Aluminum alloy is an engineering material made by injecting small amounts of other different metals into pure aluminum. The properties of different aluminum alloys vary with different alloying elements to meet specific production requirements. Aluminum is typically the metal material of choice for most rapid fabricators and is one of the most popular of all metals. Among them, aluminum 6061 and aluminum 5052 are aluminum alloy grades that are highly valued in the manufacturing industry. Therefore, choosing which one is the best choice for your CNC machining project can seem a bit confusing. Each alloy has its unique advantages and disadvantages, such as excellent durability, versatility, mechanical properties, processability, and more. In this article, we will explore the differences between aluminum 6061 and aluminum 5052 in terms of performance, cost, and applications, and guide you on which one you should choose to make the right decision for your CNC project.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is aluminum alloy 5052 ?
Aluminum 5052 is a member of the 5xxx grade aluminum alloy family, in use since 1930 and receiving its standard designation in 1954. The main alloying element of 5052 aluminum alloy is magnesium, about 3-5%. Therefore, it is also called aluminum-magnesium alloy. The main characteristics of 5052 aluminum alloy are low density, high tensile strength, high elongation, and cannot be heat treated. Aluminum 5052 has excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability, and high fatigue strength.
Aluminum 5052 is the strongest non-heat treatable aluminum grade commonly used. Therefore, Aluminum 5052 performs very well as a plate or sheet metal. In this way, the metal sheet or plate combines excellent weldability and formability with increased strength. 5052 aluminum does not contain copper, which makes it less susceptible to salt water corrosion. Therefore, 5052 aluminum is widely used in marine environments, construction, pressure vessels and fuel containers. The density of 5052 aluminum is 2.68g/cm3, which is slightly lower than pure aluminum, so it is very commonly used in the aerospace field, such as aircraft fuel tanks. 5052 aluminum is also widely used in some traditional industries, such as 3C products, fuel tank materials, high-end curtain wall panels, blinds, pressure vessels and medical equipment.

What is aluminum alloy 6061 ?
The main elements added to the 6000 series aluminum alloy are magnesium and silicon, and the representative aluminum alloy is 6061. The 6061 aluminum alloy has the characteristics of medium strength, good corrosion resistance, weldability, no deformation after processing, easy coloring, and good oxidation effect. Aluminum 6061 is one of the most widely used aluminum alloys and can be found in almost every corner of the manufacturing industry. Aluminum 6061 is said to be the most versatile aluminum alloy while retaining most of aluminum’s useful properties. This aluminum grade was developed in 1935 and was originally called “Alloy 61S“.
Aluminum 6061 is a precipitation hardening aluminum alloy that is widely used in various industrial structural parts that require a certain strength and high corrosion resistance, such as mobile phone slots, mobile phone casings, manufacturing trucks, tower buildings, structural materials, ships, railway vehicles , precision processing, etc.
What is the difference between aluminum 5052 and aluminum 6061?
Both aluminum 5052 and aluminum 6061 have excellent properties. They have different elemental compositions and serve different purposes. Additionally, both aluminum alloys can be used for the same purpose. It sounds confusing. To facilitate understanding, we will compare the properties exhibited by the two alloys. This is to ensure you have a deeper understanding of Aluminum 5052 and Aluminum 6061 so you can make the best choice for your next CNC project.
