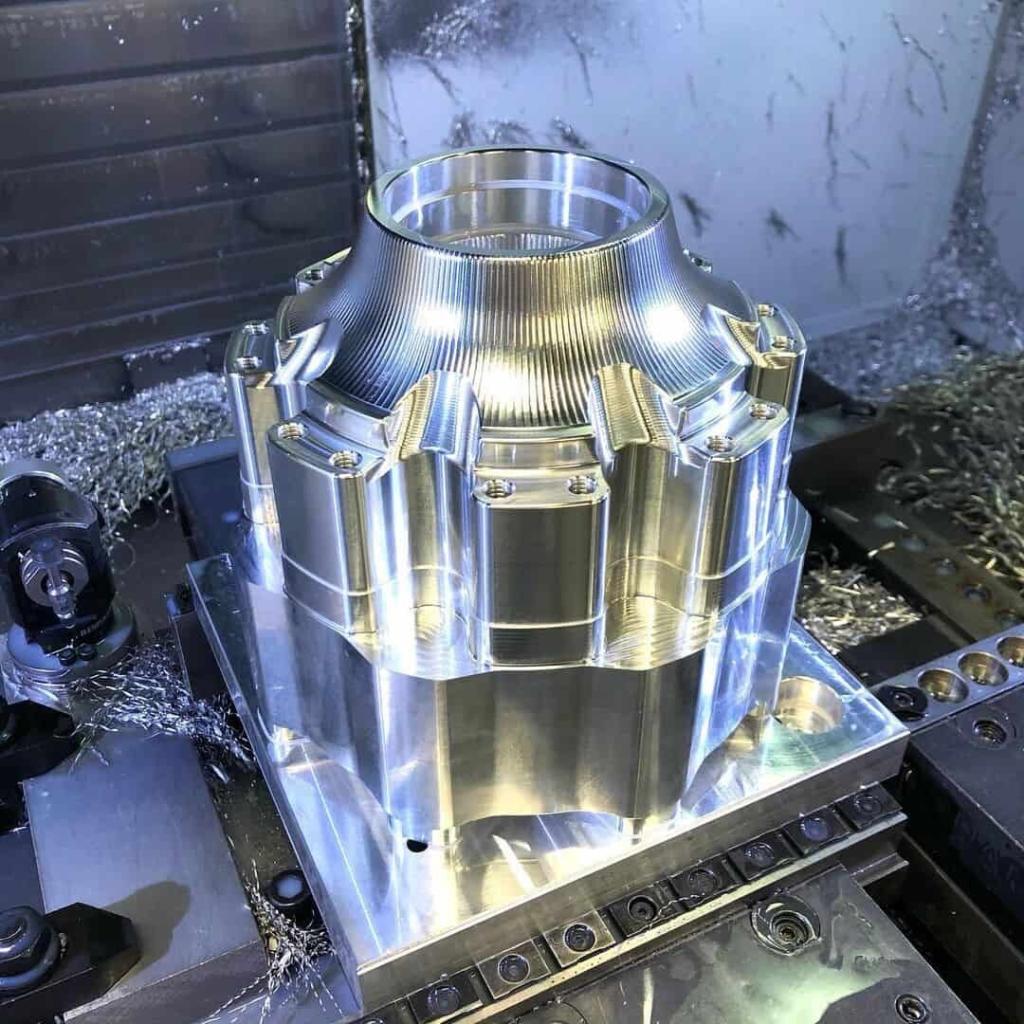
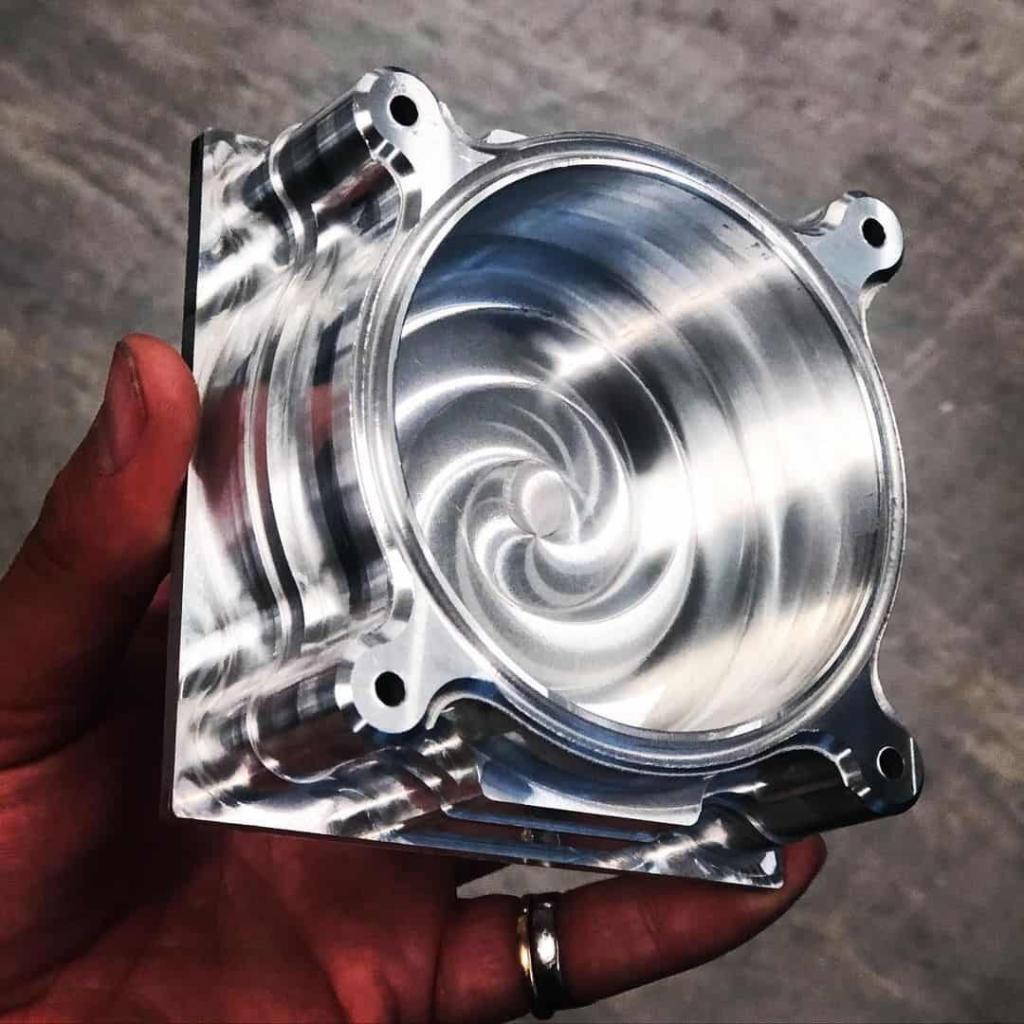
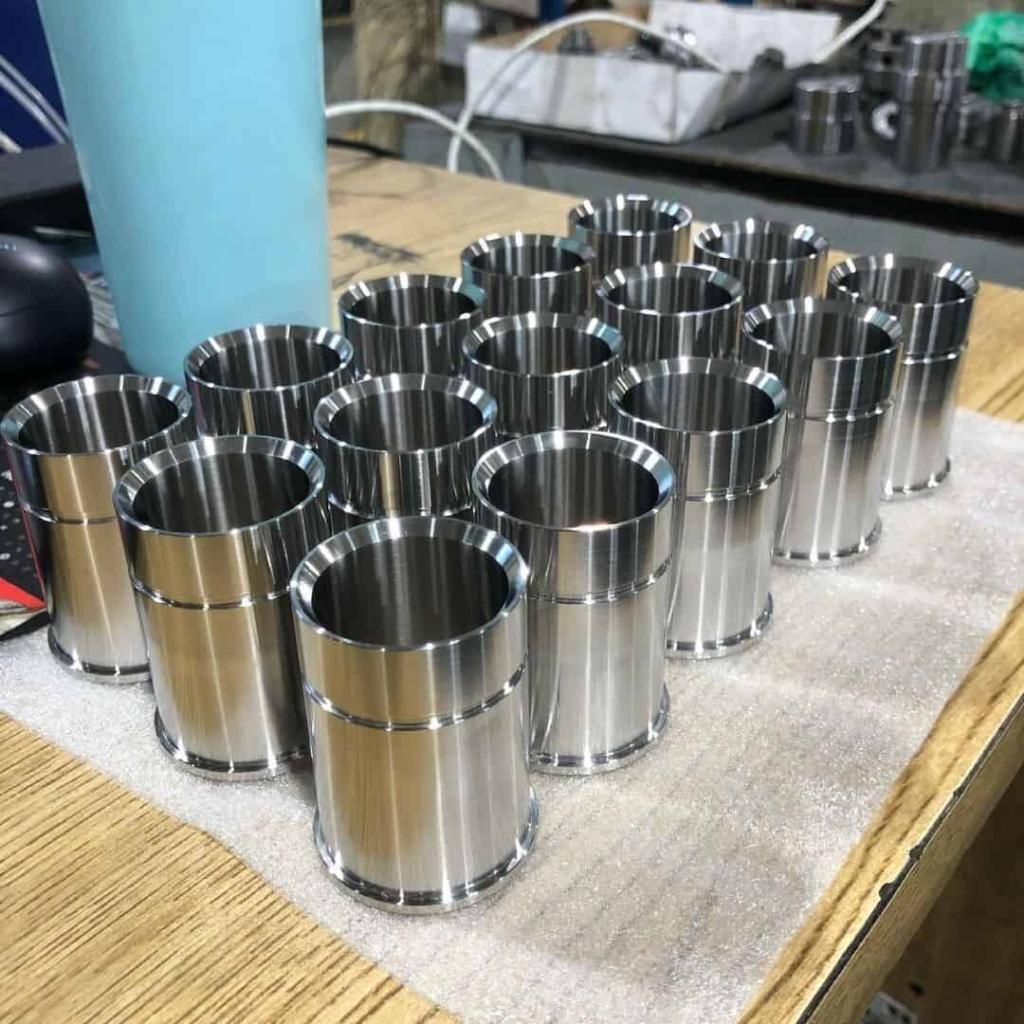
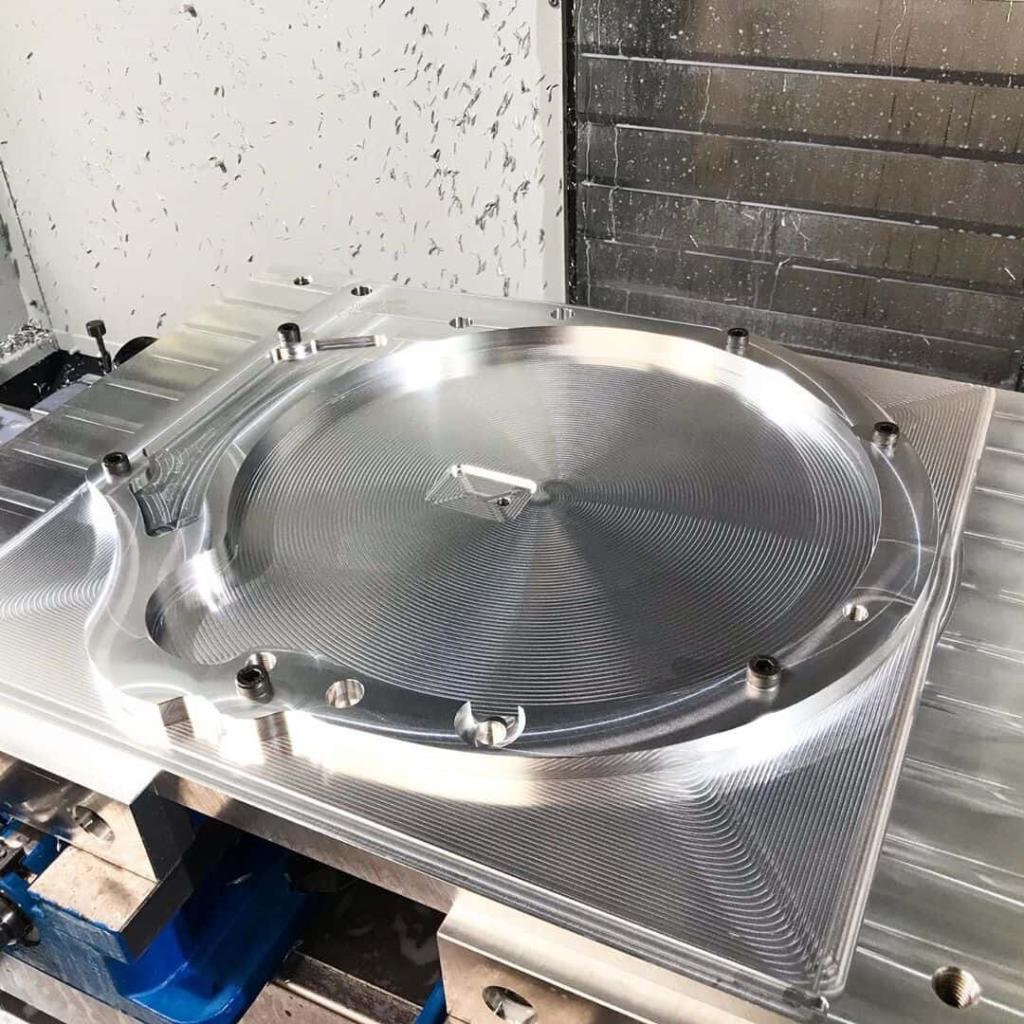
CNC prototyping is an important part of new product development as it helps evaluate whether a design will look and function as expected. CNC prototyping technology has been developed for more than 70 years, and has long been the mainstay of modern production and is indispensable in every industry. CNC prototyping enables the manufacture of prototypes in a relatively short period of time and at low cost.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is CNC prototyping?
