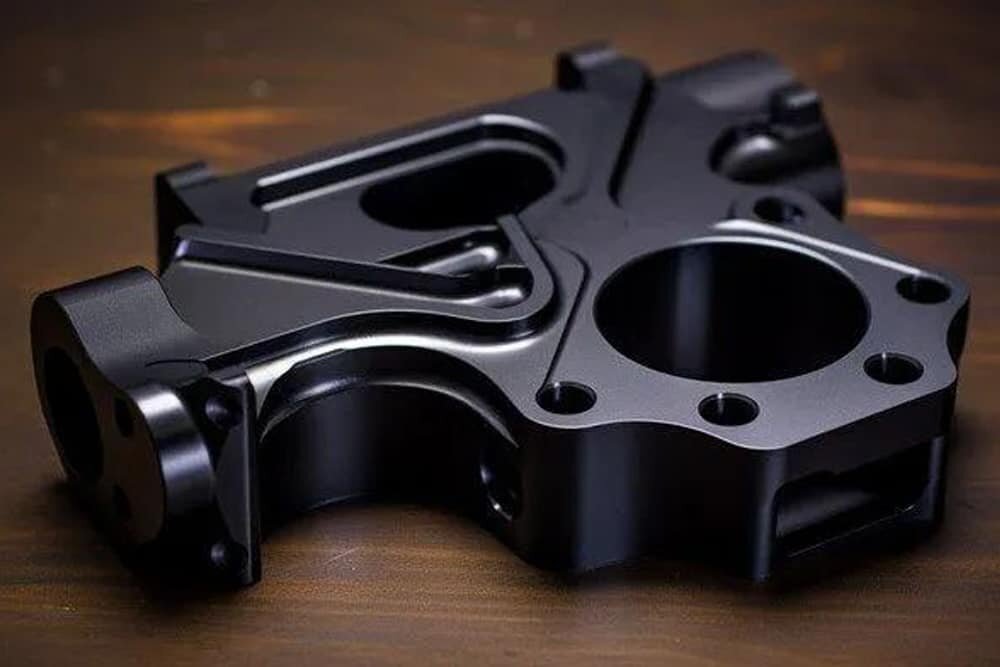
Aluminum is a popular choice in many industries due to its lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance. However, the surface of aluminum can be subject to wear and tear, and its properties can degrade over time. That’s why many designers opt for hard coat anodizing as a way to enhance the performance and longevity of their aluminum parts. In this ultimate guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of hard coat anodizing, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this process.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Hard Coat Anodizing?
Hard coat anodizing, also known as Type III anodizing, is an excellent corrosion-resistant coating that utilizes a thick coating of aluminum oxide to produce a protective layer on the surface of the aluminum. The process involves passing a current through an electrolytic solution, and the aluminum part is the anode, hence the term anodizing.The resulting coating is much denser and thicker than regular anodizing, providing superior protection against abrasion, corrosion, and impact.While regular anodizing produces a thin layer of aluminum oxide on the surface of the part, hard coat anodizing creates a much thicker layer. The thickness of the coating can range from 0.002 to 0.0045 inches, depending on the specific requirements of the application. The resulting coating is much harder, more wear-resistant, and offers superior electrical and thermal insulation properties. Additionally, the coating is much more resilient and able to withstand harsh environments.

