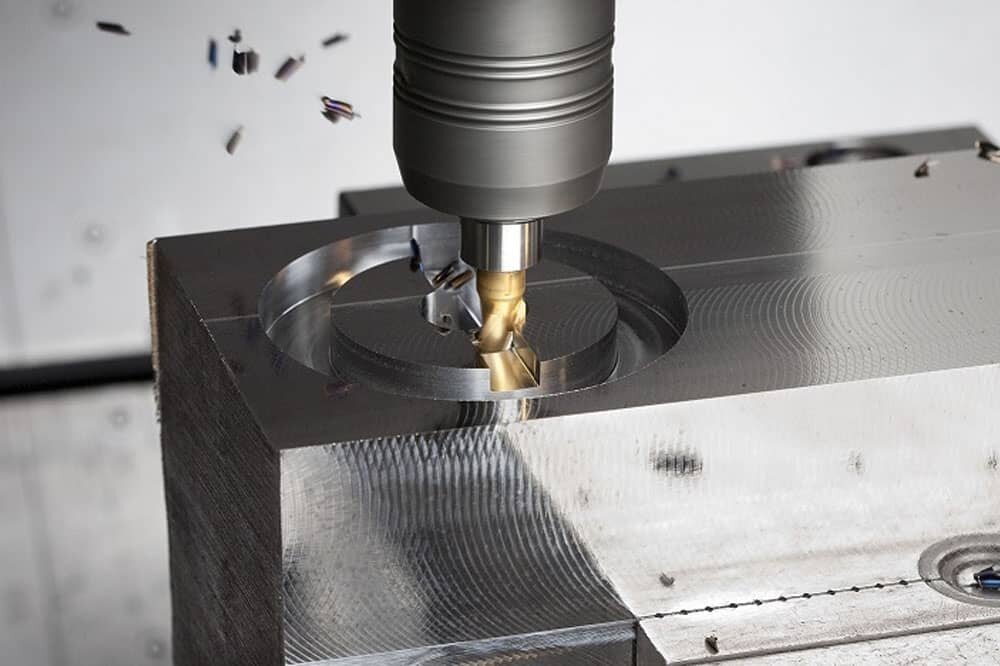
Precision CNC machining stainless steel parts are the choice of industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical and military due to their ideal mechanical properties. Stainless steel has excellent machinability and excellent uniformity, as well as good processability and weldability, making it ideal for a variety of CNC machining projects. Stainless steel is also highly ductile and formable to meet the specifications of any project. CNC machining stainless steel has proven to be one of the most popular metals in the rapid manufacturing industry. Stainless steel also has very high tensile strength and is highly resistant to corrosion and wear, increasing product durability and the life of the part. Stainless steel is distinguished from ordinary steel by the presence of chromium in its alloy. All stainless steel chemistries contain at least 10.5% chromium. The addition of chromium makes these steels more resistant to corrosion. Different grades of stainless steel contain various alloying elements that further improve corrosion resistance, heat treatability and machinability. It should be noted that heat treatment can significantly affect the mechanical properties of metals.
Table of Contents
ToggleAN-Prototype's CNC Machining Stainless Steel Capabilities

