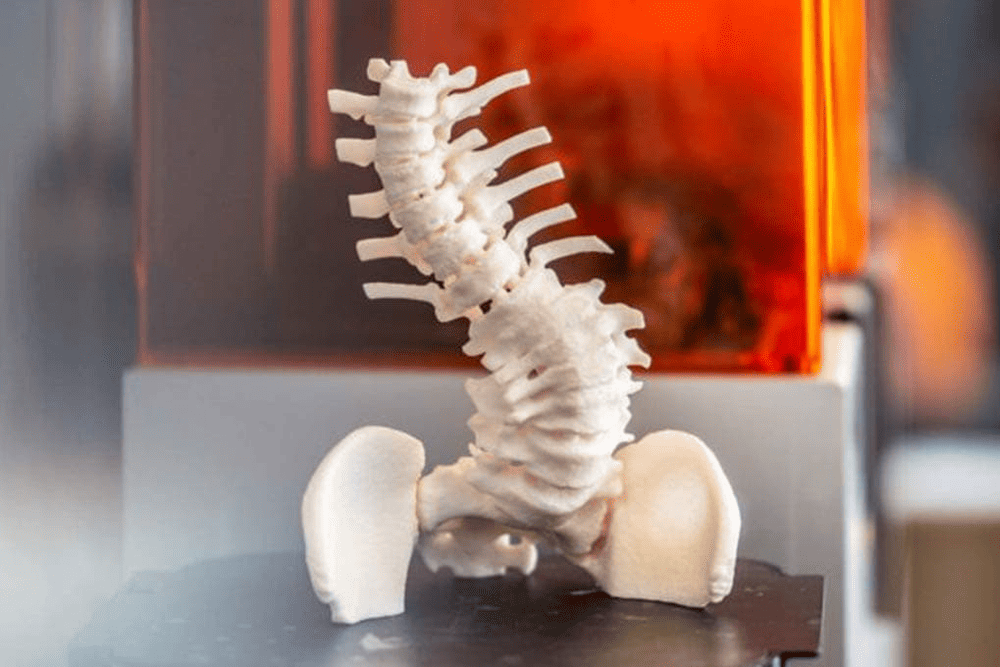
3D printing offers multiple solutions for the development of medical devices as the field is evolving with time. 3D printing has helped the healthcare industry bring important medical tools and devices to the market at relatively less cost and time.
In this guide below, you will learn how 3D printing has helped the medical industry evolve and how it proves to be helpful in medical prototyping. So, let’s read below.
Table of Contents
Toggle1.What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, helps manufacture a solid object with 3 dimensions. In this process, layers of the material are deposited one after the other to create an object. These layers are observed to have a finely sliced cross-section of the object manufactured.
3D printing is the opposite process of subtractive manufacturing in which the material is cut. Instead, in 3D printing, no cutting and milling occur; rather, the material is added layer after layer to achieve a desired object.
3D printing allows the creation of shapes with complex textures, and as compared to other methods, it is more suitable because it uses less material.

1.1 Plastic 3D printing
Plastic 3D printing is one of the very common kinds of methods used in manufacturing 3D printed objects. This technique helps to manufacture products in the medical field which are simple and low-cost. Such parts may also be machined, but still, it is preferred to have them manufactured through 3D printing.
The different kinds of plastics used in plastic 3D printing comprise ABS, PLA, nylon, TPU, PETG, HIPS, PVA, etc. Each type of plastic has its quality and features. Some are flexible, some resist wear and tear, and some are waterproof.
Plastic 3D printing offers less accuracy at the consumer level. However, basic medical devices may be manufactured through this process having simple designs.
Also, medical devices subjected to heavier loads are usually not opted to be manufactured using this technique of 3D printing because the voids between the layers of plastic are quite common in them.
However, the SLS is also a process of 3D printing where complex geometrical devices can be manufactured using plastics. This method is highly suitable for undercuts and interior textures with thinner walls. The finishing is rough, but the layer lines are still not very visible.
Medical devices manufactured under SLS 3D printing include nylon 11 and 12 and TPU because of their flexibility and impact resistance.