NO.1 5052 vs. 6061 aluminum chemical composition
Element | Composition (%) | |
5052 Alloy | 6061 Alloy | |
Si | 0.25 | 0.4-0.8 |
Fe | 0.4 | 0.7 |
Cu | 0.1 | 0.15-0.4 |
Mn | 0.1 | 0.15 |
Mg | 2.2-2.8 | 0.8-1.2 |
Cr | 0.15-0.35 | 0.04-0.35 |
Ni | – | – |
Zn | 0.1 | 0.25 |
Ti | – | 0.15 |
Others:Each | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Others:Total | 0.15 | 0.15 |
Aluminumin | Remainder | Remainder |
NO.2 5052 vs 6061 aluminum specification
Alloy | 5052 | 6061 |
Thickness(mm) | 0.1-600 | 0.3-500 |
Width(mm) | 20-2650 | 100-2800 |
Length(mm) | 500-16000 | 500-16000 |
NO.3 5052 and 6061: Alloy series
5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum exist in different forms. These changes can be used for comparison. In this section, we will differentiate between each alloy by listing their respective alloy variations. There are approximately 19 alloy variations of 5052 aluminum. They include:
- Aluminum 5052-O
- Aluminum 5052-H38
- Aluminum 5052-H39
- Aluminum 5052-H34
- Aluminum 5052-H36
- Aluminum 5052-H32
- Aluminum 5052-H322
- Aluminum 5052-H26
- Aluminum 5052-H28
- Aluminum 5052-H22
- Aluminum 5052-H24
- Aluminum 5052-H18
- Aluminum 5052-H19
- Aluminum 5052-H14
- Aluminum 5052-H16
- Aluminum 5052-H112
- Aluminum 5052-H12
- Aluminum 5052-F
- Aluminum 5052-H111
The 6061 aluminum grades exist in pre-tempered and tempered grade. This include:
- 6061-O Aluminum
- 6061-T1 Aluminum
- 6061-T4 Aluminum
- 6061-T42 Aluminum
- 6061-T451 Aluminum
- 6061-T4510 Aluminum
- 6061-T4511 Aluminum
- 6061-T51 Aluminum
- 6061-T6 Aluminum
- 6061-T62 Aluminum
- 6061-T651 Aluminum
- 6061-T6510 Aluminum
- 6061-T6511 Aluminum
- 6061-T652 Aluminum
- 6061-T89 Aluminum
- 6061-T94 Aluminum
NO.4 5052 vs 6061 aluminum density
The density of 5052 aluminum alloy is 2.68 g/cm 3 (0.0968 lb/in 3 ), which is slightly lower than pure aluminum. Therefore, it can be used in applications that require lightweighting, such as aircraft fuel tank materials, new energy vehicles and other fields. Aluminum 6061 has a density of 2.7 g/cm 3 (0.0975 lb/in 3 ) and its weight is approximately the same as pure aluminum.
NO.5 5052 vs 6061 aluminum mechanical properties
Relatively speaking, 6061 aluminum alloy has better machining, while 5052 is more used in sheet metal and welding applications. This difference is caused by differences in alloy composition. The mechanical properties of a material are the physical properties it exhibits when a force or impact is acted upon. Both 5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum exhibit a variety of mechanical properties.
Properties | 5052 Aluminum | 6061 Aluminum | ||
Units | English | Metric | English | Metric |
Shear Modulus | 3760 ksi | 25.9 Gpa | 3770 ksi | 26.0 Gpa |
Modulus of Elasticty | 10200 ksi | 70.3 Gpa | 10000 ksi | 68.9 Gpa |
Fatigue Strength | 17000 psi | 117 Mpa | 14000 psi | 96.5 Mpa |
Shear Strength | 20000 psi | 138 Mpa | 30000 psi | 207 Mpa |
Electrical Resistivity | 3.99 x 10-6 ohm-cm | 5.15 x 10-6 ohm-cm | ||
Machinability | Good | Fair | ||
Hardness (Brinell) | 95 | 150 | ||
Elastic Modulus
The modulus of elasticity is a measure of how well an alloy material resists plastic deformation in the presence of external forces. Materials with a higher modulus are said to be more elastic. This is because additional force is required to cause the material to permanently deform. Therefore, alloys with higher modulus indicators are preferred for forming applications. In addition to this, elastic materials are less likely to break when deformed. We compared 5052 aluminum to 6061 aluminum and found that 5050 aluminum has the highest elastic modulus (70.3 GPa). Therefore, if resiliency is a consideration when choosing an alloy for your CNC project, 5052 aluminum is a more suitable choice.
Conductivity
Conductivity is the degree to which a material conducts electricity. It is measured as the ratio of current density to the electric field causing the current to flow. In a comparison using the same volume of 5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum, the conductivity of 5052 aluminum was approximately 7% lower than that of 6061 aluminum. This suggests that 6061 aluminum may be superior to 5052 aluminum in applications where conductivity is more important.