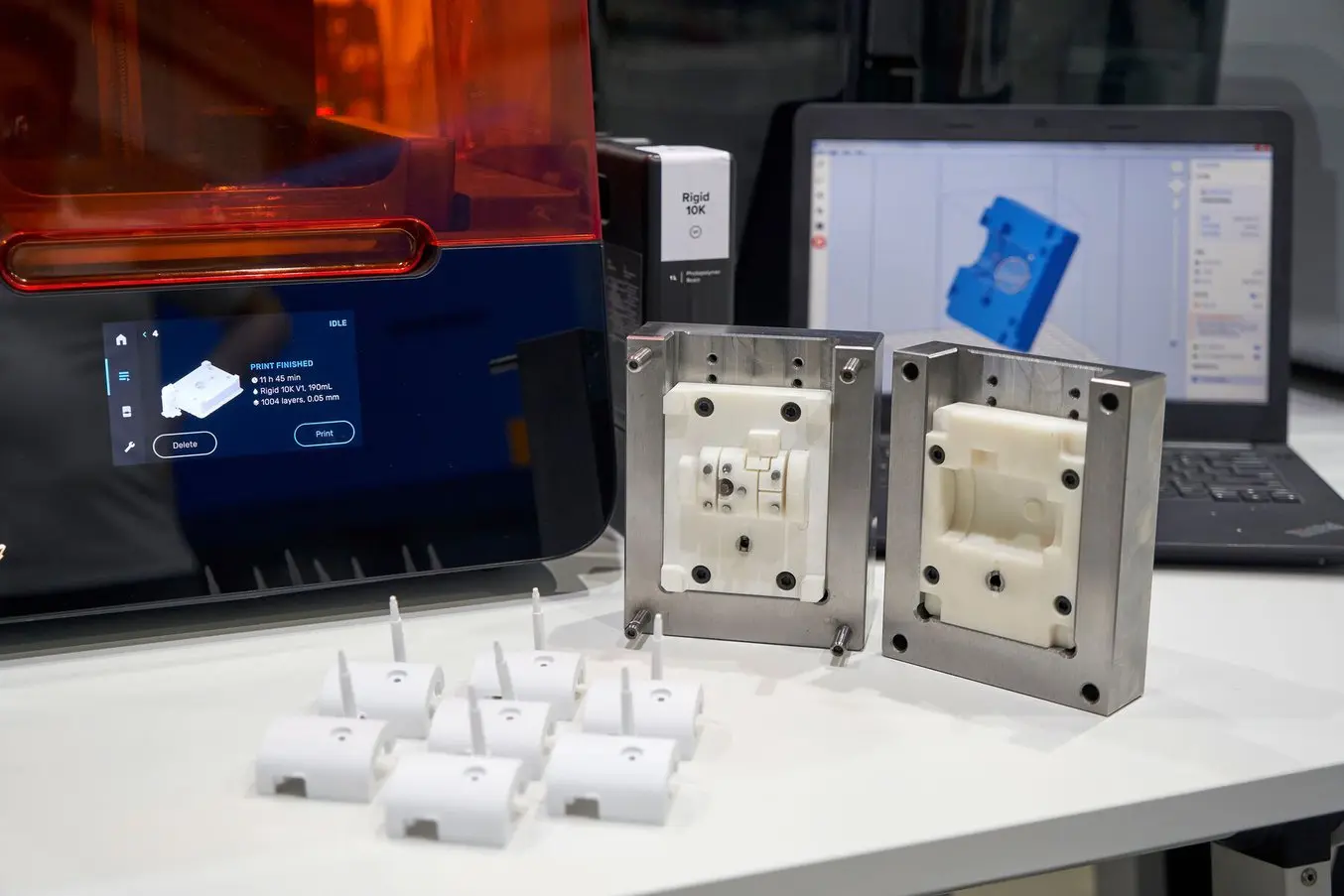
CNC prototyping is the process of quickly creating high-quality prototypes using CNC machine tools. Product designers and engineers often create prototypes for future production runs. The CNC machining process helps create the final part, designed to provide a visual and functional representation of the final product. In other words, CNC prototyping achieves the physical result of a digital design. Designers can easily detect and eliminate design flaws through CNC prototyping before commencing high-volume manufacturing. Of course, production becomes more cost-effective when design flaws are eliminated during the prototyping stage.
Why is CNC machining suitable for prototyping?
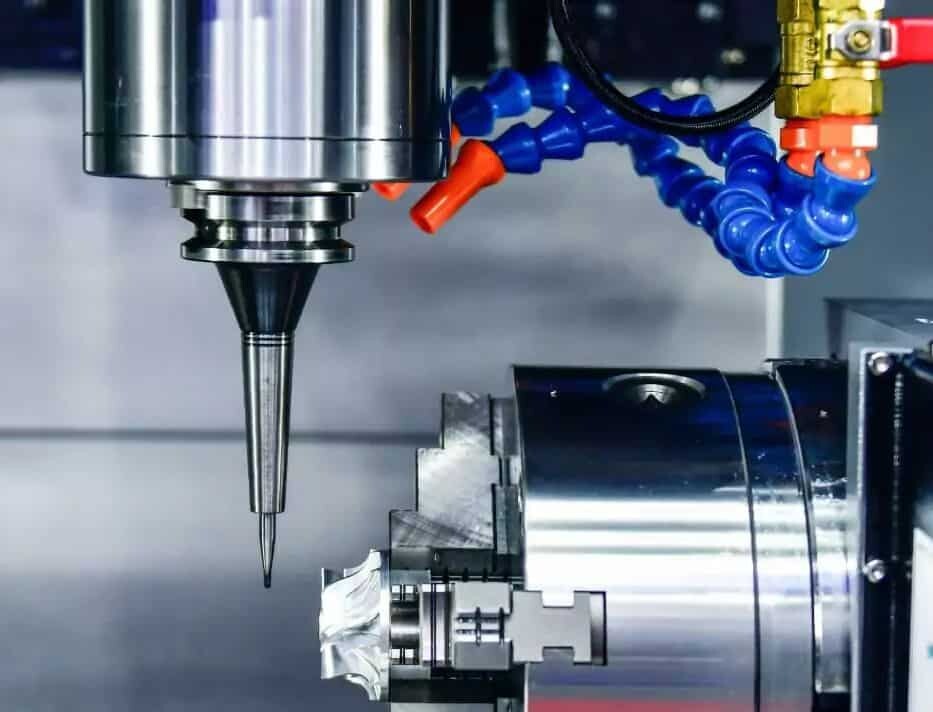
CNC machining is an ideal process for prototyping. First, the process offers a high level of accuracy and precision due to the use of computers to control the movement of the tool and detect the workpiece. These computer controls consider every angle of the design, ensuring that prototypes are accurately created to final part specifications, and identical parts are manufactured repeatedly.
Another reason CNC is good for prototyping is its speed. CNC prototyping is very different from processes such as injection molding, where manufacturers and product developers must wait weeks or even months for molds to be ready.
CNC prototyping process
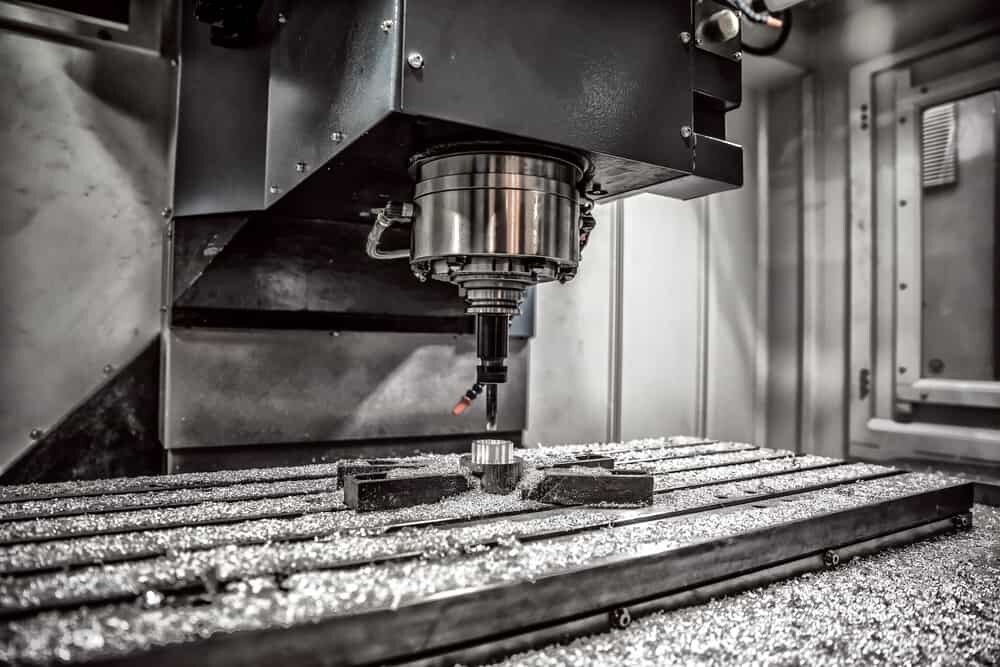
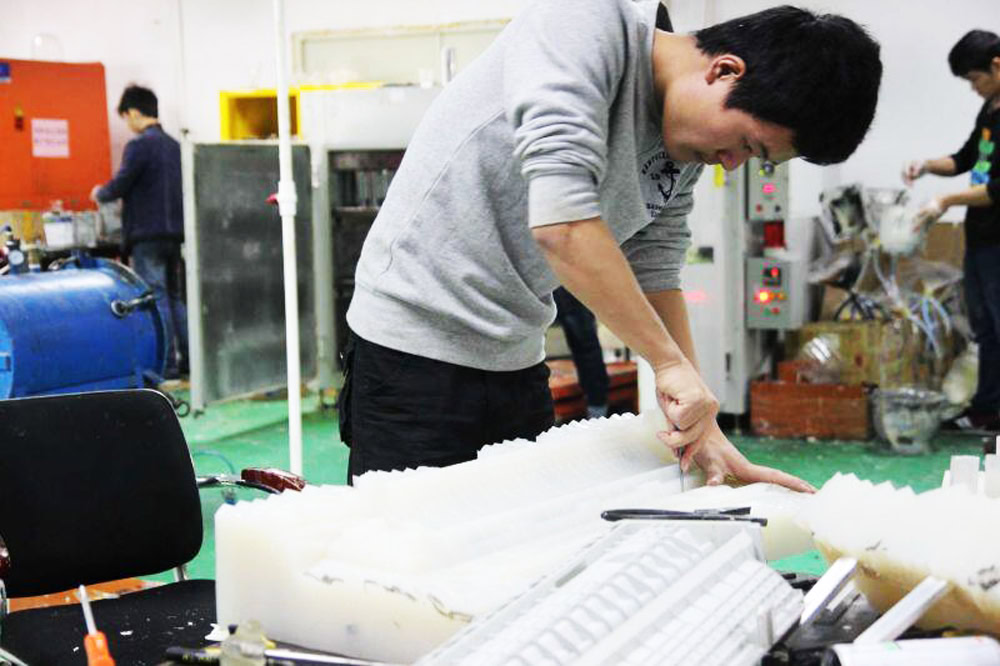
Using a CNC system, prototyping starts with creating a 3D CAD model of the final part and converting it to a CAM file. CAM files contain G-code, including many different instructions, that control the movement of the CNC machine during prototype creation. The CNC machine will cut the material following these instructions. Thanks to the CNC system, there is very little human supervision throughout the prototyping process. This is a major advantage over traditional machining, which is time-consuming and requires close supervision.