1.2 Resin 3D printing
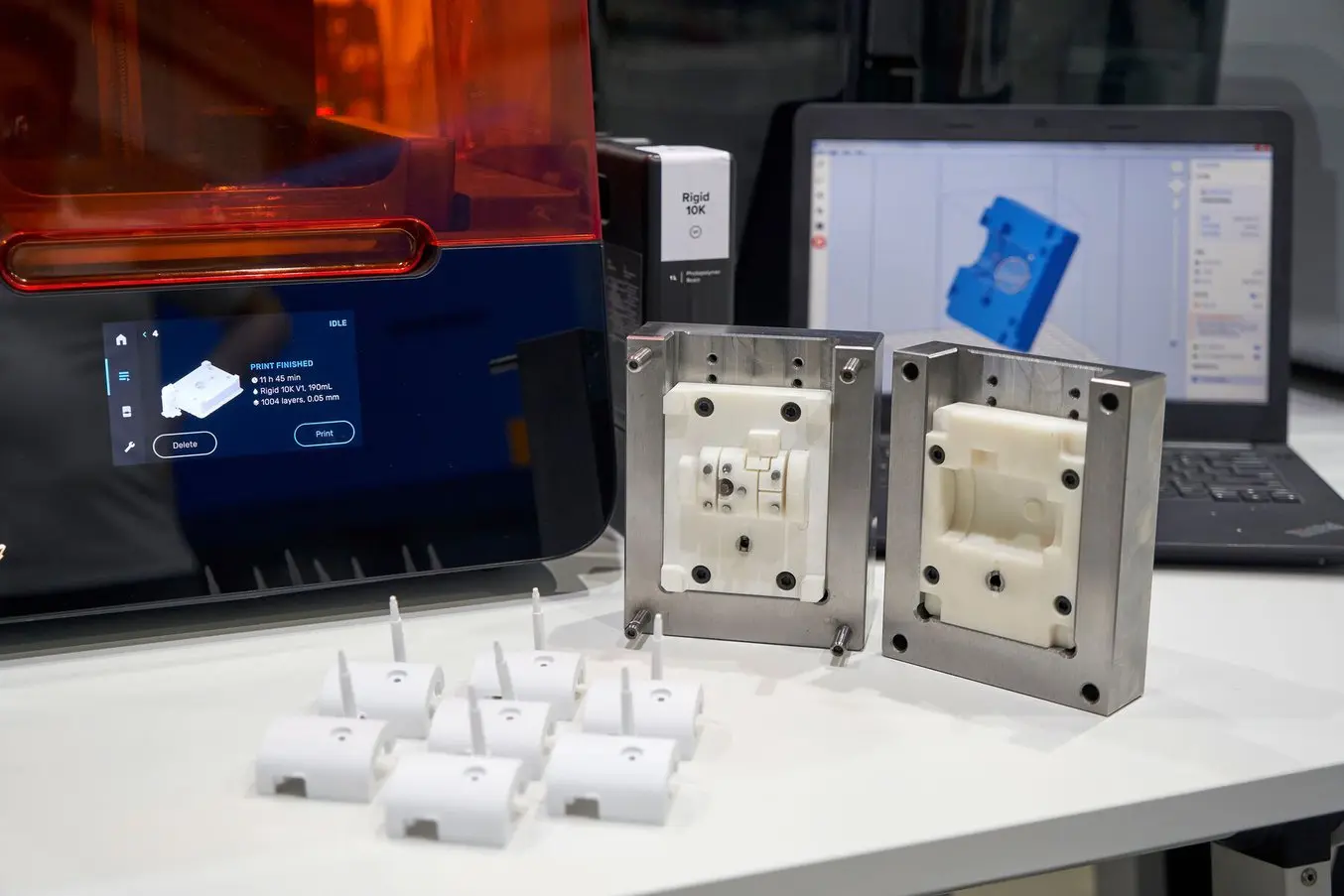
Resin 3D printing, also known as SLA 3D printing, can produce the most accurate parts with high accuracy and resolution. The surface created by the resin 3D printing is the smoothest compared to the other 3D printing types.
Hence, resin 3D printing is highly successful for most medical devices because there is no room for medical negligence regarding accuracy and perfection.