The hard coat anodizing process:
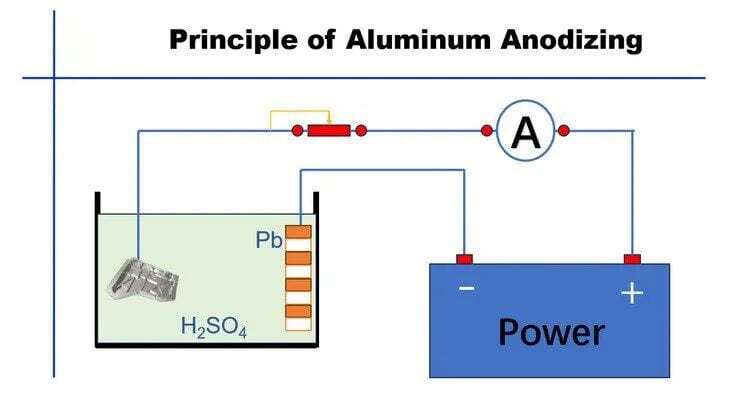
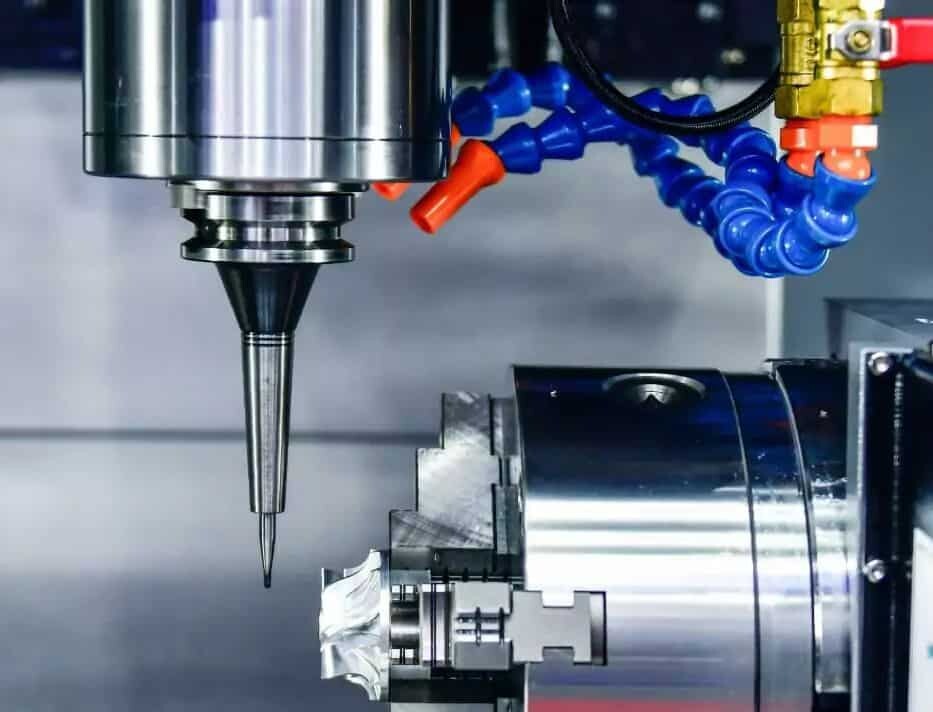
Before the hard coat anodizing process begins, the aluminum part is cleaned and prepared to ensure that the surface is clean and free of any impurities. The anodizing process begins with placing the part in an electrolytic solution, usually sulfuric acid. The process requires a precise mix of acid, current flow, solution temperature, and duration of process to achieve the desired outcome. The part is submerged in this electrolyte, and the solution actuates the anodizing process. The process creates a precisely controlled oxide layer on the surface of the piece. The thickness of the oxide is a specific function of the time the aluminum is exposed to the acid bath and the current density at which the aluminum part is subjected.
Advantages of Hardcoat Aluminum Anodizing
1. Durability
Hardcoat aluminum anodizing produces a highly durable surface that is resistant to wear and corrosion. The anodic film created during hardcoat anodizing is denser and thicker than that produced during standard anodizing processes. This makes components well-suited for use in harsh environments, such as those found in the aerospace and automotive industries. The increased durability also makes the components more resistant to scratches, making them ideal for applications that require frequent handling.
2. Aesthetics
Components that undergo hardcoat aluminum anodizing have a unique and aesthetically appealing appearance. The process produces a surface that is matte in finish, which is ideal for components that require a non-reflective surface. Additionally, the hardcoat aluminum anodizing process can dye the components in various colors, which not only enhances their aesthetics but also allows for easy identification and differentiation.
3. Electrical Insulation
Hardcoat aluminum anodizing produces a surface that is electrically insulating, making it ideal for components that need to be electrically isolated from other parts. The anodic film created during hardcoat anodizing is non-conductive, which means it does not allow current to pass through it. This makes the components well-suited for use in electronic devices, as they allow for ease of electrical isolation.
4. Adhesion
Hardcoat aluminum anodizing creates a surface that is highly adhesive, making it ideal for applications that require coating the components with other materials. The anodic film on the surface of the component provides an ideal surface for the deposition of various types of coatings, such as lubricants, paints, and adhesives. The adhesion properties of hardcoat aluminum anodizing also contribute to enhancing the corrosion resistance of the component when paired with an appropriate coating.