Unlike 3D printing, CNC prototyping is a subtractive method that requires less material. Individual parts of the original block are cut bit by bit until the desired form is created. Since the CNC machine is controlled by a computer, the process is characterized by high precision. In addition, complex designs and intricate geometries can also be easily CNC machined for rapid prototyping.
CNC Prototyping Operations
Rapid manufacturers can use different CNC prototyping operations depending on the design of the final part. Which specific operation to choose usually depends on several factors, including design specifications and materials used, among others. AN-Prototype summarizes the following common CNC prototype processing operations based on years of CNC processing experience.
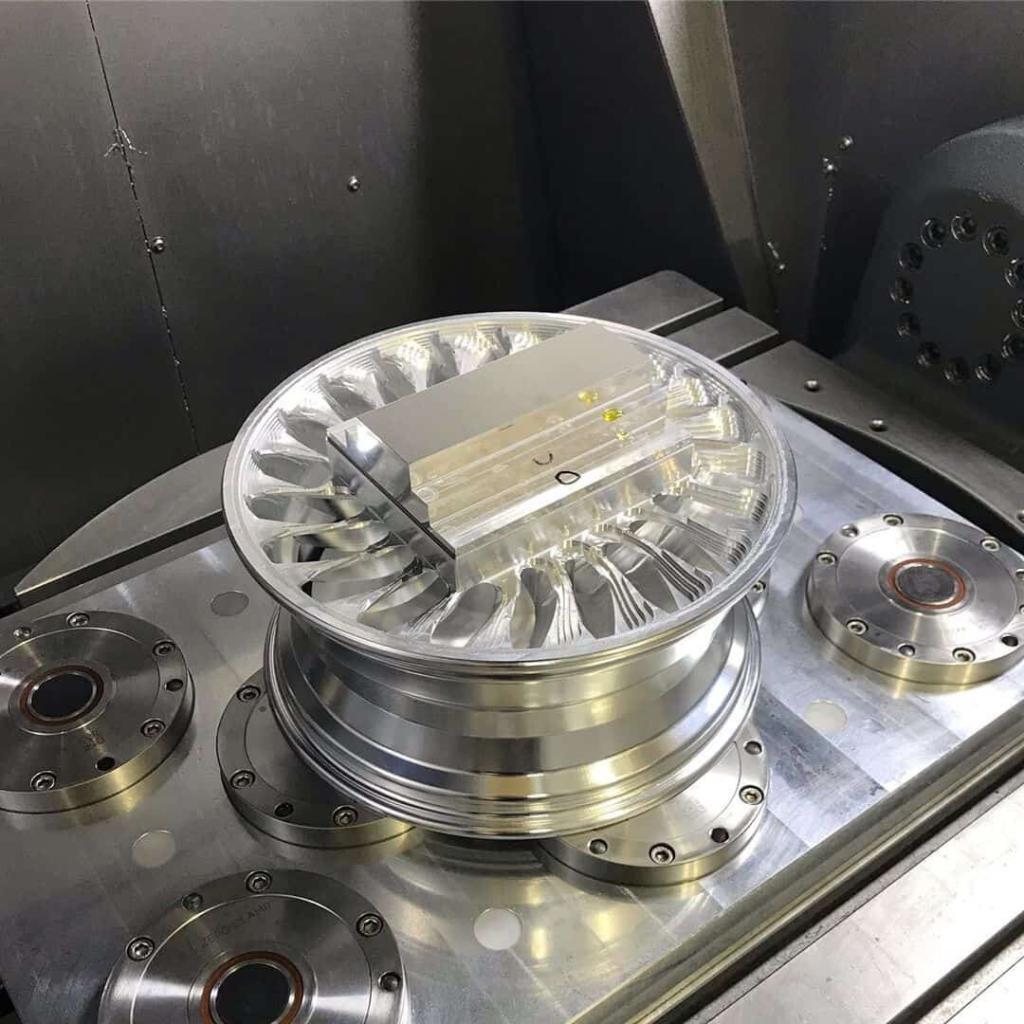
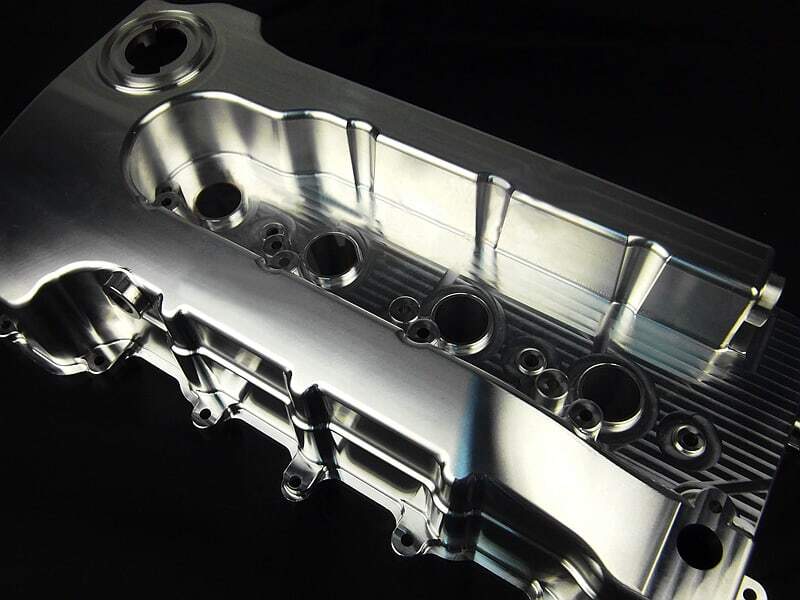
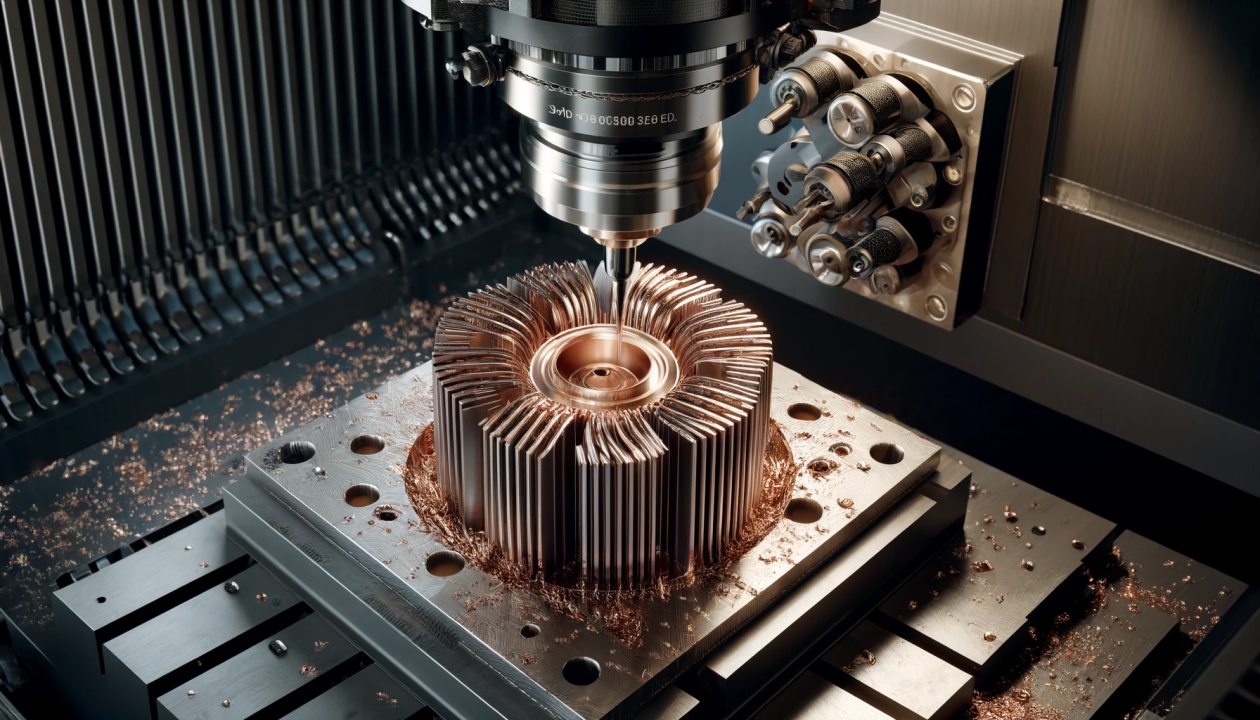
CNC milling, the most common operation of CNC machining, refers to the creation of prototypes with the help of a CNC milling machine. The CNC milling process is a subtractive process because the machine removes material from the workpiece to create prototypes of different geometries. Milling machines have multi-point cutting tools, each of which makes sharp cuts of different shapes and lengths on a rotating workpiece. The depth of cut and motion profile of the tool and the axes used by the machine depend on the complexity of the design. In order to achieve higher cutting accuracy, CNC milling machines are also equipped with additional axes to enhance their motion capabilities, such as 4-axis, 5-axis CNC machines.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
5-axis CNC machining allows complex parts with multiple side features to machine up to five sides in a single setup. This brings huge benefits in terms of greatly increased CNC machine utilization, reduced setup and cycle times, and improved quality. 5-axis CNC machining can produce high-precision parts with extremely complex geometries.
CNC Swiss machining is a manufacturing technique utilizing specialized tool cutting designed to machine metal or plastic blanks into complex, slender or delicate components requiring tight tolerances. CNC Swiss machining technology is widely used in the medical industry, aerospace, IT, electronics, energy and fuel systems, precision timepieces and military defence.
