Even as today’s 3D printing technology becomes more sophisticated, CNC machining is still irreplaceable. CNC machining of metal or plastic parts is an efficient and economical method. If your next project uses CNC machining parts, then CNC machining costs will be a topic of greater concern to you. Calculating the cost of CNC machining is difficult because the price depends on various factors. For example, the average cost of CNC machining in Europe or the United States is $35 to $150 per hour. However, lower prices are available at AN-Prototype, a leading CNC machining shop in China, with costs as low as $10 to $30 per hour for 3-axis CNC machining, 4-axis CNC machining, and 5-axis machining. In this article, we will explore the factors that influence the cost of CNC machining, provide you with valuable knowledge about cost considerations, material selection and optimization expenses, and guide you in estimating the cost of a CNC custom part or prototype.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is CNC machining?
CNC machining is a versatile subtractive manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control (CNC) machines to remove material from a workpiece. The process involves using rotating cutting tools to cut materials from metal or plastic to create precise, complex parts. CNC milling can be used in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and more. From complex prototypes to large-scale manufacturing, CNC machining delivers accuracy, repeatability and consistency. Currently, CNC machining of prototype parts remains the most popular process.

Factors affecting CNC machining costs
CNC machining is a complex process involving various aspects that directly impact the overall cost. Before you can calculate the cost of CNC machining, you must first understand what are the main factors on which the cost depends. Let’s explore the main factors that influence processing costs:
CNC Machine Tools and CNC Machine Tool Costs
The type of CNC machine used plays an important role in the cost of the machining process. Parts machined on a 3-axis CNC mill or lathe/lathe are more economical than parts machined on a 4- or 5-axis CNC mill. Two factors influence the cost of CNC machining: the upfront investment in purchasing a CNC machine and its expected annual usage (usually around 5,000 hours). CNC machining service providers determine the hourly cost of each CNC machine tool by dividing the price of the CNC machine tool by its total annual usage hours. The table below compares the prices of various types of CNC machine tools.
CNC Machine | Description | Approximate Price Range (USD) |
CNC Milling Machine | Used for milling and drilling operations on metal or plastic prototypes | $8,000 – $80,000 |
CNC Lathe | Primarily used for CNC turning round structure parts | $12,000 – $50,000 |
CNC Router | Ideal for cutting softer materials, like foam or wood | $2,500 – $30,000 |
CNC Plasma Cutter | Used for cutting metal and other materials | $10,000 – $40,000 |
CNC Laser Cutter | Precision cutting tool for various materials | $15,000 – $80,000 |
3-Axis CNC Machine | Most popular CNC machines are for making metal or plastic parts | $20,000 – $100,000 |
4-Axis CNC Machine | Saving a lot of time for machining prototype parts with complex structures | $50,000 – $200,000 |
5-Axis CNC Machine | Advanced CNC machine for manufacturing complex geometries parts | $75,000 – $500,000 |
CNC Swiss Machine | Specialized for precision and complex small parts | $25,000 – $120,000 |
CNC Grinding Machine | Used for surfance finishing operations | $10,000 – $100,000 |
If your CNC project has a tight budget, AN-Prototype is a CNC machining shop worth considering. AN-Prototype invests in precision machine tools every year, continuously improves advanced technology and exquisite craftsmanship, and perfectly combines cost-effectiveness and high-quality manufacturing. In-house streamlined processes ensure competitive pricing while maintaining excellent quality standards, making them ideal for a variety of CNC machining services.
3-axis, 4-axis or 5-axis CNC machining services?
When a machinist is considering manufacturing a CNC part, the first thing that comes to mind is which CNC machine to choose to machine the part. Typical costs for using individual CNC machines with AN-Prototype.
Typically, the total cost per hour for 3-axis CNC milling services ranges from $5 to $15.
However, the total cost per hour for 4- or 5-axis CNC machining is between $15 and $25.
Because these multi-axis machines have higher tooling costs and more complex operations, the result is that CNC machining will be more expensive. CNC processing prices in Europe or the United States are generally 2-3 times higher than in China. For example, 3-axis CNC machining typically costs $15 to $50 per hour, while 4- or 5-axis CNC machining costs $80 to $150 per hour. No matter where you go, the cost of CNC turning is relatively low. Not only is the cost of CNC lathes lower, but the operation of CNC lathes is simpler.
