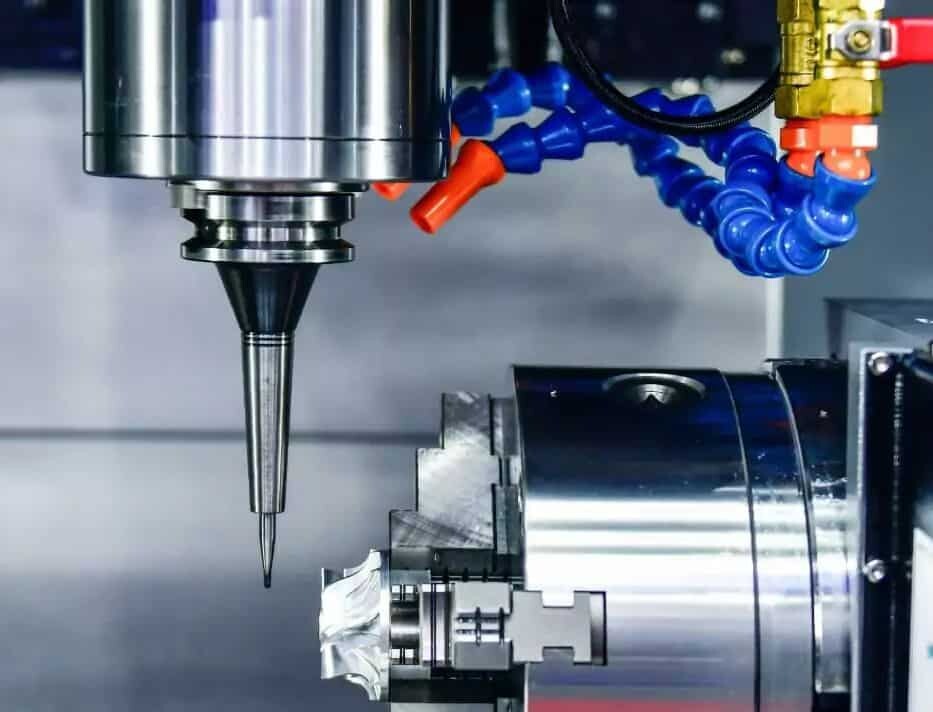
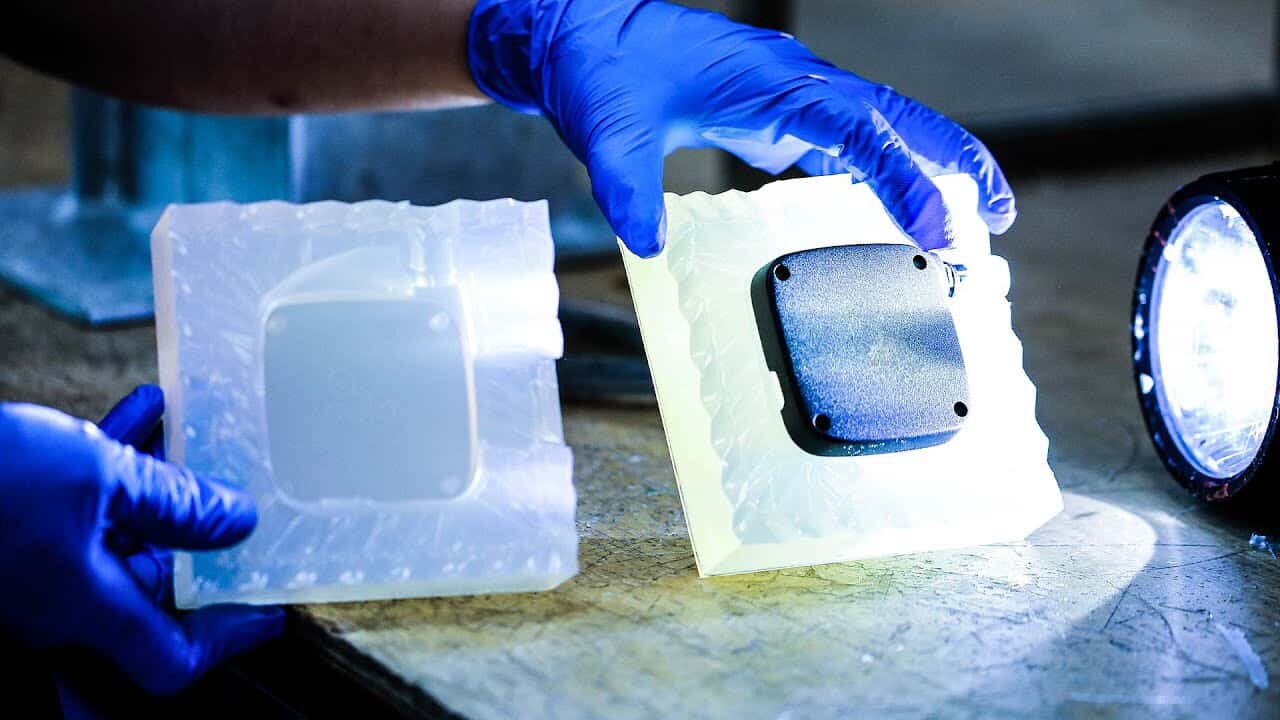
Vacuum casting (polyurethane casting) is one of the low-cost processes used to manufacture rigid or rubber-like plastic parts. Urethane casting is suitable for prototypes and certain end-use parts that don’t require expensive hard molds, instead silicone molds are used to make a limited number of copies of the master model. The process of polyurethane casting involves creating a silicone casting mold from a master model of the part (CNC machined or 3D printed) and then cutting the mold in half for production. Urethane casting is compatible with a wide range of possible part designs and is commonly used for plastic part prototyping, bridge moulding, and the manufacture of plastic parts with fine details, varying wall thicknesses and complex geometries.
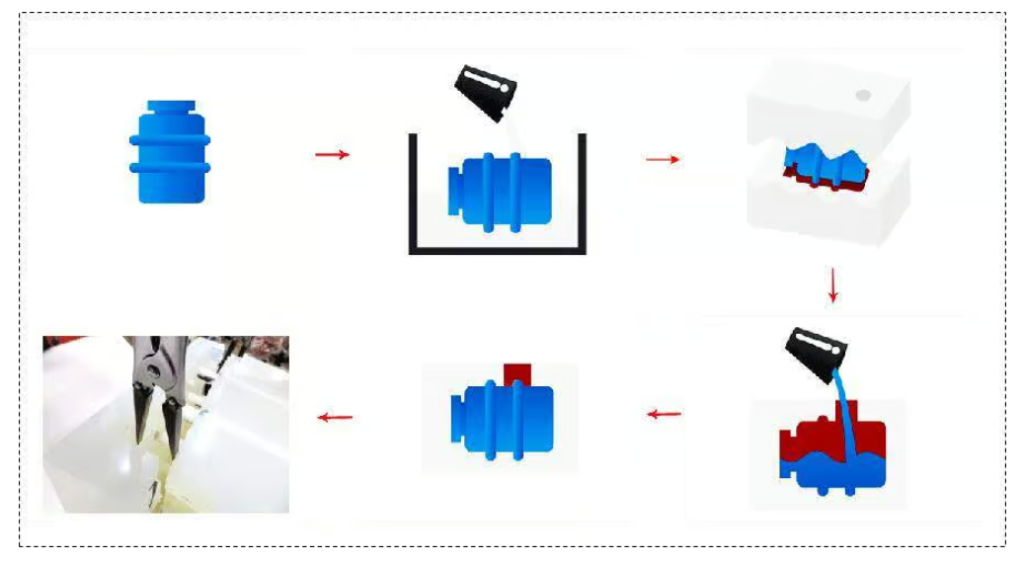
One of the significant advantages of polyurethane casting is the faster time to market, as most plastic parts can be manufactured in less than two weeks. Additionally, cast parts tend to shrink less than parts produced by processes such as injection molding. Considering that polyurethane casting is a highly versatile manufacturing process, material selection can involve a variety of factors. When it comes to polyurethane casting, customers have a variety of options. In addition to choosing between rigid or flexible parts, they can easily add color to their castings during or after fabrication, and even use transparent materials to create custom plastic parts like clear housings and presentation boxes. Product teams must do their due diligence to ensure the most appropriate vacuum casting material is selected for a particular project, which can affect the quality of the final plastic part.