- Price:$ $ $
- Lead Time:< 10 days
- Wall Thickness:0.5 mm
- Tolerances:±0.005mm
- Max Part:2000 x 800 x 1000 mm
- Grinding & CNC Drilling & CNC Tapping
- 3 Axis, 4Axis, 5Axis, CNC Milling & Turning
- CNC Swiss Machining, Sinker EDM, Wire EDM
Advantages of stainless steel
Strength
Stainless steel is popular for CNC machining projects because of its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, which allows for thinner parts. Because stainless steel can withstand extreme temperatures, its strength can be further increased through cold hardening and heat curing processes to suit specifications. Martensitic stainless steel has the highest strength.
Highly versatile and Flexible.
The flexibility of stainless steel allows it to be easily formed, welded, cut and CNC machined. Elemental sulfur can be added to further improve its formability, and austenitic stainless steels are generally considered the most formable and versatile variant, enabling their use in a variety of applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, allowing it to be used in harsh environments, withstanding exposure to acids, chlorides, and alkaline solutions. Austenitic stainless steels with higher chromium content have higher corrosion resistance.
Low Cost and Durable.
Stainless steel is one of the preferred materials for CNC machining projects because it requires less maintenance. Stainless steel can withstand harsh environments and a wide temperature range. Compared to other metals, stainless steel achieves a longer life cycle at a cost-effective price.
Aesthetic Appeal
Stainless steel is available in a variety of finishes such as passivated, media-blasted, sanded, hand-polished, and powder coated to create an attractive, contemporary look that complements any medical device, kitchen, home design and theme .
High Tensile Strength
Stainless steel has higher tensile strength than mild steel, brass and aluminum alloys. This is an important quality over the life of many products, especially for parts that experience a lot of bending and rolling.
Compared to metals such as Inconel, brass, nickel and titanium, stainless steel offers greater resistance and longer life at a lower cost. Non-metallic materials such as plastic, glass, and ceramics are weaker, less durable, and cannot withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive usage like stainless steel.
Type of Stainless Steel
There are more than 150 grades of stainless steel. These different stainless steels are divided into different categories. Let’s explore the five types of stainless steel one by one:
Austenitic stainless steel
Austenitic stainless steels are the most popular type of all stainless steels. These stainless steels have an austenitic structure and are non-magnetic. In addition, they cannot be hardened by heat treatment because they contain elements such as nickel, manganese and nitrogen. Austenitic stainless steels are divided into two subgroups:
AISI 200 and AISI 300. Molybdenum is sometimes added to austenitic stainless steels to improve corrosion resistance.
- Type 304
- Type 316
- Type 321H
- Type 309S
- Alloy 20 (Carpenter 20)
Properties of austenitic stainless steel
- Corrosion resistance: very high
- Heat Treatable: No
- Magnetic: Non-magnetic
- Toughness: very high
- Extensibility: very high
- Welding Capability: High
- Chromium content: average 18%
- Nickel content: typically 8% to 12%
- Molybdenum content: 2%~7%
- Carbon content: less than 0.1%
- Stress corrosion cracking: Low resistance
Application of Austenitic Stainless Steel
Grade 200 stainless steel is used in household products such as washing machines, cars, buildings, tanks, and dishwashers.
Grades 300 stainless steel are used in the manufacture of aerospace, medical, mining, tableware and storage equipment.
Ferritic Stainless Steel
Ferritic stainless steel was discovered in 1912. However, the use of ferritic stainless steels did not become popular until the 1980s. Ferritic stainless steels belong to the AISI 400 series. In terms of physical properties, ferritic stainless steel is not superior to other steels. However, they have excellent qualities in terms of magnetic properties and chemical resistance. The strength of ferritic stainless steels lies in their ability to resist corrosion cracking.
Examples of ferritic stainless steels:
- Type 405
- Type 409L
- Type 410L
- Type 430
- Type 439
- Type 447
Properties of ferritic stainless steel:
- Corrosion resistance: very high
- Heat Treatable: No
- Magnetic: Yes
- Toughness: Moderate
- Extensibility: Medium
- Soldering capacity: low
- Chromium content: 10.5% to 30%
- Nickel content: usually nickel-free
- Molybdenum content: usually 1% to 2%
- Carbon content: less than 0.08%
- Stress corrosion cracking: High resistance
Application of ferritic stainless steel
Ferritic stainless steel can be used to make kitchen utensils, auto parts and industrial parts.
Martensitic stainless steel
Martensitic stainless steel is named after Adolf Martens and is known for its extreme hardness. Martensitic stainless steels are heat treated to obtain high hardness and temper.
Examples of Martensitic Stainless Steels:
- X12Cr13
- X20Cr30
- X50CrMoV15
- X17CrNi16-2
Properties of martensitic stainless steel:
- Corrosion resistance: high
- Heat Treatable: Yes
- Magnetic: most are Yes, some are non
- Toughness:high when tempered
- Extensibility: High
- Welding Capability: High
- Chromium content: 12% to 17%
- Nickel content: usually nickel-free
- Molybdenum content: none to 1%
- Carbon content: 0.1% to 1.2%
- Stress corrosion cracking: poor resistance
Application of martensitic stainless steel
Martensitic grades are used in surgical instruments, dental equipment, bumpers, firearms, tableware and ball bearings.
Duplex stainless steel
Duplex stainless steels are designed with two structural components. Duplex alloys are combinations of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. Duplex stainless steels improve the quality of these two structural elements. There are three grades of duplex stainless steel: standard duplex, super duplex, and lean duplex alloys.
Examples of duplex stainless steels:
- X2CrNiN22-2
- X2CrCuNiN23-2-2
- X2CrNiMoSi18-5-3
- X2CrMnNiMoN21-5-3
- X2CrNiMoCuN25-6-3
- X2CrNiCuN23-4
Properties of duplex stainless steel:
- Corrosion resistance: good to very high
- Heat Treatable: Yes
- Magnetic: Yes
- Toughness: high
- Extensibility: Medium to High
- Welding ability:Yes
- Chromium content: 18% to 30%
- Nickel content: 1% to 9.5%
- Molybdenum content: 0.1%~5%
- Carbon content: no
- Stress corrosion cracking: very high resistance
Application of duplex stainless steel
Duplex stainless steels are used in heat exchangers, tubes, shells, columns, condensers, reactors, piping, and other commercial equipment.
Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steel
Precipitation hardening stainless steels are also known as PH stainless steel alloys. These alloys have small additions of elements such as titanium, copper, phosphorus or aluminum. After alloying, these steels are age hardened. The yield strength of precipitation hardening stainless steels is 3-4 times that of austenitic stainless steels.
Examples of precipitation hardening stainless steels:
- 17-4 PH stainless steel
Application of precipitation hardening stainless steel
PH hardened steel for extremely high strength requirements. Common examples are marine construction, aircraft, nuclear power plants and the chemical industry.
Common CNC machining stainless steel grades
As a rapid manufacturing service company, AN-Prototype provides a full range of CNC machining services, and the optional materials are not limited to engineering plastics, aluminum alloys, stainless steel and titanium. We specialize in multi-axis CNC milling, turning with tight tolerances (+/-.005mm). Our standard CNC milling drills range from 0.010” to 4.0”, allowing us to machine your custom parts as efficiently as possible. With fast cycle times and consistently accurate results, we can deliver your parts on time and to specification with 100% full-scale inspection reports.