Medical devices that need tight tolerance and smooth surfaces are usually made with 3D printing. It is an ideal process for manufacturing the functional parts, which can be polished after printing.
The orientation of the chemical bond between the layers of the parts produced is highly consistent; hence, the strength of these devices is also commendable. Therefore, medical fixtures and functional prototypes used in medicine are usually manufactured through resin.
Medical and dental resins are typically used for medical devices as these are biocompatible resins and produce multiple dental and medical appliances. The commonly manufactured medical appliances are dentures, surgical guides, and prosthetics.
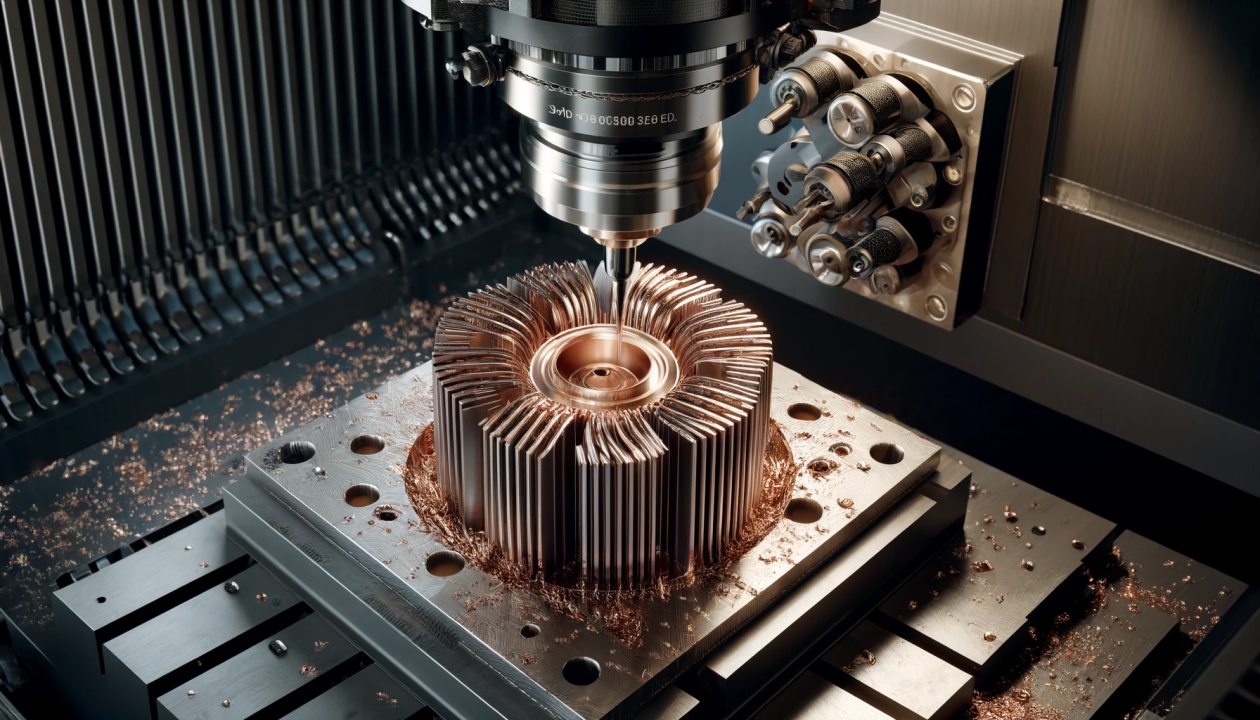
1.3 Metal 3D printing
Metal 3D printing is also one of the common forms of 3D printing, which is based on different methods. The metal FDM printers are traditional printers that use metal rods to carry out printing.
On the other hand, the SLM and DMLS are also two kinds of 3D printers that are the same as SLS, but they use metal powers that are fused layer by layer to create the required medical prototype.