Machinability
6061 aluminum offers better machinability. Machinability is a measure of how responsive an alloy material is to CNC milling, die cutting, CNC turning, or other machining operations. These processability operations can be measured using some processability scales. Our scale will be reported as a Likert scale. The rating is expressed in terms of Excellent, Good, Fair, and Poor ratings. In terms of machinability, 6061 aluminum is rated “Good” while 5052 aluminum is rated “Poor”. This is because 6061 aluminum is more brittle and breaks more easily when machined, resulting in fewer chips. 5052 aluminum, on the other hand, is rated poorly due to its elastic properties.

Material hardness
The hardness of an alloy material depends on its resistance to indentation or penetrating deformation. In this case, different amounts of force were used to penetrate two aluminum alloys, and the results showed that 6061 aluminum was able to resist penetration under pressure without much deformation. This means that 6061 aluminum (276 MPa) is more difficult to permanently deform than 5052 aluminum (193 MPa).
Thermal Conductivity
As we all know, aluminum alloys are good conductors of heat. Therefore, 5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum are no exception. Thermal conductivity is a measure of how much heat a metal alloy can transfer. The primary factor to consider when manufacturing parts for heat exchangers and radiators is the thermal conductivity of the material. The thermal conductivity of 6061 aluminum is higher than that of 5052 aluminum. Therefore, 6061 aluminum is an ideal material for CNC-machined heat sinks.
Yield Strength
Yield strength represents the maximum stress that results in non-permanent (elastic) and permanent (plastic) deformation. The yield tensile strength of 5052 aluminum is approximately 193 MPa and the ultimate tensile strength is 226 MPa. The yield tensile strength of 6061 aluminum is approximately 276 MPa and the ultimate tensile strength is 310 MPa. This shows that 6061 aluminum has better yield strength than 5052 aluminum.
Shear strength
Shear strength refers to the maximum load that can be supported to the axis of a fastener before breaking when applied at a right angle. In this regard, 5052 aluminum has a shear strength of 138 MPa (20,000 psi), while 6061 has a shear strength of 207 MPA (30,000 psi). This shows that 6061 aluminum has higher shear strength than 5052 aluminum.
Fatigue strength
Fatigue strength is the ability of a material to withstand cyclic load cycles. If given enough time, small repetitive forces can cause “metal fatigue,” or weakening due to molecular microfractures, ultimately reducing the strength of the alloy. The fatigue strength of 6061 aluminum alloy is lower than that of 5052 aluminum alloy (96.5MPa vs. 117MPa), which means that 5052 aluminum alloy can withstand more deformation cycles.
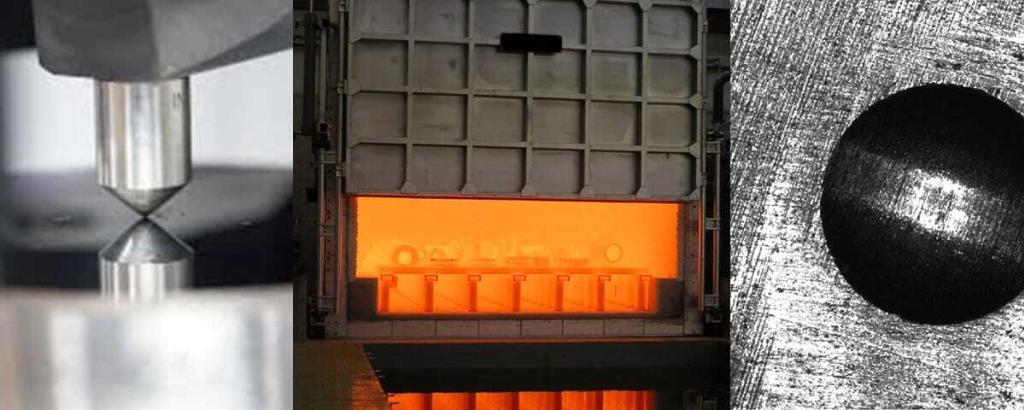

NO.6 5052 vs 6061 aluminum alloy heat treatment
5052 is a non-heat treatable aluminum alloy. This means that 5052 aluminum alloy can be strengthened by cold working or strain hardening (such as rolling or forging). However, 6061 aluminum alloy can be heat treated to increase its strength and durability. It will be heated in a submerged furnace at 533 °C (990°F) and then water quenched. 6061 T4 aluminum alloy and 6061 T6 aluminum alloy are the most common heat treatment states of 6061 and are often used in heavy-duty structures.