303 Stainless Steel
303 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel containing sulfur and selenium elements, easy to cut, and is one of the easiest stainless steels to process among all austenitic stainless steels. 303 stainless steel has excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance, moderate cost, cannot be hardened by heat treatment, and is not suitable for marine applications.
- Tensile strength σb (MPa): ≥520
- Conditional yield strength σ0.2 (MPa): ≥205
- Elongation δ5 (%): ≥40
- Reduction of area ψ (%): ≥50
- Hardness: HB≤187HB; HRC≤90HRB; HV≤200HV

304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is a common material in stainless steel, with a density of 7.93 g/cm³; it is also called 18/8 stainless steel in the industry, which means it contains more than 18% chromium and more than 8% nickel; it can withstand high temperatures of 800 ° C and has good processing performance , high toughness, widely used in industry, furniture decoration industry and food medical industry.
- Tensile strength σb (MPa)≥515-1035
- Conditional yield strength σ0.2 (MPa)≥205
- Elongation δ5 (%)≥40
- Hardness: ≤201HBW; ≤92HRB; ≤210HV
- Resistivity (20℃, 10-6Ω·m2/m): 0.73

316 Stainless Steel
The 316 series is the second most commonly used stainless steel. 316 stainless steel has better resistance to chlorides, such as salts, which makes it the first choice for applications involving chlorides and salts. The molybdenum content of 2% to 3% in Series 316 enhances the heat resistance and wear resistance of Series 316.
- Elongation δ5 (%): ≥30
- Reduction of area ψ (%): ≥40
- Tensile strength σb (MPa): ≥ 620
- Conditional yield strength σ0.2 (MPa): ≥310

420 Stainless steel
420 stainless steel is a martensitic stainless steel that has good corrosion resistance similar to 410, and is stronger and harder. 420 stainless steel is magnetic in both the annealed and hardened conditions. Maximum corrosion resistance is only obtained when fully hardened. But it will never be used in the annealed state.
- Tensile strength σb (MPa): quenched and tempered, ≥635
- Elongation δ5 (%): quenching and tempering, ≥20
- Reduction of area ψ (%): quenching and tempering, ≥50
- Impact energy Akv (J): quenching and tempering, ≥63

430 Stainless Steel
430 stainless steel is a general purpose steel with good corrosion resistance. It has better thermal conductivity, smaller thermal expansion coefficient and thermal fatigue resistance than austenite. Stainless steel 430 is used for architectural decoration, oil burner parts, household appliances, household appliance parts.
- Density: 7.75g/cm³
- Melting point: 1427℃
- Expansion coefficient: mm/℃(at 20-100℃)
- Young's modulus: kN/mm²

440 Stainless Steel
440 stainless steel has strong rust resistance. 440 stainless steel is mainly used to manufacture bearing parts that work in corrosive environments and non-lubricated environments. 440C has good high-temperature dimensional stability, so it can also be used as a corrosion-resistant high-temperature bearing steel.
- Hardness: Annealed, ≤269HB;
- Quenching and tempering, ≥58HRC
- Internal stress (250 N/mm2)
- Tensile strength (560 N/mm2)