5. Cost-Effective
Hardcoat aluminum anodizing is a cost-effective surface treatment method that enhances the lifespan and durability of components, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Since hardcoat aluminum anodizing is effective in ensuring that components don’t corrode or wear out, it solves the problems of frequent replacements, which translates to cost-effective operations for the CNC machining industry.
Compare Hard Coat With Regular Anodize Of Aluminum
Comparing hard coat with regular anodize of aluminum is essential for CNC machining designers as it helps to understand the benefits and drawbacks of each process. Hard coat anodizing provides superior protection and durability, while regular anodizing offers a variety of colors and finishes. When choosing between the two, it’s crucial to consider the application of your parts and the level of protection required.
Feature | Hard Coat Anodizing | Regular Anodizing |
Process | Performed at lower temperatures and higher current densities, resulting in a harder and thicker layer. | Conducted at room temperature with lower current densities, producing a thinner and somewhat softer layer. |
Oxide Layer Thickness | Typically, the thickness ranges from 0.002 to 0.0045 inches . The thicker layer provides superior wear resistance. | Regular anodizing usually results in a thickness of 0.0002 to 0.0012 inches (5 to 30 µm). |
Hardness and Wear Resistance | Hard Coat anodizing provides high wear resistance, typically scoring a weight loss of 1.0-1.5 mg/1000 cycles in the ASTM D4060 abrasion resistance test. | Regular anodizing offers moderate wear resistance, scoring a weight loss of about 20-35 mg/1000 cycles in the same test. |
Corrosion Resistance | Hard Coat anodizing offers superior corrosion resistance, often withstanding over 2000 hours of salt spray as per ASTM B117 standard. | Regular anodizing provides good corrosion resistance, generally withstanding around 336 hours of salt spray under the same test conditions. |
Color and Dyeability | Due to its thicker, denser layer, Hard Coat anodizing may have limitations with brighter colors, often resulting in darker and muted hues. | Regular anodizing allows for a wide range of vibrant color options due to its more porous surface layer. |
Cost Considerations | Due to the higher processing requirements, Hard Coat anodizing can be more expensive initially. However, reduced maintenance and replacement costs often prove more cost-effective in the long run. | Regular anodizing is generally less costly upfront but might not offer the same level of long-term durability as Hard Coat anodizing. |
Factors That Influence Hard Coat Anodizing
The hard coat anodizing process is complex and requires attention to detail. As a CNC machining designer, understanding the factors that influence hard coat anodizing is fundamental to producing high-quality products with durable and aesthetically pleasing anodic coatings. The alloy type, surface quality, and anodizing parameters all influence the anodic coating properties. It is necessary to consider the dyeing process and post-processing techniques such as sealing to enhance the results further. In conclusion, by understanding the factors that influence hard coat anodizing, designers can optimize the process and achieve the desired results.
1. Alloy Type – Different metals and alloys will generate a different anodic coating layer. Aluminum is the most commonly anodized material, but other alloys such as titanium and magnesium are also anodizable. The alloy type governs the pore size and depth of the anodic coating, which impacts the coating’s hardness and durability.
2. Surface Quality – The surface quality of the metal directly affects the quality of the anodic coating. Imperfections such as scratches, dents, or debris may result in uneven anodizing, leading to inconsistent thickness or poor adhesion. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the surface of the metal is thoroughly cleaned, prepped, and inspected before anodizing.
3. Anodizing Parameters – The parameters in the anodizing process represent the voltage, current, temperature, and acid concentration. Changing any one of these variables can create different anodic coating properties. Anodic coatings that are thicker, have larger pores, and are harder typically form at higher voltages and lower temperatures. Increasing the acid concentration will result in a more significant anodic coating thickness.
4. Dyeing Process – The anodic coating process includes dyeing when color application is necessary. The dyeing process affects the aesthetic, durability, and heat resistance of the anodic coating. It is essential to know the dyeing process and to select the right dye to ensure that it meets the required specifications.
5. Post Processing – The post-processing technique such as sealing helps improve the anodic coating’s durability and minimize its porosity. The sealing process takes place after the anodizing and optional dyeing process. It involves immersing the anodized part in boiling distilled water to seal the pores, making the surface more resistant to corrosion, and increases durability.
Quality Testing And Specifications Of Hard Coat Anodizing
1. Developing Quality Testing Methods:
To ensure the quality of hard coat anodizing, there is a need to develop an effective and comprehensive testing system that covers the critical aspects of the process. ASTM International has developed specific standards for testing hard coat anodizing that involve a series of tests that check the coating thickness, adhesion, corrosion resistance, and surface finish. These tests are not only important to meet regulatory standards but also ensure that the hard coat anodizing meets the desired quality specifications.