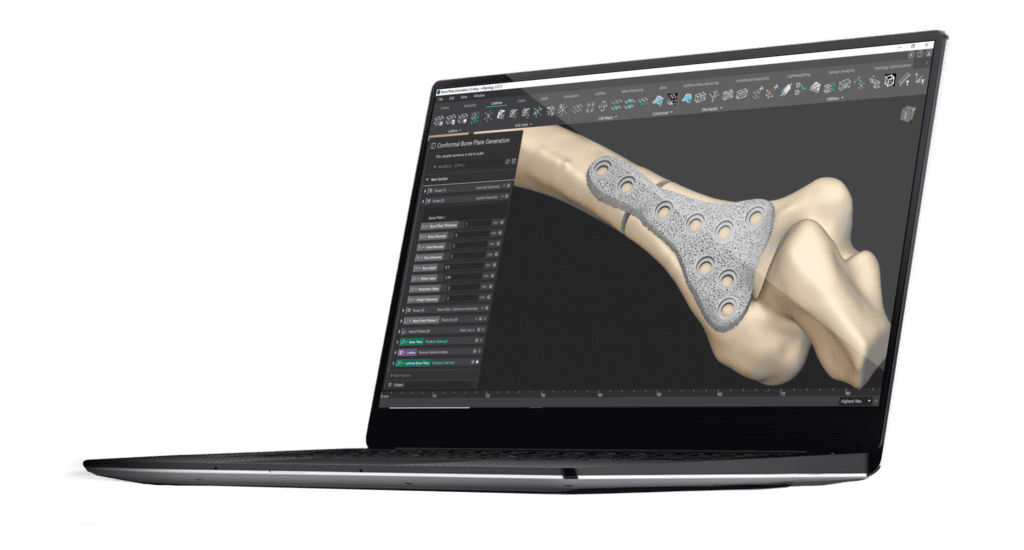
The SLS and DMLS 3D Printers can create highly accurate, strength-oriented, and even suitable for complex medical parts. Hence, these are highly suitable for medical applications.
Metal powders used are titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, and tool steel due to their durability, scratch resistance, and other resistive properties.
1.4 Color 3D printing
By way of considering color 3D printing, multicolored parts can be manufactured. This kind of printing is carried out through colorjet printers, and the object is manufactured layer by layer through printing.
Multiple medical devices that are colored are also subjected to this kind of printing as an additive manufacturing process; it is very economical and helps reduce waste.
2.Advantages of 3D printing
There are multiple advantages of 3D printing for every application, and in the medical industry as well, the 3D printing techniques prove to be highly helpful, and some of the common advantages are as follows:
Flexibility in Design
3D printing is one of the most flexible printing techniques compared to the traditional methods. 3D printing leads to the creation of flexible designs with multiple material options. In medicine, there are different kinds of medical devices, each having its own requirements, and due to the versatility of this method, manufacturing these medical devices is easier.
3D printing is a process that can be carried out within hours, so if any medical device is needed, the part can be manufactured immediately. Machining still takes time and is expensive, whereas 3D printing is one of the quickest methods.
Helps Avoid Overstocking
3D printing works with the method of print on demand, this means that there is no need to pile the stock of medical devices, and rather, you can have it manufactured within no time. By having less excessive inventory, a lot of space can be saved.
Strength Oriented and Lightweight Parts
3D printing is known for producing high-quality parts used in different applications. It is highly suitable for the field of medicine because it can help manufacture most medical devices that need sufficient strength yet are light in weight.
3.Surface treatment of 3D-printed parts
3D printed parts after manufacturing also need an added surface treatment for a smoother surface depending on the object’s layout and the kind of material it is used for its manufacturing. There are different ways in which the surface treatment for these parts could be carried out, and some of these are as follows:
Sanding
Sanding is a very popular method through which the 3D-printed parts can be finished. It is one of the basic processes in which sandpaper is rubbed against the object in an area where the surface is rough. If the object has any imperfections and sharp corners, those could be smoothened.
The sanding technique is very cost-effective and suitable for most materials, and there are multiple sizes in which the sandpaper comes and can be chosen according to the object’s size.
Machining
3D printing can further be equipped with CNC machining. Once the object is manufactured through 3D printing, it can be finished through CNC machining. To have a fine surface finish, machining and grinding of the object could be carried out.
This surface treatment method is ideally suitable for objects that need tight tolerance and can reach areas that are deep and hard to reach for finishing purposes.

Bead Blasting
One of the popular methods of surface finishing is 3D printing. This process involves using plastic or glass beads, and when they strike the rough surface, they smooth it out and flatten out all the imperfections.