AN-Prototype - 3-axis CNC machining cost calculation
AN-Prototype takes the CNC project at the end of December 2023 as an example. A small aluminum part and a stainless steel part of the same size (152*142*80), comparing the cost and processing time of CNC machining.

No. | Material | Finish | Quantity | Unit Price | Lead timeDays | Cost SavingFrom 1x |
1 | Aluminium | As machined | 1 | $198.00 | 5 | – |
2 | Aluminium | As machined | 10 | $86.37 | 7 | -56.37% |
3 | Aluminium | As machined | 100 | $75.90 | 12 | -61.67% |
4 | Aluminium | As machined | 1000 | $72.18 | 32 | -63.54% |
5 | Stainless steel | As machined | 1 | $256.00 | 5 | – |
6 | Stainless steel | As machined | 10 | $108.32 | 7 | -57.68% |
7 | Stainless steel | As machined | 100 | $88.20 | 15 | -65.62% |
8 | Stainless steel | As machined | 1000 | $85.98 | 30 | -66.79% |
For CNC machined aluminum parts, we can see that from 1 part to 100 parts, we can save -56.37% of the unit price. 100 parts and 1,000 aluminum parts can only save 1.8% of the unit price cost. This shows that increasing the number of parts can significantly reduce the cost of a single part, however the economic benefits decrease for larger quantities of parts. Parts manufactured in small batches are the most cost-effective. This explains why engineers choose alternative manufacturing methods, such as die casting, when manufacturing parts in high volumes. From 1 part to 10 parts, the CNC machining time only increased by 2 days, but the price of each part was significantly reduced by 56.37%. This is because the amount of work required to set up items before CNC machining (preparing materials, CNC programming, purchasing tools, etc.) is similar whether you are processing 1 part or 10 parts.
CNC machined stainless steel parts follow the same trend in terms of quantity. However, from 1 part to 100 parts, the cost saving is 57.68%, and when processing 1000 parts, the saving is another 1%. It’s worth noting that for CNC machining, stainless steel costs approximately 2-3 times more than aluminum, depending on the complexity of the part. This is because the cost of stainless steel materials is more expensive, and stainless steel is harder and increases the wear of the tools.
AN-Prototype - Cost of 5-axis CNC machining
No. | Material | Finish | Quantity | Unit Price | Lead timeDays | Cost SavingFrom 1x |
1 | Aluminium | As machined | 1 | $489.36 | 7 | – |
2 | Aluminium | As machined | 10 | $215.98 | 7 | -55.86% |
3 | Aluminium | As machined | 100 | $139.65 | 15 | -71.46% |
4 | Aluminium | As machined | 1000 | $116.75 | 30 | -76.14% |
From the table we can see that part quantity is very important for 5-axis machining costs. The unit price cost from 1 part to 10 parts has been reduced by 55.86%. However, the time for CNC machining remains the same. 5-axis CNC machining of 1,000 parts can save 71.46% of the cost. For parts with very complex structures, a 5-axis CNC machining center is often required, and it takes a lot of time for advanced CNC programming engineers to set up/program the first time. Once the early setup for 5-axis CNC machining is complete, it only takes a small amount of time to make more parts.
AN-Prototype -CNC Turning Cost

No. | Material | Finish | Quantity | Unit Price | Lead time Days | Cost SavingFrom 1x |
1 | Aluminium | As machined | 1 | $22.90 | 3 | – |
2 | Aluminium | As machined | 100 | $3.60 | 4 | -84.27% |
3 | Aluminium | As machined | 1000 | $0.96 | 7 | -95.80% |
4 | Aluminium | As machined | 10000 | $0.95 | 12 | -95.85% |
5 | Stainless steel | As machined | 1 | $28.00 | 3 | – |
6 | Stainless steel | As machined | 100 | $5.68 | 3 | -81.62% |
7 | Stainless steel | As machined | 1000 | $1.98 | 7 | -93.94% |
8 | Stainless steel | As machined | 10000 | $1.89 | 15 | -94.05% |
For high-volume manufacturing, CNC turning is an ideal machining method. The data shows that increasing aluminum parts from 1 to 100 can save 84.27% of the cost without affecting CNC turning time. That’s because CNC turning is a fast process, so going from 1 to 100 doesn’t require much additional labor once engineers set up the program. Increasing the number of turned parts to 1,000 reduces the price significantly by 95.8%, but increasing to 10,000 makes the cost savings negligible as CNC manufacturing efficiency is fully optimized. The cost reduction for CNC turning stainless steel is similar to that of aluminum. However, stainless steel raw materials cost more, so the starting price is higher. CNC turning is a faster machining method than 3-axis CNC machining.