NO.7 5052 and 6061 aluminum: corrosion resistance comparison
When aluminum alloys are exposed to air or water, they form a layer of oxide. This oxide layer prevents the alloy from reacting with corrosive elements. The corrosion resistance of such materials depends on water/atmospheric conditions such as temperature, airborne chemicals, and chemical composition. 5052 aluminum does not contain any copper elements and therefore performs very well under ambient conditions. When used in saltwater environments, it is less susceptible to corrosion, which can weaken and corrode copper metal composites. Therefore, 5052 aluminum is preferred over 6061 aluminum in chemical and marine applications.
Additionally, when both alloys are exposed to alkaline soil, a reaction called pitting may occur. However, due to the magnesium content of 5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum, they are both resistant to corrosion caused by ammonia, ammonium hydroxide, and nitric acid. To avoid corrosion, alloy coatings can be used to create a protective layer for both alloys.
NO.8 5052 and 6061 aluminum: weldability comparison
Both alloys have excellent weldability. 5052 aluminum has the best welding properties of all aluminum alloys, making it ideal for manufacturing aluminum enclosures. With 6061 aluminum, care must be taken when welding filler metal. To restore the weld to its original “T” mark, post-weld heat treatment may be required.
NO.9 5052 and 6061 aluminum: price comparison
The price of a 6061 aluminum plate of the same volume is higher than that of a 5052 aluminum plate. This is because 6061 aluminum is more difficult to process. However, the price of both alloys depends heavily on the specification requirements and also on the requirements of your specific project.
NO.10 5052 vs 6061 aluminum alloy applications
Application of 5052 aluminum alloy
5052 aluminum alloy is widely used in various industries due to its excellent tensile strength, elongation, corrosion resistance and rust resistance. The product characteristics of 5052 make it widely used in marine industry, electronic industry and chemical applications.
Marine applications: large marine structures, LNG storage tanks, marine equipment.
Architectural decoration: building facade.
Household appliances: electronic casings, kitchen cabinets, electrical appliances, fans and fan blades, household freezers, clock plates, fences, etc.
Transportation: Aircraft, bus and truck manufacturing, road and name signs, fuel lines and tanks, street lights, and other signs for the transportation industry.
Industrial manufacturing: pressure vessels, sheet metal parts, heat exchangers, chemical equipment, aluminum pedals, etc.
Application of 6061 aluminum alloy
6061 aluminum alloy is one of the commonly used extruded aluminum profiles. Thanks to its formability, it can be formed into sheets, rounds, squares, extrusions, rolling, or any form. Due to its good formability, the uses of 6061 aluminum alloy mainly include the following aspects:
Ship manufacturing: sailing boats, yachts, marine frames, marine accessories, and hardware.
Automotive manufacturing: truck and bus bodies, wheels and various transportation end use, brakes, and hydraulic pistons.
Aerospace: aircraft structural parts, fuselage parts.
Rail transportation: railway vehicle components, subway platforms, stairs, floors, covers, and walkways.
Food industry: canned food, food and beverage cans.
Others: Diving cylinders, pipe fittings, hinge pins, valves and valve parts, bicycle frames, fire ladders, bridge parts, camera lens mounts, couplings, electrical accessories and connectors, magneto parks, structural frames, basic Equipment and gussets.

Conclusion
No matter which grade of aluminum alloy you plan to use, they all have their own advantages. However, choosing the right alloy for your CNC machining aluminum project is crucial. The perfect aluminum alloy will help save time and money due to its excellent properties. These properties include weldability, corrosion resistance, cost efficiency, strength-to-weight ratio, and more. AN-Prototype helps our customers achieve successful projects in CNC metal and plastic machining. Our knowledgeable and enthusiastic team will be happy to work with you on your next CNC project. Contact us for more information.