Compared to sanding, bead blasting is a quick method and hence helps in smoothing the inaccessible areas.
Plating
Plating involves applying a thin metal coat on the object’s surface manufactured through 3D printing using an electrical circuit.
There are multiple benefits to opting for this method of surface treatment. It helps to improve the object’s material properties as the plastic parts are susceptible to break, and when plated appropriately, their durability and wear resistance can be improved.
Painting
Painting is another very straightforward process that helps improve the appearance of the objects in no time. It helps to smooth the surface and fill the gaps, and to a certain extent, it even helps with the sealing process of the object.
4.The Market for 3D Printing in Healthcare
The market for 3D printing in the healthcare sector is consistently growing. The advancements taking place in technology have led the medical sector to invest in research and development. As the patient pool is increasing, so are the biomedical applications driving the market growth of 3D printing.
In the year 2020, the valuation of the market size of 3D printing in the healthcare sector was $1036.58 million. However, it is expected to reach $5,846.74 in the year 2030, leading to a rise in CAGR of 20.10 percent from 2021 to 2030.
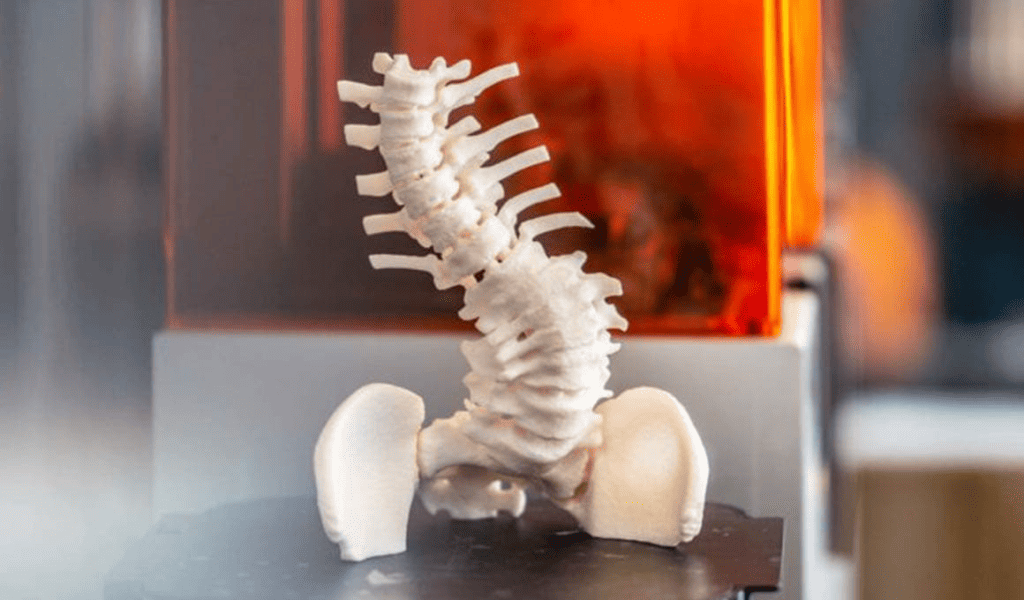
5.Materials For 3D Printing Medical Prototyping?
Different materials are used in 3D printing when it comes to medical prototyping, and some of these materials are discussed below:
Polylactic Acid
PLA is a form of plastic highly popular with FDM 3D printing. It is affordable and very easy to work with when it comes to printing and offers biodegradability. Using PLA and 3D printers, working ventilators were even created during COVID-19 to help treat patients by medical professionals and engineers. It is also used in many orthopedic devices, like plates, fixation pins, screws, and bone scaffolds.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
ABS is also a form of plastic used in 3D printing, and it is a very lightweight and strong material that can be melted in liquid form and then turns out to be a solid when cooled. It is used in the medical sector for manufacturing the models used in surgeries, prostheses, and orthopedic corsets.
Polyetheretherketone
PEEK is a highly-performing thermostat that offers resistance against chemicals and has seamless mechanical properties. It is used instead of metals in many cases and has a lot of medical applications that consist of implants and customized medical devices.