Table of Contents
TogglePolyurethane Casting Material Selection Factors
Polyurethane casting is compatible with a variety of rigid and flexible plastics, so polyurethane cast parts can be manufactured in a variety of colors, textures and finishes. However, with so many options to choose from, it is important to follow design for manufacturability (DFM) best practices when selecting materials. You will weigh a complex range of factors, including:
1. Required properties of the final product:
The first consideration when choosing a material for polyurethane casting is the desired properties of the final product. Different polyurethane casting materials have different properties, such as impact resistance, heat resistance, UV stability and hardness. For example, if you are manufacturing a product that will be exposed to extreme pressure, it is critical to choose a polyurethane casting material that can withstand that pressure range.
2. Product operating environment:
Polyurethane casting materials respond differently to different environments. When choosing polyurethane castable materials, it is necessary to consider the environment in which the product will be used. For example, some polyurethane castables are susceptible to moisture, which can lead to a decline in product performance. Nonetheless, choosing a moisture-resistant polyurethane casting material is critical if you manufacture products that are regularly exposed to moisture.
3. Cost
The cost of polyurethane castables is another factor to consider. While price should not be a major factor, it is still very important to choose a cost-effective polyurethane casting material. It is possible to use cost-effective materials without compromising the quality of the final product.
Ultimately, identifying the most suitable material for a specific application is critical to ensuring success throughout the production cycle. Polyurethane casting materials, including silicone, foam, and polyurethane casting resins, can generally be classified according to the hardness of the material. Below is a quick overview of durometers, Shore hardness and some of the most common polyurethane casting materials.
A Note on Durometer and the Shore Scale
A durometer is a standardized measure of the hardness of a material, that is to say how resistant it is to localized deformation. Durometers for most vacuum cast materials fall into one of three categories: Shore 00, Shore A or Shore D, each representing a range of hardness, with Shore 00 being the softest and Shore D being the hardest. Urethane materials typically range in durometer from 25 shore 00 (similar to a sofa) to 75 shore D (similar to a bowling ball).
Rigid polyurethane material
ABS-like polyurethane is a low-cost, general-purpose resin comparable in strength and impact resistance to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is a thermoplastic polymer commonly used in automotive exteriors.
With a typical hardness of 80-85 Shore D, ABS-like resins make excellent product casings and components that can withstand heavy handling (such as game console controllers). Polyurethane is susceptible to UV radiation and therefore requires stabilizers or coatings if used in exterior applications.
Acrylic urethane is another common casting material. Hard and transparent, these resins have properties similar to polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), a lightweight acrylic resin often used as a glass substitute. These materials have a hardness of approximately 87 Shore D, making them ideal for durable, transparent parts such as light tubes.
Softer, rigid resins, such as those with a durometer hardness between 60 and 75 Shore D, can also be used to make strong parts with some flexibility, such as car tires or hard hats. These resins have low viscosity, making them ideal for filling complex mold designs.
Elastomeric polyurethane
Elastomeric polyurethanes have properties similar to flexible materials such as TPE, TPU and silicone rubber, making them ideal for products such as wear parts and bumper pads.
Much like rigid resins, elastic polyurethanes offer many mechanical advantages. Materials with a hardness of 50 Shore A and below provide high tensile strength, toughness and flexibility, while materials with a hardness of 60 to 80 Shore A are well suited for the production of wear-resistant parts and fixtures with some flex. Shore A resins can also be used to make polyurethane casting molds that are more durable than their silicone counterparts.