Material costs and their workability
The material of a CNC machining project plays a decisive role in determining its cost. The material itself has a cost, and the difficulty of processing the material is also an important factor in determining the cost. AN-Prototype summarizes commonly used CNC materials and their approximate costs:
Aluminum: Aluminum is the most popular metal material because it is lightweight, workable, and cheap. It is widely used in automobile, medical, aerospace, bicycle and other industries. Aluminum costs from $1 to $6 per pound, depending on the grade and quantity required. Aluminum 6061 is by far the most cost-effective metal material for manufacturing metal prototypes because of its low cost and very good machinability.
Steel: Steel offers durability, high strength, and a variety of grades and finish options. Steel costs vary widely, depending on factors such as alloy composition, size and part complexity. On average, steel costs between $0.30 and $6 per pound.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetics and is commonly used in industries such as medical, food processing, sports, aerospace and more. Stainless steel prices range from $2 to $20 per pound, depending on the grade and quantity required.
Brass: Brass is valued for its beautiful appearance and excellent electrical conductivity. It can be used on musical instruments, plumbing fixtures, and decorative hardware. Brass typically costs about $3 to $10 per pound.

Plastic: Plastic materials such as ABS, acrylic, and nylon are versatile and affordable. They are commonly used in industries such as electronics, automotive and consumer goods. The cost of plastic materials varies depending on the type and quantity required, but typically ranges from $1 to $7 per pound.
Material | Surface Finish | Quantity | Unit Price (Estimated) | Lead Time (Estimated) |
Aluminum | As Machined | 1 | $30 – $80 | 1 – 5 days |
|
| 10 | $15 – $35 | 3 – 10 days |
|
| 100 | $10 – $30 | 7 – 15 days |
|
| 1000 | $5 – $20 | 15 – 30 days |
Stainless Steel | As Machined | 1 | $30 – $80 | 3 – 7 days |
|
| 10 | $25 – $50 | 7 – 10 days |
|
| 100 | $20 – $40 | 10 – 20 days |
|
| 1000 | $15 – $30 | 20 – 30 days |
Steel | As Machined | 1 | $25 – $45 | 1 – 5 days |
|
| 10 | $20 – $40 | 5 – 10 days |
|
| 100 | $15 – $30 | 10 – 20 days |
|
| 1000 | $10 – $30 | 20 – 30 days |
Brass | As Machined | 1 | $20 – $40 | 2 – 5 days |
|
| 10 | $15 – $40 | 5 – 7 days |
|
| 100 | $10 – $30 | 7 – 1 days |
|
| 1000 | $10 – $25 | 15 – 20 days |
Copper | As Machined | 1 | $25 – $50 | 3 – 7 days |
|
| 10 | $20 – $40 | 7 – 10 days |
|
| 100 | $15 – $35 | 10 – 20 days |
|
| 1000 | $10 – $30 | 20 – 30 days |
ABS | As Machined | 1 | $10 – $30 | 2-5 days |
|
| 10 | $5 – $30 | 5-7 days |
|
| 100 | $5 – $20 | 7-10 days |
|
| 1000 | $5 – $10 | 10-20 days |
Nylon | As Machined | 1 | $10 – $30 | 2-5 days |
|
| 10 | $10 – $20 | 5-10 days |
|
| 100 | $5 – $20 | 10-15 days |
|
| 1000 | $5 – $15 | 15-20 days |
POM (Delrin) | As Machined | 1 | $20 – $60 | 2-5 days |
|
| 10 | $20 – $50 | 5-10 days |
|
| 100 | $10 – $40 | 10-15 day |
|
| 1000 | $10 – $20 | 15-20 days |
Mechanical properties determine how easy a material is to cut. The higher the machinability, the faster CNC machining can be done, shortening manufacturing time and thus reducing costs. Processability depends on the physical properties of each material. Generally, the softer and more ductile a metal alloy is, the easier it is to work. For example, compared with C360 brass, the cost of stainless steel 316 is higher. Therefore, higher-cost metal parts are more suitable for high-volume production. In this case, economies of scale come into play, as shorter CNC machining times offset higher material costs. As far as plastics go, ABS, nylon and PTFE cost about the same as aluminum 6061. PEEK, commonly used in medical prototype parts, is a very expensive plastic material, and the corresponding prototype parts are also more expensive.It is important to note that these cost estimates are approximate and may vary based on market conditions and specific project requirements.