15-5 stainless steel
15-5 Stainless Steel is a precipitation hardening (PH) metal. This process gives it excellent toughness, strength and corrosion resistance. Mechanical properties are enhanced by low-temperature heat treatment, making this material ideal for aerospace and nuclear applications.
- Tensile Strength, Yield (MPa):1208
- Shear Modulus (GPa):75
- Elongation at Break (%):9.8
- Hardness (Brinell):420
- Density (g/cm^3):7.8
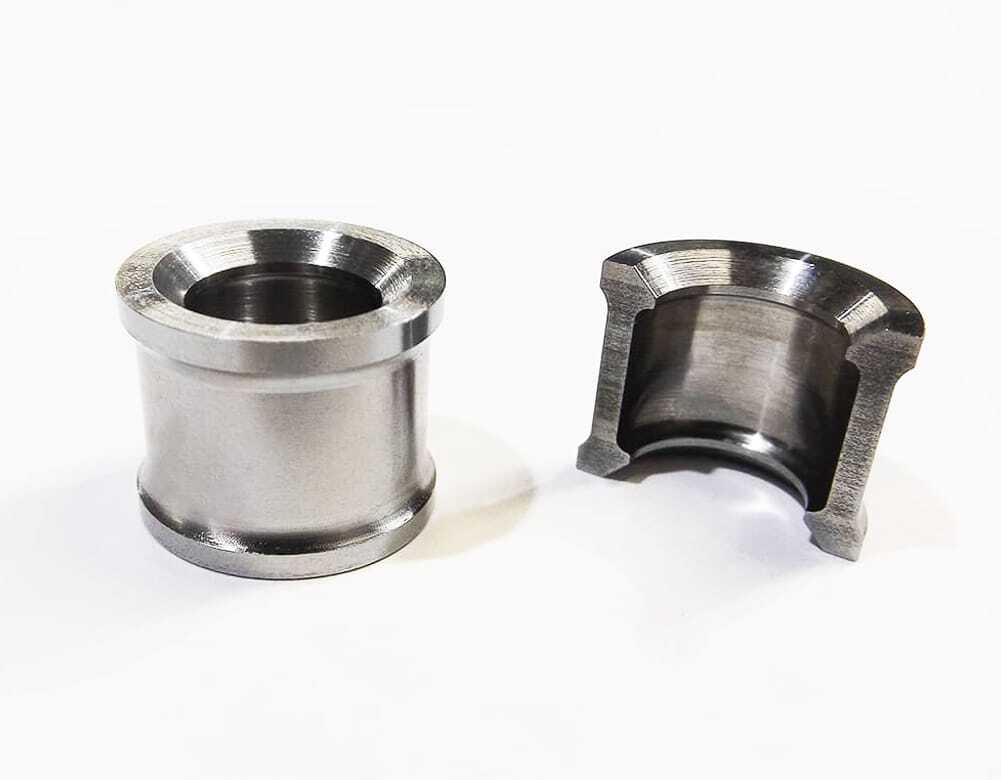

17-4 stainless steel
Compared with 15-5 stainless steel, 17-4 stainless steel has better corrosion resistance at high temperature. It increases corrosion resistance by sacrificing mechanical strength. 17-4 stainless steel applications include chemical processing parts and gas turbines.
- Tensile Strength, Yield (MPa):1090
- Shear Modulus (GPa):77.4
- Elongation at Break (%):6
- Hardness (Brinell):352
- Density (g/cm^3):7.70
Stainless Steel CNC Machining Technology
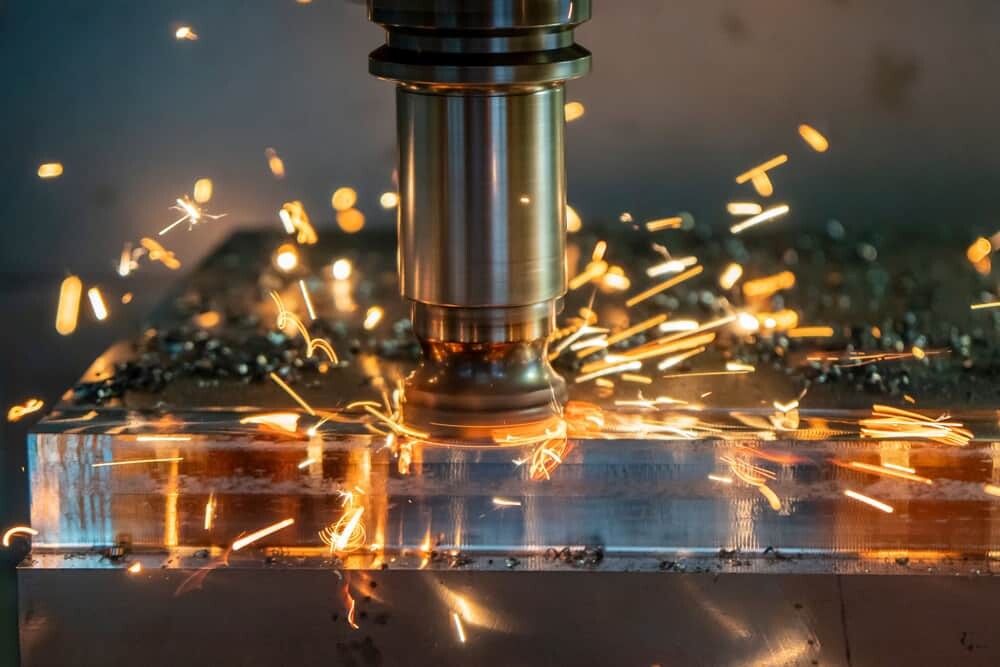