2. Surface Preparations:
The effectiveness of hard coat anodizing is highly dependent on the surface preparation of the substrate. It is essential to ensure that the surface is free of contaminants like oil, grease, and dirt before the coating is applied. Any residual contaminants can affect the bonding of the coating or create defects in the coating, leading to corrosion and premature failure.
3. Hard Coat Anodizing Specifications:
The specifications of hard coat anodizing are essential in determining the effectiveness and quality of the coating. The specifications include the coating thickness, surface finish, color, and coatings’ adhesion, amongst others. The thickness of the coating is generally between 0.002 to 0.0045 inches, and it is critical to ensure that it meets the minimum thickness requirements to provide the desired corrosion protection.
4. Quality Control Measures:
To ensure that hard coat anodizing meets the necessary quality specifications, quality control measures must be implemented throughout the process. Quality control measures involve monitoring and measuring critical parameters throughout the coating process to ensure that the desired quality parameters are met. Some of the measures include regular check-ups of the baths used in the coating process, measuring the coating thickness and hardness, and evaluating the surface uniformity.
5. Importance Of Quality Testing And Specifications:
The quality of hard coat anodizing is essential in providing protection against corrosion and abrasive wear. Choosing the right hard coat anodizing specification for your product is critical to ensure that it meets the desired quality standards. Furthermore, regular quality testing and control measures must be implemented to ensure that the hard coat anodizing provides the necessary protection and extends the product’s lifespan.
Applications of Hard Coat Anodizing
Hard coat anodizing is a versatile surface treatment that offers a wide range of benefits, including improved durability, resistance to wear and corrosion, and protection against harsh environments. As a CNC machining designer, understanding the applications of hard coat anodizing will enable you to design more robust, longer-lasting metal components that can withstand harsh environments and heavy use. By using hard coat anodizing, you can ensure that your components will last longer, perform better, and require less maintenance over time.
1. Aerospace Industry: Hard coat anodizing is extensively used in the aerospace industry to improve the durability and corrosion resistance of aircraft components. The aluminum parts of an aircraft like landing gear struts, wing skins, and engine components are hard coat anodized to protect them from wear and tear caused by the harsh environment of flight. The anodized layer is also an excellent electrical insulator, which provides additional protection against electrical arcing and short circuits.
2. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry also uses hard coat anodizing on certain car components, such as wheels, engine blocks, and transmission cases. Hard coat anodizing makes these parts more resistant to corrosion, abrasive wear, and chemical exposure. Anodized aluminum wheels, for instance, are becoming increasingly popular as they are lighter, more durable, and less prone to corrosion than traditional steel wheels.
3. Construction Industry: Hard coat anodizing is also commonly used in the construction industry to protect aluminum components from exposure to harsh environments. Windows and doors are often anodized to provide protection against the elements and to improve their longevity. Hard coat anodizing can also give aluminum a matte or shiny appearance, making it more aesthetically appealing for architectural uses.
4. Military Applications: Hard coat anodizing is also used in military applications, particularly in rifles and other firearms. The process is used to protect the aluminum or titanium components from the wear and tear associated with gun use. Not only does hard coat anodizing improve the longevity of the firearm parts, but it also helps to make them more resistant to corrosion and abrasive wear.
5. Medical Industry: The medical industry also makes use of hard coat anodizing, particularly with orthopedic implants. When metallic implants are placed into the human body, they are subjected to a harsh environment that can cause wear and corrosion. Doctors use hard coat anodizing to improve the durability and longevity of metallic implants, making them more resistant to wear, corrosion, and bacterial infection.
Trusted Hard Coat Anodized Aluminum Services
At AN-Prototype, we specialize in providing precision CNC machining services with superior quality and accuracy. We understand the importance of timely delivery and product performance, and that’s why we use the latest technology and expert techniques to meet your unique requirements. Our team of skilled professionals ensures that each part is machined with the highest industry standards for tolerance, surface finish, and accuracy, up to +/- 0.0002 in. With our state-of-the-art facility and experienced personnel, we can guarantee that your aluminum parts will achieve the desired strength and durability levels.