CNC machining time
Time is more expensive than any other factor. The longer the CNC processing time, the higher the corresponding cost. CNC machining can be divided into CNC turning and CNC milling, and the calculation of the processing time of the two processes is different. To help you better understand CNC machining time, AN-Prototype has summarized the machining time formula based on years of experience.
Calculate CNC turning time:
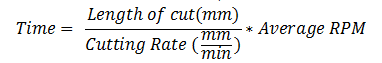
And average RPM can be calculated with the following simple formula:
Calculate CNC milling time:
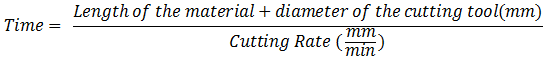
CNC machining labor costs
Even though CNC machining eliminates manual labor, operators are still needed and you also need to consider their income. If the prototype part is difficult to machine and requires the expertise of a more advanced, trained machinist, then the corresponding costs will increase. These additional skills and experience come at a cost because they come primarily from on-the-job experience rather than formal education and training. The labor cost of CNC machining consists of 3 parts:
Programming:
Since CNC programming involves digitization and requires professional programmers, their labor cost is very expensive, higher than the cost of any other labor force. Typically, prototype manufacturers hire one or more CNC programmers. Before they process the parts, they will carefully evaluate your 3D drawings and decide which CNC machine to use. In addition, programmers also need to convert CAD files into files that can be read by CNC machine tools, such as CAM files.
Settings:
After converting from CAD to CAM, you also need an operator who can operate the CNC machine to ensure the best end result for the prototype part and ensure that every part performs as it should. At the same time, after each process, the operator uses a caliper or micrometer to measure the parts to ensure the accuracy of the parts until the parts are processed. This detection process may take dozens of times.
Quality control:
The quality of different CNC machining service providers varies, but every CNC machining shop has a quality inspection team to ensure that CNC-made parts can meet customer expectations.

Complexity of prototype part design
The complexity of the prototype design is another important factor affecting the cost of CNC machining. Parts of different complexity require different manufacturing methods. For example, prototypes with complex geometries require complex CNC programming and precise control, require longer processing times, and even require the use of more expensive 5-axis CNC machining centers. Tight tolerances and complex structural features require specialized tools and methods. The cost of this special processing method is very high. Prototype features such as sharp internal corners, deep cavities, or thin walls can increase CNC machining costs. Larger prototype parts require more raw materials and time, so they cost more than smaller parts. Therefore, the more complex the prototype design, the greater the impact on CNC machining costs, which is caused by a combination of factors such as the use of advanced multi-axis CNC machining centers, skilled labor and long CNC machining times.

Quantity of CNC machined parts
Quantity has a huge impact on CNC machining costs. As production volumes increase, economies of scale come into play, resulting in lower costs per prototype part as fixed expenses such as setup, machining time, personnel wages, etc. are spread over more units. In high-volume production, setup expenses per part are much lower, allowing for more efficient use of setup time and lowering overall expenses. Conversely, a prototype part means setup costs and time represent a larger percentage of the total expense, thus increasing costs. In CNC machining, the right balance between throughput and setup efficiency is critical. Manufacturers have been searching for a production volume that benefits from economies of scale without leading to excess inventory. Therefore, optimizing throughput is a strategy that has a significant impact on the cost of CNC machined parts.