CNC milling is the use of a computer-controlled system combined with a cutting tool, or milling cutter, to cut material from a solid block to create parts made of materials such as metal, plastic, wood, and fiberglass.
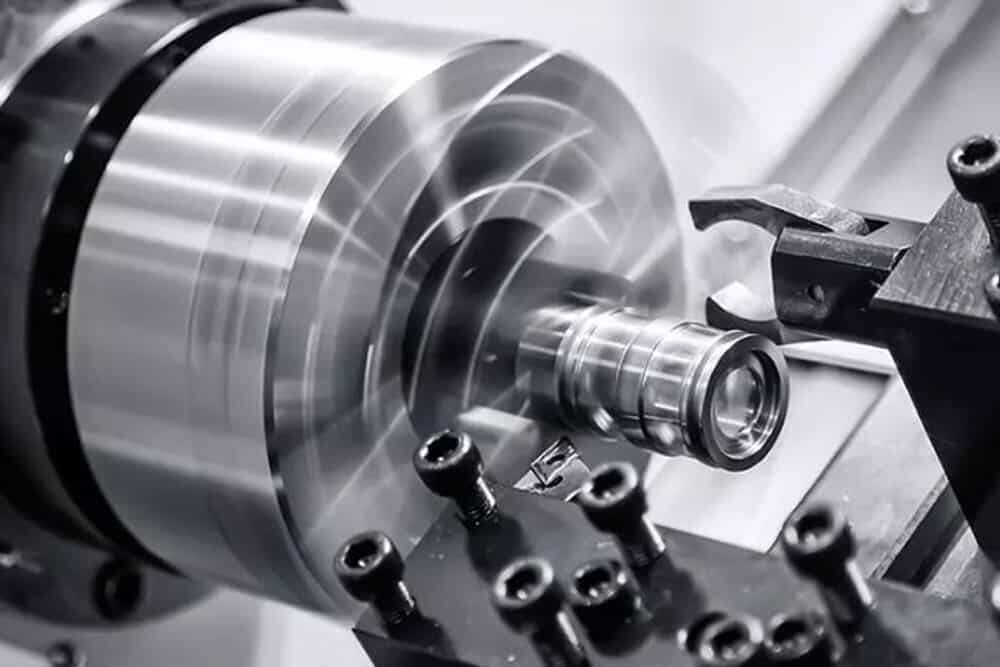

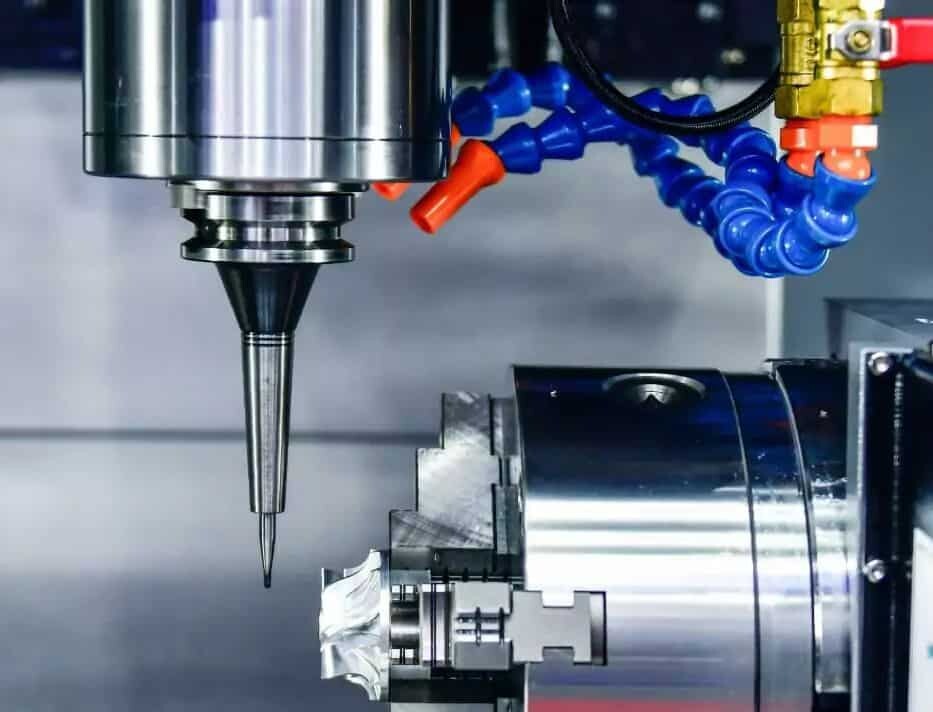
CNC turning is when a rod of material is held in a chuck and rotated while a tool is fed into the workpiece and removes material to create the part in the desired shape. CNC turned parts are mostly circular features.
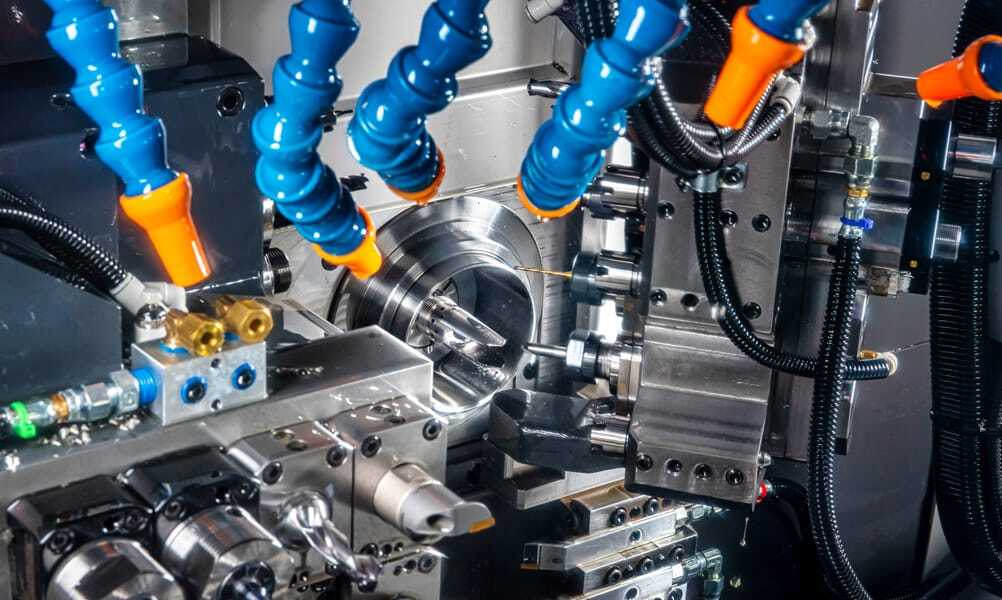