Rigid elastomeric polyurethane materials are available in a hardness range of 90 Shore A to 60 Shore D, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as forming molds and gears. In some cases, these resins are more durable than metal models.
List of Commonly Used Vacuum Casting Materials
Material | Shore Hardness | Description | Technical Info. |
General Purpose | D 76-80 | An impact-resistant, ABS-like material, used from enclosure housings to concept models. | TC-878, TC-852, or equivalent |
Rigid Clear | D 80 | A versatile, clear polyurethane. | Poly-Optic 1410 or equivalent |
ABS-Like, FR | D 78-82 | A tough Shore 80D flame retardant material that is UL Listed with a flammability rating at 1/16″ (1.6 mm). | TC-891-FR or equivalent |
Polypropylene-Like | D 65-75 | A tough and abrasion-resistant flexible urethane with polypropylene-like ductility. | TC-872, HP-2270D, or equivalent |
Polycarbonate-Like | D 82-86 | A stiff, high impact, high HDT, material with a wide variety of uses. Simulates polycarbonate (non-clear), Shore 84D. | TC-854 or equivalent |
Glass-Filled Nylon-Like | D 85 | A stiff, USP Class VI, high-performance urethane with high impact strength and a HDT of 190°F (88°C). | PT8902 or PT8952 (FR) |
Rubber-Like Polyurethane | A 25-95 | A Shore A elastomer with a high elongation to break. | F-130 to F-190 or equivalent |
Clear Rubber-Like Polyurethane | A 40-95 | A colorless Shore A elastomer with a high elongation to break. | WC-540 to WC-595 or equivalent |
AN-Prototype is a trustworthy vacuum casting service provider.
AN-Prototype has emerged as a reliable vacuum casting service provider that meets the needs of mechanical designers. With a commitment to high-quality standards, expertise, cost-effective services, quick and reliable delivery, and excellent customer service, AN-Prototype is the go-to prototyping service provider for mechanical designers. Their services are available online, making it easier for mechanical designers all around the world to access their exceptional services. Trust AN-Prototype to help you bring your designs to life today.
1. What is Vacuum Casting and Why is It Important?
Vacuum casting is a process that involves creating a mold from a three-dimensional model and then using that mold to cast parts. This method is important in the production of complex parts, particularly for mechanical designers. When compared to other prototyping methods such as 3D printing and CNC machining, vacuum casting is an excellent choice for those who require high-quality, low-volume productions that require a low-cost manufacturing process. AN-Prototype offers this service to mechanical designers, creating parts that are durable and dimensionally accurate.
2. AN-Prototype Offers Exceptional Quality and Expertise
AN-Prototype boasts of a team of experienced engineers with extensive experience in the vacuum casting process. Their team is equipped with the latest manufacturing techniques and equipment, ensuring that they can meet the exact specifications of any mechanical design. They also use high-quality raw materials, ensuring that the end product is both durable and cost-effective.
3. Cost-Effective Service
AN-Prototype understands the value of cost-effective prototyping services, and this is why they offer a vacuum casting process that is both affordable and efficient. They use advanced techniques that allow them to produce high-quality parts in a short amount of time, allowing mechanical designers to reduce the number of production processes required. This reduces the overall cost of production of the parts while still ensuring that they are of high quality.
4. Quick and Reliable Delivery
AN-Prototype offers quick delivery of vacuum cast parts, with most parts taking only a few days to complete. They have an efficient delivery system that ensures that the parts are delivered to mechanical designers within the shortest time possible. This quick turnaround time allows mechanical designers to complete their projects within the given timelines, ensuring that they stay ahead of the competition.
5. Excellent Customer Service
AN-Prototype prides itself on offering exceptional customer service to its clients. Their team of friendly and competent customer service representatives is always on-hand to answer any questions and offer advice on the best manufacturing methods for your specific project. This ensures that clients are always satisfied and confident in the service that AN-Prototype delivers.