Advantages of CNC prototyping
There are hundreds of advantages to CNC prototyping. Let’s list a few of them:
1. High accuracy and precision
CNC machining facilitates the manufacture of prototypes with high precision, tolerance and accuracy. This precision and accuracy is due to the computer’s control of the cutting tool’s motion. Due to the accuracy and precision of the CNC machining process, most of the errors or flaws in the manufactured prototypes originate in the design itself.
2. Cost-effectiveness
CNC prototyping can save product designers money in the long run. This is because any flaws and mistakes can be corrected in the prototype instead of being ruled out in the mass of final parts produced during the production phase.
Additionally, future changes require only minor modifications to the CAD file rather than creating a new design from scratch.
3. Consistency and repeatability
CNC prototyping is highly repeatable. CNC prototype machined parts are consistent and will accurately mimic the original no matter how many copies are produced. This is very different from other prototyping processes such as injection molding, where the mold depreciates after many repetitions, whereas CNC machining prototypes does not.
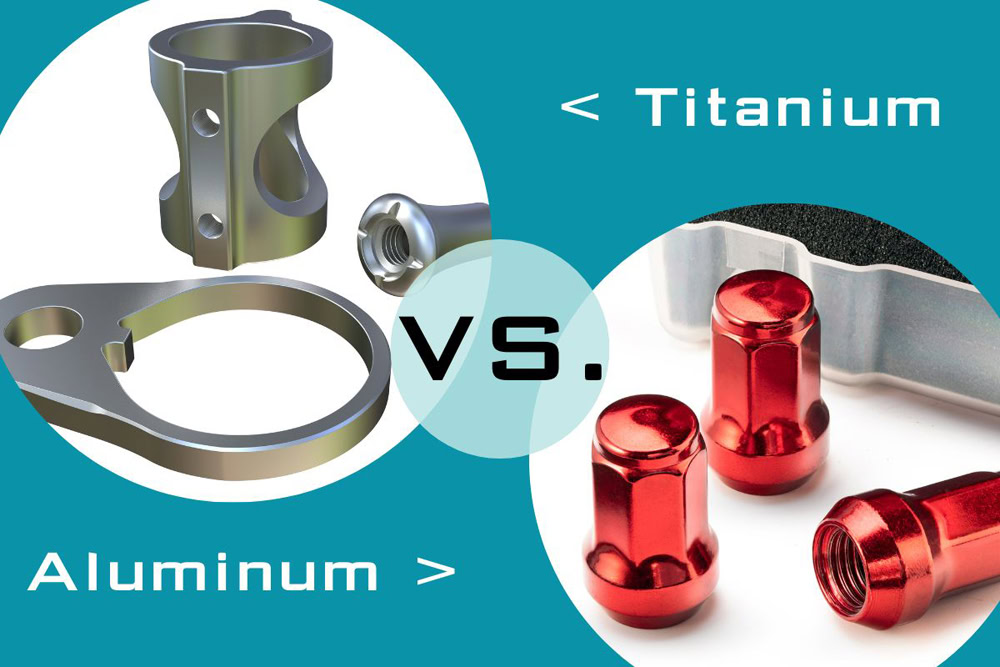
4. Versatility of materials
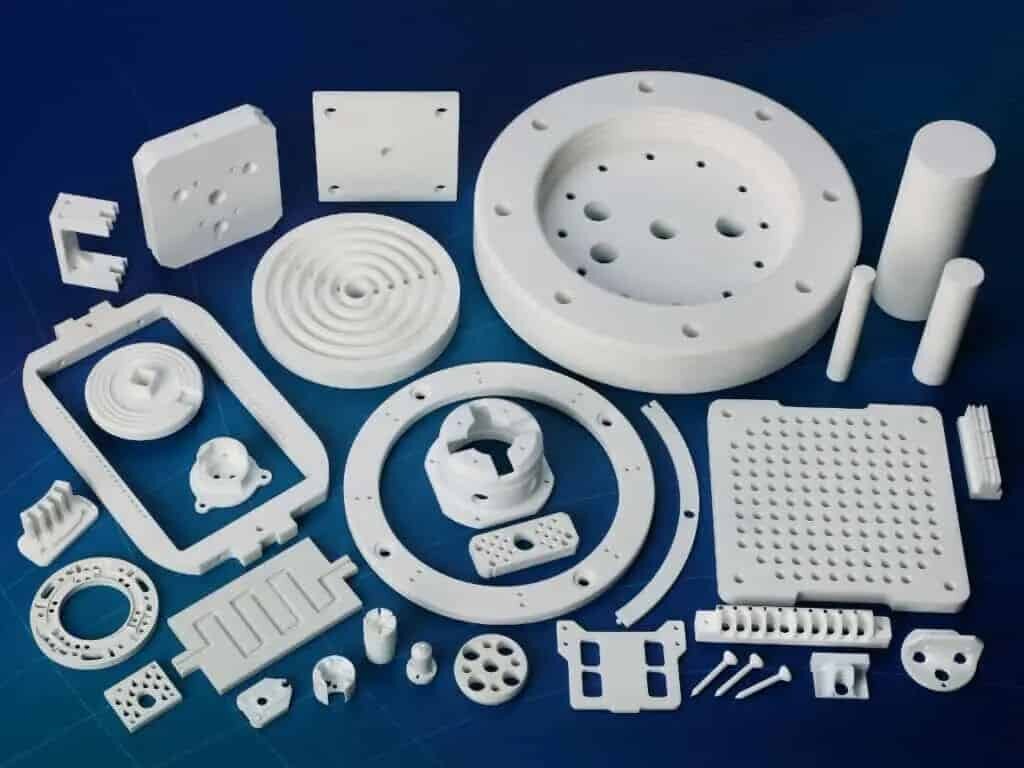
Compared with other manufacturing processes such as 3D printing and injection molding, CNC prototyping can use more materials from plastics, wood to the strongest metals, and even ceramics. Some material options suitable for CNC prototyping services include:
Metals
- Aluminum
- Steel
- Stainless steel
- Magnesium
- Titanium
- Zinc
- Brass
- Bronze
- Copper
Plastics
- ABS
- PMMA
- PTFE
- PCGF
- PAGF
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
5. CNC Machining is fast
CNC machining for mass production began in the 1970s, and as machines and software have evolved, it is now one of the fastest and most reliable ways to create complex-shaped parts from metals and hard plastics. Once CNC programmed, a good mill or lathe can machine steel or aluminum with astonishing speed, turning a metal blank into a finished part in minutes.