Swiss CNC Machining
CNC Swiss machining is an advanced manufacturing technique utilizing specialized tool cutting designed to machine metal blanks into complex, slender or delicate components requiring tight tolerances.
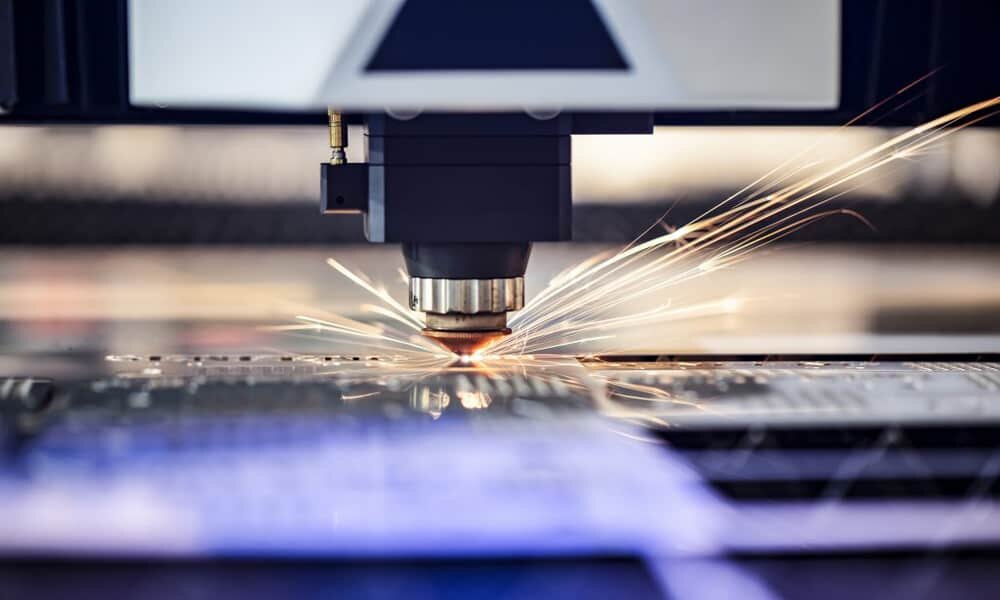

CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting uses a focused, high-power laser beam to cut or engrave material to form custom shapes. It is highly accurate, especially when cutting complex shapes and small holes.
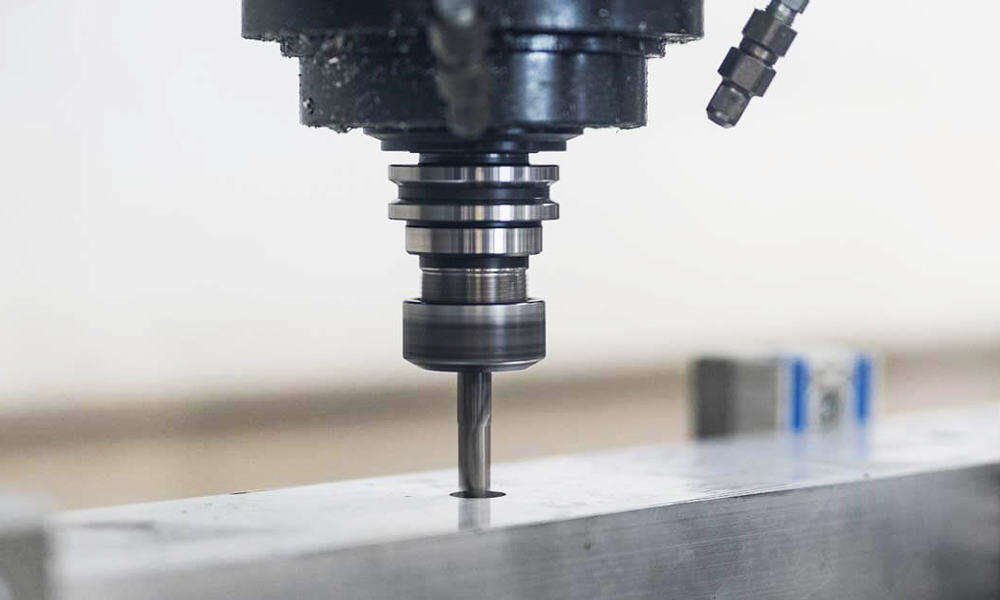

CNC Drilling
CNC drilling is a machining process that uses a rotating cutting tool to create a round hole in a workpiece. These holes are usually to accommodate screws or bolts for assembly purposes.
CNC Tapping
CNC tapping is the process of creating threads on a part. It must be drilled with a tap and threaded in the hole while chamfering the end so that the screw or bolt can be screwed into the hole.
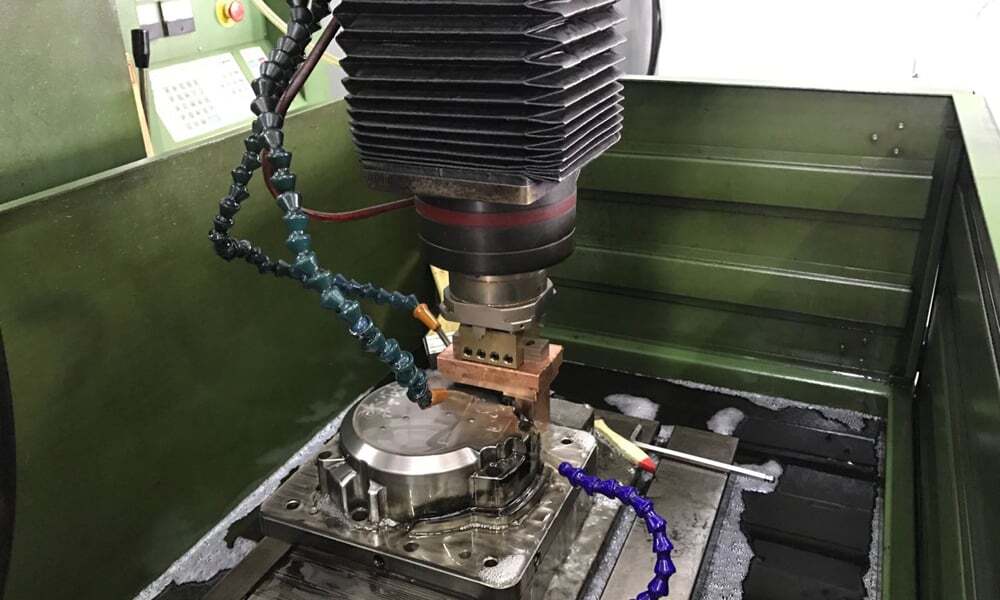

Sinker EDM
Sinker EDM is the process of immersing two conductive parts in some insulating liquid (dielectric) to create high precision parts by controlling the sparks, cooling the workpiece and flushing away eroded particles.
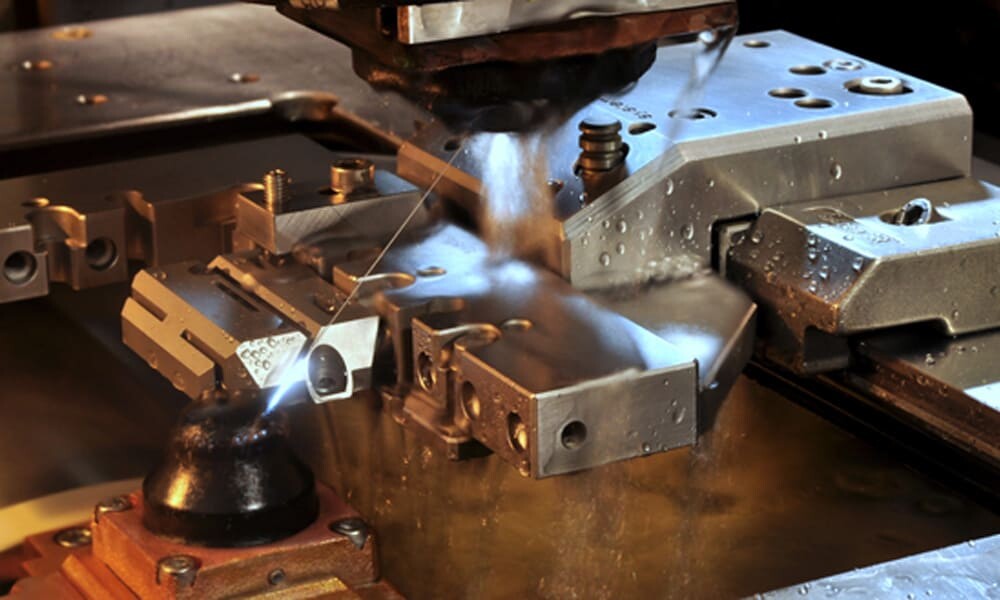