Surface treatment
The surface finish of a part refers to the texture and appearance of its surface and is critical for functionality and aesthetics. The cost of surface treatment depends on the time and effort required to complete the machining operation to achieve the desired effect. More complex finishes require additional machining operations, special tooling and longer time, adding expense. Instead, a simpler finish is more cost-effective. Certain surface treatments, such as polishing and plating, can be time-consuming and require specialized equipment, which adds to the cost. On the other hand, other surface treatments such as sandblasting and anodizing are faster and therefore less expensive. Balancing expected results with cost implications is critical in design and manufacturing planning, especially for materials that require specific finish techniques. The table below shows the cost and lead time for different surface treatments for aluminum machined parts.

Material | Surface Finish | Quantity | Unite Price (Estimated) | Lead Time (Estimated) |
Aluminum | As Machined | 1 | $10 – $25 | 1 – 5 days |
Aluminum | Anodizing | 1 | $10 – $30 | 2 – 5 days |
Aluminum | Bead Blasting | 1 | $10 – $30 | 2 – 6 days |
Aluminum | Polishing | 1 | $15 – $30 | 3 – 7 days |
Aluminium | Bead blasted + Anodised | 1 | $15 – $40 | 3 – 7 days |
Aluminum | Brushing | 1 | $15 – $45 | 3 – 7 days |
Aluminum | Powder Coating | 1 | $25 – $50 | 4 – 7 days |
Aluminum | Electroplating | 1 | $30 – $60 | 5 – 10 days |
Aluminium | Mirror polished | 1 | $40 – $80 | 7 – 10 days |
As you can see from the table, mirror polish is the most expensive surface treatment. It is a very time-consuming manual process and also requires the use of higher grades of aluminum, such as AL7075, which further increases the cost of the prototype part. Anodizing is a relatively inexpensive surface treatment process, which is why anodizing is the most popular surface treatment service for aluminum parts. The effect of sandblasting is better, and the corresponding parts cost increases by about 10%.
CNC machining vs 3D printing costs
The cost of 3D printing tends to be directly proportional to the number of prototypes produced. In contrast, with CNC machining, the cost per unit of prototype typically decreases as production quantity increases because multiple parts can be manufactured more efficiently from the same block (or a slightly larger one). For highly complex designs, CNC machining may not be as cost-effective as 3D printing. This is because the complexity of the process requires more expertise, advanced CNC machines and tools. And no matter how complex the part, 3D printing can keep costs relatively stable. Since 3D printing is a layer-by-layer process, the complexity of the design does not have a significant impact on cost. Understanding the cost difference between the two can help you make informed decisions about which manufacturing process may be more cost-effective based on your specific project. To better understand how to calculate the cost of 3D printing, contact AN-Prototype’s team of engineers today.
Tips for reducing CNC machining costs
Reducing CNC machining costs requires a combination of optimized design, material selection and manufacturing processes. Here are some tips to help you minimize your CNC machining costs:
Optimize your designs: Complex designs and tight tolerances often require more advanced CNC machines and tooling as well as longer programming time and more advanced labor. Reducing unnecessary features or complex geometries and following ISO2768-M tolerance standards can significantly reduce costs.
Use compatible material alternatives: CNC machining processes are compatible with a wide range of materials. Especially during the prototyping stage, explore compatible, cost-effective materials that serve the purpose without compromising on quality.
Avoid multiple finishing operations: Proof-of-concept prototypes typically do not require delicate surface finishing and extensive surface treatment. Eliminate unnecessary steps and try to incorporate missing elements directly into the final design.
Ordering in batches: Consider producing parts in large quantities. CNC machining benefits from economies of scale. Manufacturing more parts in smaller batches reduces the setup cost per part, thereby lowering overall costs.
In-house vs. outsourced: It’s worth considering outsourcing your CNC project to a CNC machining shop in China. CNC machining services in China are so cheap that they are worth considering, but whether they can guarantee quality is a concern? In this case, our advice is to research the company’s reputation, check reviews or contact them directly.
Get an estimate: Prepare your CNC machining process, send initial drawings to get a pre-sales quote, and then ask for their advice. Often, they will be able to point out areas that can be improved or modified to reduce unnecessary costs.
Conclusion
This blog introduces in detail the factors that affect CNC machining costs, and uses actual cases to demonstrate the price of processing prototype parts. So, how much budget do you need for CNC parts? Upload your 3D CAD to AN-Prototype’s quoting tool, marking required technology, materials and surface treatments to get a free quote. An expert from our engineering team will respond to you within 24 hours.