Limitations of CNC Machining Prototyping
Although CNC machining is one of the best strategies for manufacturing prototypes, it still has certain limitations. These restrictions include:
long time accumulation of experience
Before prototyping CNC machining, it is advisable to have technical knowledge of design CAD files and how to generate CAM files from them. The installation and programming of CNC machine tools requires a certain amount of technical expertise and long-term programming experience. What’s more, testing procedures, innovative approaches, and creative vision are essential for CNC prototyping. Not all CNC machining service providers can complete CNC programming flawlessly.
Material Waste
CNC prototyping is a subtractive process in which material is cut from bar stock or sheet stock during prototyping. As a result, the more parts that are made, the more material is wasted, driving up material costs. Also, you may incur additional costs and waste more material, not sure if the CNC prototype will be perfect on the first try. Also, even if a small batch of prototypes meets all technical requirements, the chances of them being sold are relatively small. Therefore, they increase the amount of material waste.
Geometrical Constraints
One of the main hurdles of the CNC prototyping process is the inability to machine the geometry inside the prototype, such as sharp corners inside the part. CNC machine tools mainly only process the outside of the workpiece. Therefore, developing a prototype with internal components using CNC prototyping can be challenging. However, you can choose an alternative prototyping process such as 3D printing to create a prototype with internal components. 3D printing is ideal for manufacturing the internal geometry of a prototype because it can work from the inner area of the workpiece to the outer area.
More expensive than 3D printing
In general, CNC prototyping costs more than 3D printing processes. This is one of the main reasons why an engineer might choose the 3D printing process to manufacture a prototype, even if they intend to use CNC machining for the final part. It is understandable if businesses need to cut expenses during the (early) prototyping phase.
Applications of CNC prototyping
CNC prototyping is used in almost all precision machining industries. In most of these industries, they always need a functional prototype or . CNC machined prototypes are the best fit. Most of the time, CNC machining tools are usually better suited for these functional prototypes that require strength, mechanical stability, or other characteristics that additive processes cannot provide, so it is used in these industries.
The aerospace industry is one of the industries with a high usage rate of CNC prototyping. Machinists in the aerospace field use this process to develop functional prototypes with high precision and accuracy. Additionally, engineers utilize CNC prototyping to test the functionality of machined components and other innovations in the aerospace industry. It helps ensure the reliability of these components and prevents the aircraft from malfunctioning while in flight. Typical components of an aircraft manufactured using CNC prototyping techniques are wings, bushings, manifolds, etc.
The medical industry has a high demand for parts and medical devices with tight tolerances and precision. The medical industry benefits from CNC prototyping because it is compatible with a wide variety of CNC machined materials. In addition, as medical technology evolves, there is a demand for medical components with the tightest tolerances such as prosthetics, implanted stents, surgical scissors, biopsy tubes, and more. CNC machines produce high-quality functional prototypes with exceptional precision and accuracy for the medical industry.
The automotive industry is one of the industries with the highest use of CNC machined prototypes, with tighter tolerances and high precision. Gears, wheels, brakes and suspension components are typical examples of CNC prototyping. Additionally, these automotive components require the tightest tolerances to ensure optimum vehicle performance and safety. The automotive industry develops prototypes and tests their functionality by installing them in vehicles to ensure they serve their intended purpose. However, creating an automotive prototype that meets intended purpose and specifications can be challenging without CNC prototyping. CNC machining is responsible for developing automotive prototypes to precise specifications. CNC prototyping also makes parts for other vehicles such as boats, delivery trucks, and more.
The petroleum industry has high demand for parts with superior strength that can be mined deep within the earth’s surface to extract resources. Engineers often use CNC milling prototypes or other custom CNC machining processes to create these parts to meet requirements.
Military industry
Research and development departments benefit from the use of CNC prototyping processes in the military field. Military R&D utilizes this manufacturing technique to develop aircraft, combat vehicles and other CNC machined parts. Engineers and product developers in the defense industry rely on prototype CNC machining because it allows rapid prototyping and part fabrication regardless of the hardness of the material. CNC machined prototypes are perfect for this purpose. Examples of equipment manufactured for this industry include aircraft parts, transportation components, communications components, ammunition, and more.
Tips for CNC Prototyping
CNC prototyping is a reliable method for manufacturers to ensure that parts meet requirements and accuracy before mass production. AN-Prototype summarizes some suggestions for CNC prototype processing for your reference.
Reduce Prototype Complexity
While a complex design sounds like a good idea, it’s actually not quite that way. One thing to note about CNC prototyping is that the higher the complexity, the higher the cost of CNC machining. In addition to cost, it takes a long time to set up a machine for a design that requires multiple angles and undercuts, adding to the time spent on CNC machining. Therefore, complex designs increase development time, thereby increasing product development costs and delaying time to market.
Default tolerance
Default tolerances are usually best practice for CNC prototyping. Achieving tighter tolerances may require specialized cutting tools and additional fixtures, which affects the cost of CNC machining. It is usually best to let an experienced engineer work on your design to determine which tolerance level is best for your product prototype.
Design with tool geometry in mind
Since the machining program runs in rotation, consider the axial characteristics of the cutting tool or machined object during prototype CNC machining. Most cutting tools have a limited cutting length and are circular. Therefore, the geometry of the tool will have an impact on all cutting operations.
Work with an Experienced CNC Prototype Maker
What’s more, you should work with an experienced CNC prototyping specialist. Because they can focus on streamlining the process to create high-quality prototypes. Experts also consider the geometric constraints of the machining process needed to manufacture the desired prototype. Reaping the benefits of developing prototypes using CNC machining can be difficult without an experienced prototype maker.
Comparison Between CNC Machining Prototypes and Injection Molded Prototypes
While both prototypes provide a visual representation of the final product, they are quite different from each other. Here is a comparison between the two types of archetypes.