Wire EDM
Wire EDM is a non-contact subtractive manufacturing process that uses thin charged wires and a dielectric fluid to cut metal parts into different shapes, compatible with almost all conductive materials.
The Challenges of CNC Machining Stainless Steel
The hardness, machinability, strength and heat resistance of stainless steel are between titanium and aluminum. There are indeed some obstacles in the process of CNC machining stainless steel. For example, austenitic stainless steels are especially prone to work hardening during CNC machining, which makes them even harder. If the machinist is not familiar with machining stainless steel, this can increase tool wear and negatively affect the quality of stainless steel parts.
Additionally, stainless steel tends to have low thermal conductivity, causing heat to build up in the cut area for a short period of time. Without adequate cooling and proper cutting parameters, these temperatures may be high enough to cause stainless steel sensitization. Depending on the specification of the stainless steel part, this can mean severe compromises in corrosion and stress cracking resistance. Despite these challenges, an experienced machinist can reliably produce high-quality CNC stainless steel parts when CNC machining stainless steel with the right tools and equipment.
Which stainless steels are difficult to CNC Machining?
Every stainless steel will have some level of trouble during CNC machining. However, some stainless steels have more problems with this than others. Here are some difficult-to-machine steels and their troubles:
High-carbon steel
High carbon steel is difficult to CNC machine due to its extreme strength and hardness. In addition, these steels contain carbide-grade materials. These factors cause the tool to wear out rather quickly.
Low-carbon steel
It turns out that low-carbon alloys are also difficult to CNC machine. This is due to the high hardness of mild steel. Softness causes steel shavings to stick to cutting tools. This also shortens tool life.
316 stainless steel
316 stainless steel is one of the least machinable stainless steels. It requires specialized CNC cutting tools for machining. Therefore, 316 stainless steel is used for parts only when there are no other options.
304 stainless steel
The problem with 304 stainless steel is that it hardens during CNC machining. 304 stainless steel exhibits the property of rapid work hardening during machining. This problem was solved by adding sulfur to the workpiece.
Which stainless steel is easiest to CNC machine?
416 stainless steel is the easiest to machine. In fact, 400 series stainless steel grades are very easy to machine. On the other hand, CNC machining of 300 series stainless steel grades is difficult.
Tips for CNC machining stainless steel
CNC machining stainless steel can be made easier by employing the following tips:
High Quality Raw Materials
Use the highest quality stainless steel material for the smoothest operation. There are many grades of stainless steel. There are multiple quality options within each grade. Purchasing quality raw materials can help save a lot of cost and hassle from broken knives.
Rigid Fixture
The fixture connection and the CNC machine should be very tight. Any tool chatter will be magnified and result in poorly machined parts. In addition, the body of the machine tool should not have excessive vibration after the workpiece is installed.
Tool material
Selecting the correct tool material is critical to obtaining high-quality parts. Carbide tools are made of tungsten carbide, titanium carbide or tantalum carbide. Carbide cutters result in a better part surface finish. This makes them ideal for mass production and high cutting speeds.
Using sharp tools
Make sure you have sharp tools for consistent and precise machining. It is best to replace worn tools. Using blunt tools can lead to tool breakage and even damage to the workpiece material. When machining steel, tools also need to grind sharp edges.
Lubricant
The use of lubricants is critical when CNC machining stainless steel. Lubrication serves a variety of purposes in machining. First, it reduces the friction between the cutting tool and the metal. This equates to extending the life of the tool. Second, lubrication can reduce the temperature during CNC machining. This reduces work hardening and overheating problems. Finally, the lubricating fluid also washes off stainless steel residues from workpieces and tools.
Overall, while CNC machining stainless steel can be more challenging, it is often worth it given the benefits of CNC stainless steel parts. That’s why designers should choose a reliable CNC machine shop like AN-Prototype that can manufacture high-quality stainless steel parts at an affordable cost.