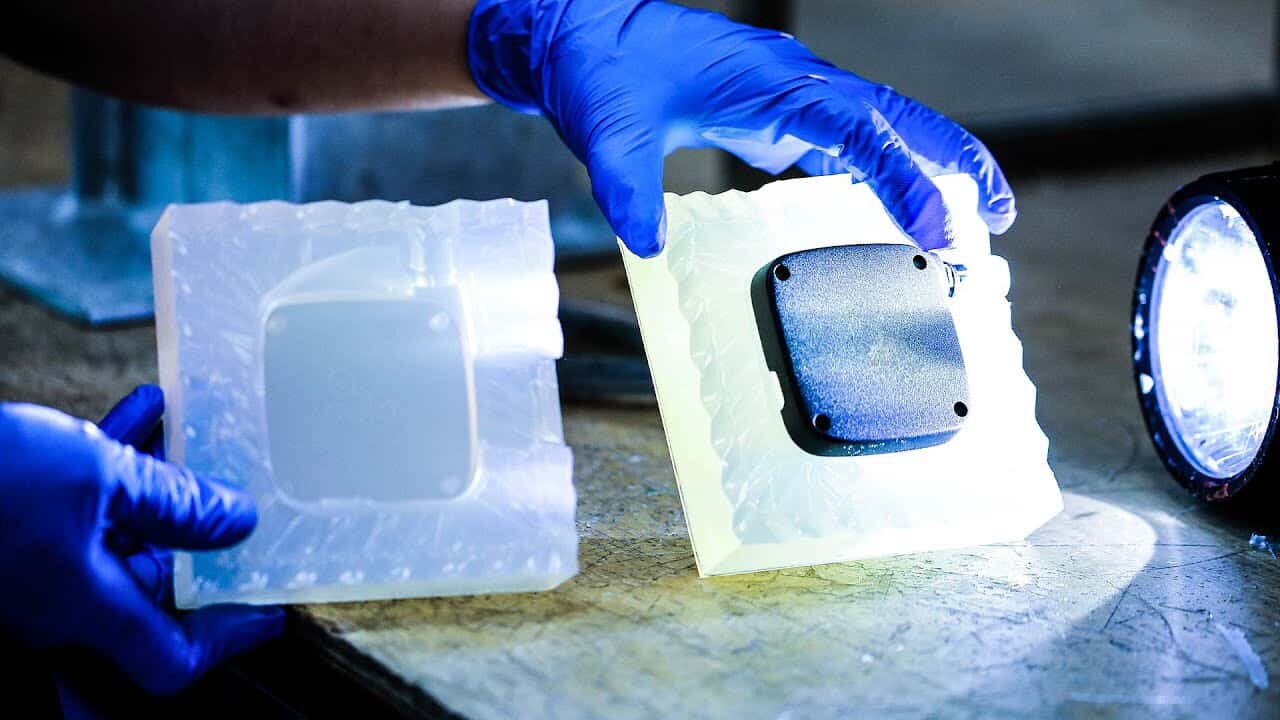
However, one of the key factors that separate AN-Prototype from other CNC machining service providers is our hard coat anodize capabilities. Anodizing is a process of creating an oxide layer on the surface of metals, typically aluminum. This layer provides better resistance to corrosion, wear, and tear and improves the appearance of the part. Hard coat anodize, specifically, is a thicker and denser anodizing process that results in a more durable and wear-resistant surface. AN-Prototype’s hard coat anodize services offer a reliable way to extend the life and performance of your aluminum parts even in harsh environments.
Another crucial aspect of our hard coat anodize services is the range of colors and finishes we can achieve. Aluminum parts often require certain aesthetic finishes for branding or recognition purposes. With AN-Prototype’s hard coat anodize capabilities, we can provide a variety of color choices to match your preference. From clear to black, red, blue, green, and other hues, our finishing options allow you to design custom aluminum parts that look great and perform even better.
Moreover, we understand that hard coat anodizing can be a complex process that requires expert knowledge and skills. That’s why we have a team of experienced technicians who can guide you through every step of the process, from pre-treatment to coating, sealing, and inspection. We use high-quality materials and equipment to ensure that your aluminum parts meet the necessary specifications and your goals.
In conclusion, CNC machining designers looking for the best hard coat anodize services for their aluminum parts should consider AN-Prototype. Our combination of precision CNC machining and expert anodizing capabilities makes us a leading service provider in China. We have the skills, experience, and technology to transform your aluminum parts into high-performance and aesthetically pleasing products. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve your manufacturing goals.