Part Tolerance
Part tolerances for injection molded prototypes range from ±. 0.1 to 0.7mm. The reason for this is due to the shrinkage after injection. On the other hand, the CNC machine prototype has an extremely high tolerance level of ±0.01 mm, proving the precision and accuracy of the machining process.
Prototype material
Injection molded prototypes are usually plastic or elastomers. This is because the production process requires molten material to be placed into molds to form prototypes. In contrast, CNC machined prototypes can be wood, plastic, or metal, depending on the material the designer chooses.
Surface Quality
Despite the precision of the injection molding process, the prototypes produced may have minor defects such as warpage, sink marks, flow lines, weld lines, etc. These defects can negatively affect the appearance of injection molded prototypes. On the other hand, CNC machined prototypes have a better surface finish due to the wide range of tools used in the CNC machining process.
Comparison Between CNC Prototyping and 3D Printing
While both are prototyping processes, they are very different in the approaches and solutions they offer. Furthermore, both processes have their pros and cons.
Material Consumption
3D printing has considerably less material waste than CNC prototyping. This is because 3D printing uses only the materials needed in the manufacturing process. CNC machining, on the other hand, removes excess material from the block to achieve the desired shape.
Prototyping Cost
The CNC process is more expensive than 3D printing. The difference in price is due to the number of accessories required for the CNC machine to function optimally. These accessories range from fixtures and cutting tools to cutting fluid delivery systems. Additionally, the high cost of purchasing CNC machines affects the cost of prototypes produced through the machining process, making them more expensive.
Supporting Material
CNC machining supports a wide range of materials from wood and plastics to metals and alloys. 3D printing, on the other hand, generally favors thermoplastics because they are easy to heat and shape.
Part Tolerance and Toughness
CNC machines have a tolerance of ±0.01 mm, while next-generation 3D printing technologies such as DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) have a tolerance of ±0.1 mm. Additionally, CNC prototyping produces parts that are stronger than those produced by 3D printing.
AN-Prototype provides high-quality CNC prototype processing services
15+ years of expertise in CNC prototyping enables AN-Prototype to optimally manufacture the parts you need. We provide professional one-stop CNC machining services, from precision prototyping to full production runs.
With our extensive industry machining experience, we can create high-quality prototypes to the required specifications, no matter the industry. Simply upload your CAD file to receive DFM and a free quote.
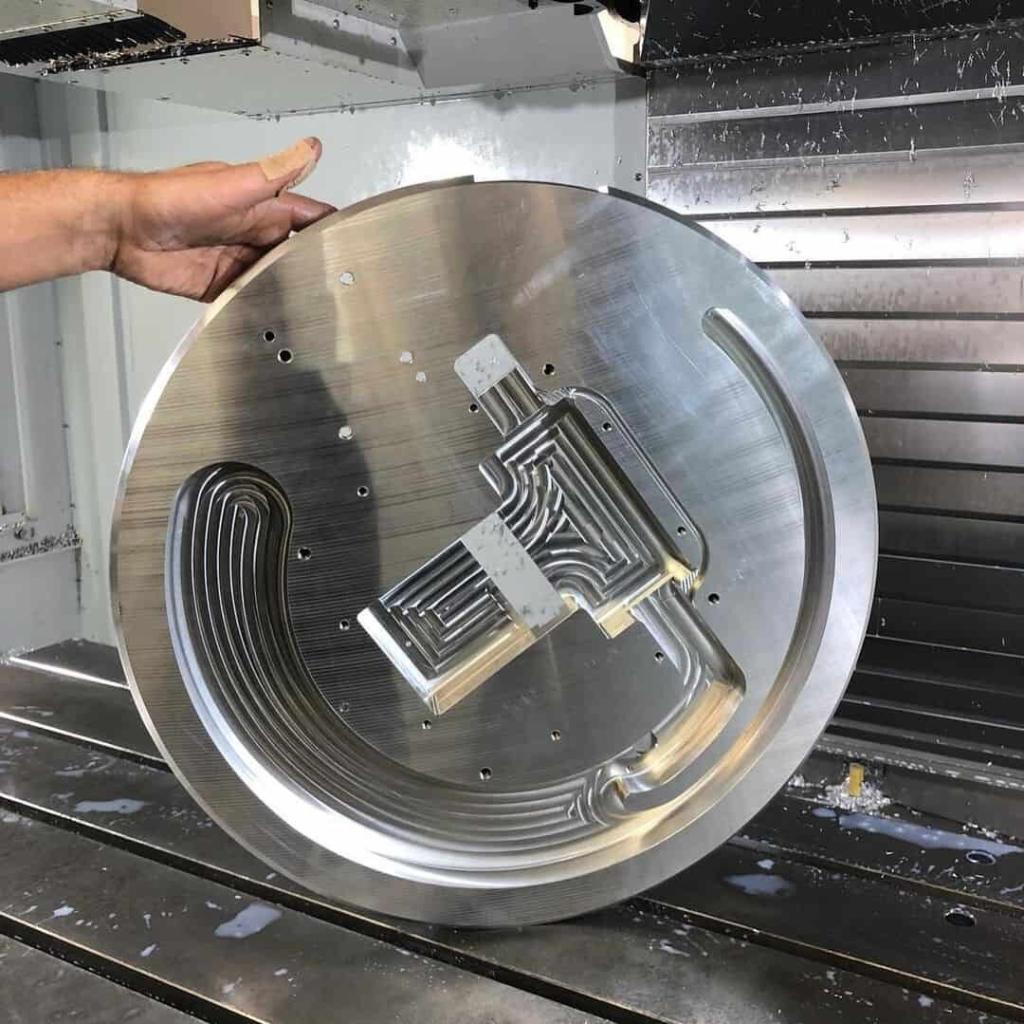
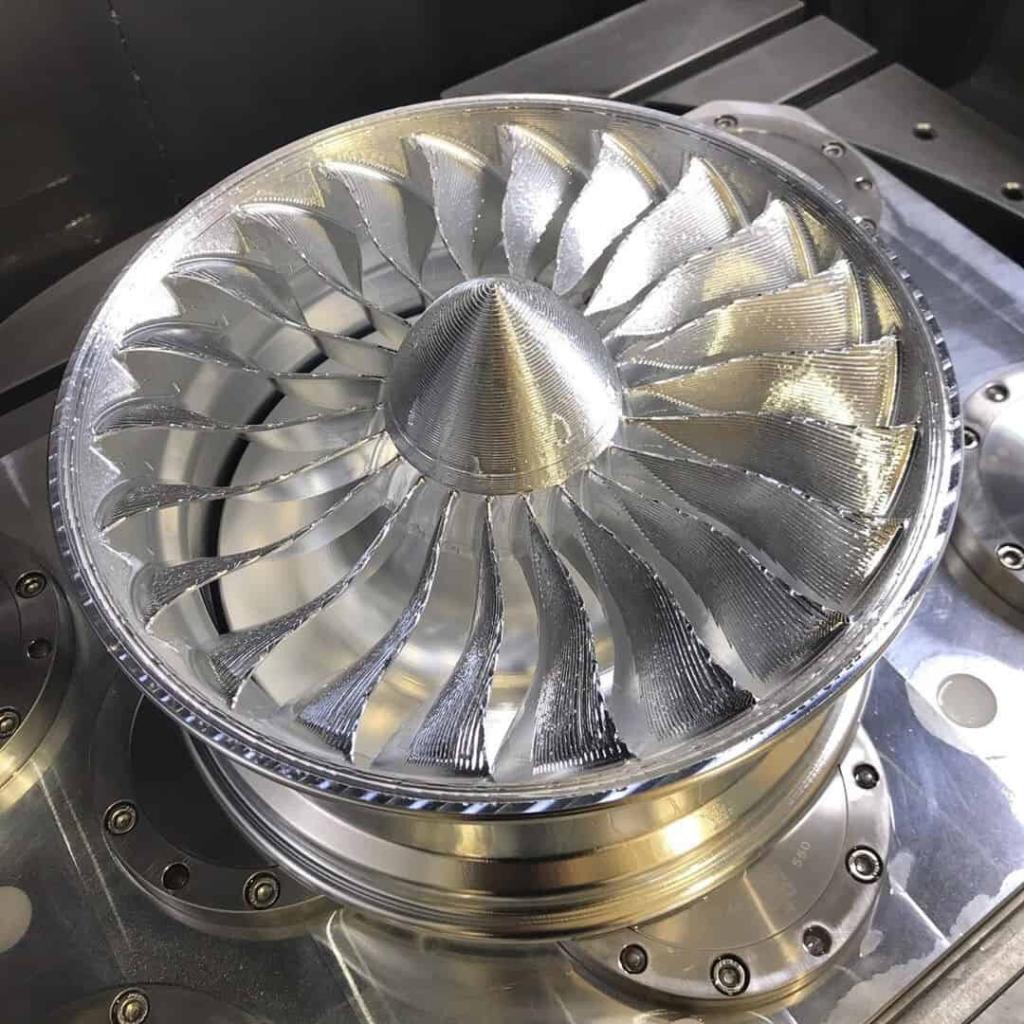
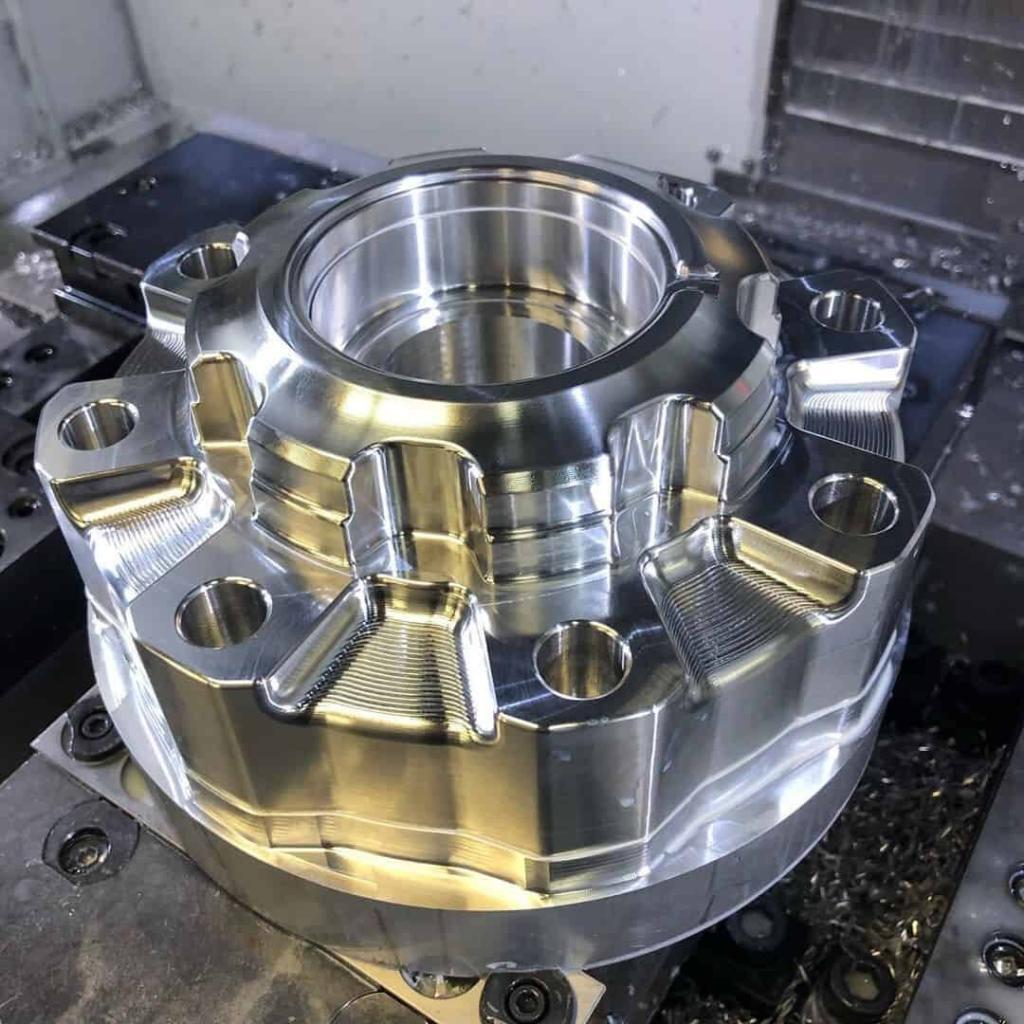
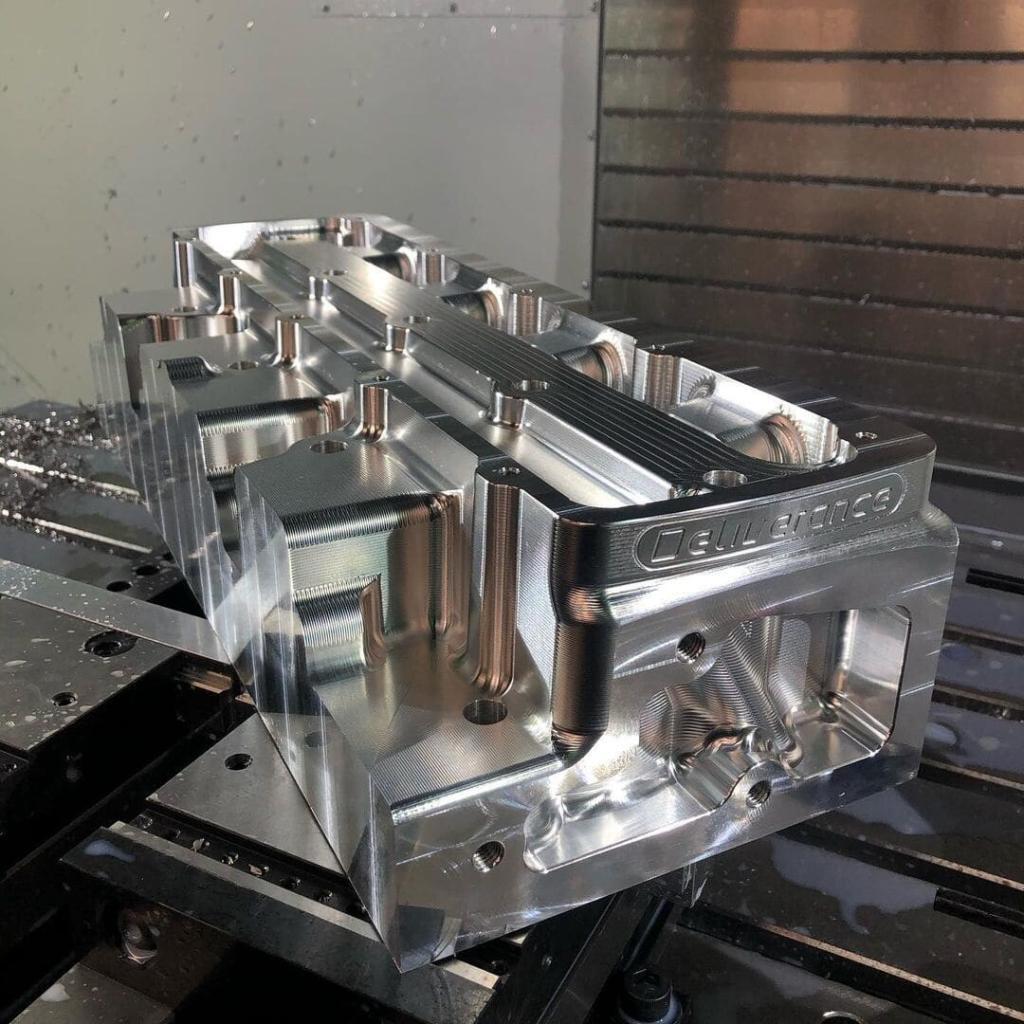
CNC Prototype Gallery