Titanium
Titanium is a commonly used kind of metal in 3D printing, and when it comes to the medical sector, it is used for manufacturing surgical tools and joint replacements. Many implants like hip, knee, and spine are manufactured using titanium in 3D printing because of their excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
Polyethylene Glycol
PEG is a form of plastic used in 3D printing, and it has biochemical characteristics that make it suitable for the medical sector. It is used for creating cartilage, bone, and vascular tissues using 3D printing.
6.How does 3D printing work in Medical Prototyping?
3D printing works in different ways for the development of varied medical devices when it comes to medical prototyping, and some of these are discussed below:
6.1 3D Printing Custom Implants
Printing custom implants will comprise a method that is followed for the process of 3D printing, and it comprises the following steps:
- Through a CT scan or any other image and modeling method, the 3D model of the implant site is created so that the implant can be designed accordingly.
- The medical practitioner designs the implant digitally based on the customization depending on the patient's anatomy that fits them.
- Usually, biocompatible materials are opted when it comes to printing a custom implant; for this, the material chosen is introduced in the printer.
- The printer prints the object layer by layer, and after the implant is ready, it may undergo a further process that helps to improve its properties, and then quality checks are performed.
- Once the implant is finalized, sterilization takes place, and it is surgically implanted for the patient.
6.2 3D Printing For Medical Device Prototyping
3D printing for medical device prototyping comprises the below-given stages:
- The concepts were first created using CAD software for medical devices.
- Once the concepts and designs are ready, 3D printing is carried out, which tends to create physical prototypes.
- The medical device prototype then goes through the testing process in which the device's safety, ergonomics, and functionality are tested.
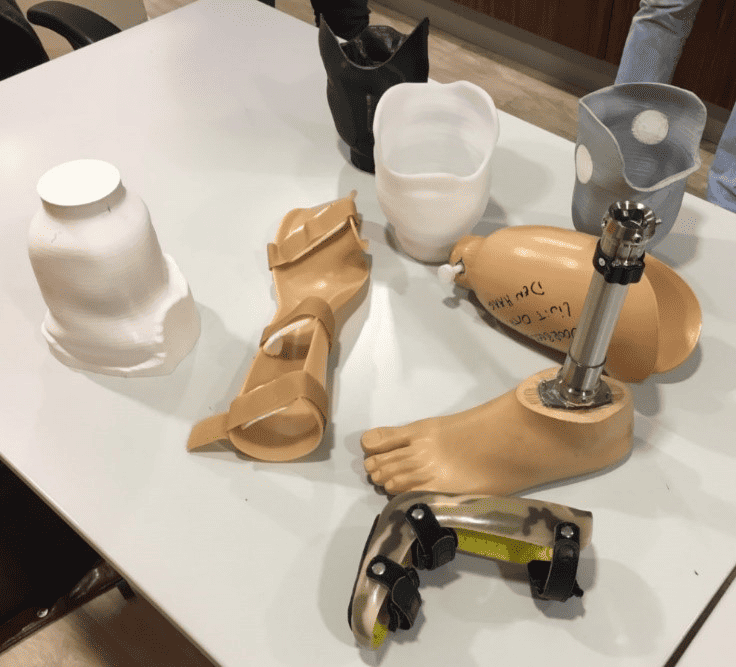
6.3 3D Printing For Custom devices & prosthetics
In order to carry out the 3D printing for custom devices and prosthetics, the below-given steps are followed:
3D scans are first obtained so that the devices’ and prosthetics’ anatomy and requirements can be understood and measurements can be assessed.
After the data has been obtained, these prosthetics are custom-designed.
Once the design is ready, the biocompatible materials are used, and 3D printing for these devices is carried out layer by layer.
The devices manufactured are then subjected to testing, and if needed, changes are made to ensure the perfection of their function and fit.
7.How to get 3D printing services?
As you have gone through the article above, you must now be well aware of everything relating to 3D printing in the medical field and the relevant materials used for manufacturing.
3D printing services for medical device manufacturing are highly specialized. The efficiency and quality of the medical devices have no room for negligence. Therefore, when choosing the right service provider, AN-Prototype should be your go-to place.
We at AN-Prototype always provide our clients with fast turnaround times, high-quality products, and affordable costs. So, get in touch with us today to have your quote.