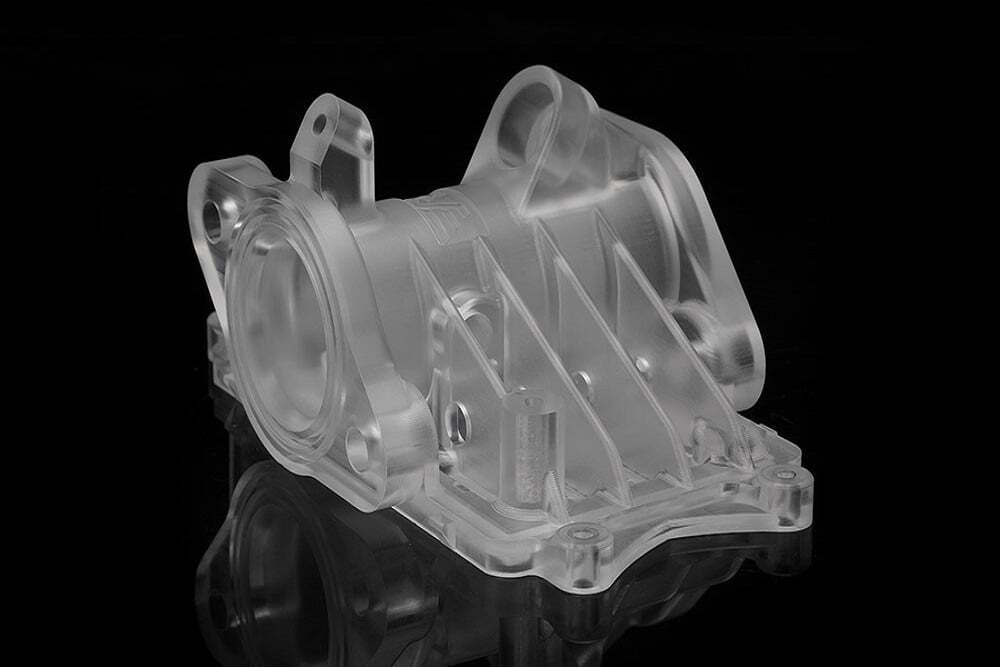
Many industries require transparent plastic parts, such as automotive lights, light guides, etc. Polycarbonate and acrylic are popular materials for making optical and transparent parts. However, choosing between polycarbonate and acrylic for your CNC project can be challenging because the two materials have similar properties. Therefore, understanding the unique properties of these materials is critical to the final outcome of your CNC project. In this article, we’ll cover what you need to know about CNC machining acrylic and polycarbonate so you can choose the best material for your CNC project.
Acrylic, also known as plexiglass or polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), and polycarbonate are lightweight, clear thermoplastics that are CNC machined to create clear parts. Acrylic is known for its strength and clarity, making it an excellent alternative to standard glass, while polycarbonate is very tough and impact resistant, making it an ideal material for applications that require transparency and greater durability, such as safety glass choose.
While acrylic (PMMA) and polycarbonate are similar in many ways, there are some important differences between these two common materials that can make one material better than the other for a particular application, or affect the CNC machining process , thus affecting leading time and cost.
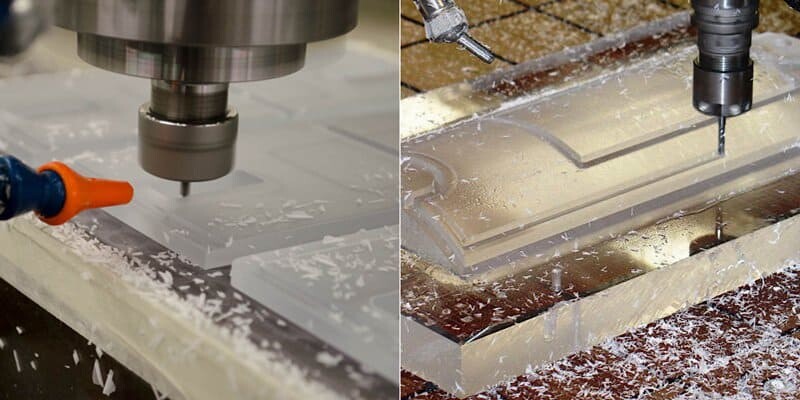

Table of Contents
ToggleCNC Machining Polycarbonate
CNC Machining PMMA
CNC Machining Acrylic and Polycarbonate: What You Need to Know
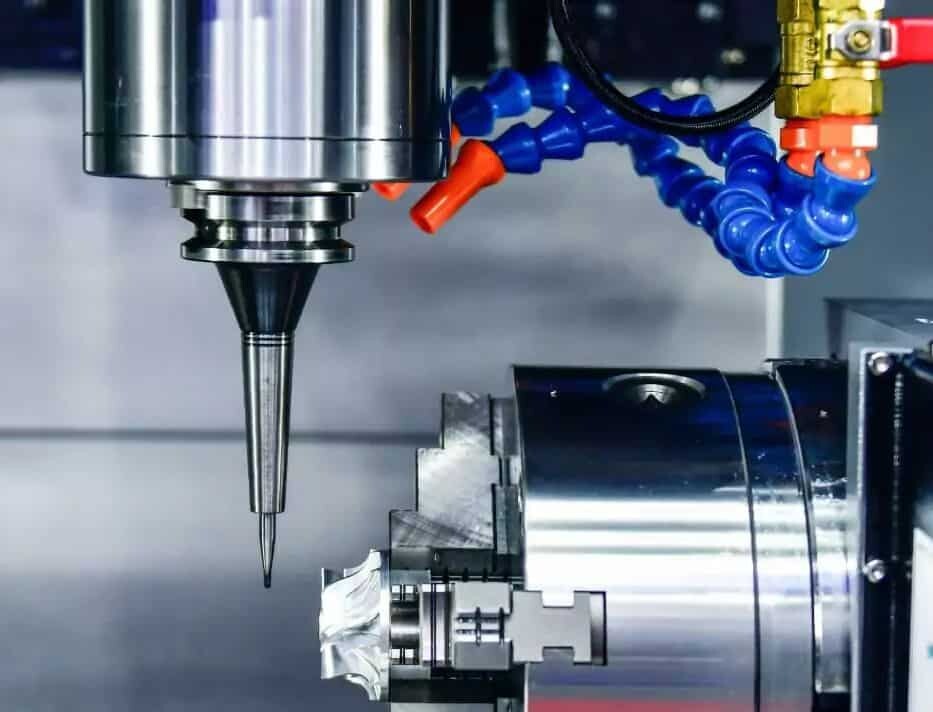
CNC machining acrylic, it is usually better to choose cast acrylic than extruded acrylic, because the latter is more likely to crack or chip during machining. This means that toolpath strategies sometimes need to be chosen carefully to avoid part fragmentation. Also, since acrylics are not very heat resistant, sharp cutting tools must be used to achieve a smooth surface finish. Acrylic’s low melting point means that lower cutting feed rates than other plastics also need to be used during machining, as higher feed rates create more friction and heat and can damage the part. If necessary, acrylic can be kept in the refrigerator prior to processing to ensure it stays as cool as possible.
CNC Machining Polycarbonate.Polycarbonate is tough and impact resistant, making it more suitable for machining, especially CNC milling. However, the sharpness of the cutting tool is still important when CNC machining polycarbonate, as the polycarbonate sheet may melt if too much heat is generated during CNC machining. Since polycarbonate is less brittle than acrylic, it tends to be easier to CNC machine and allows for more standard toolpath strategies. Additionally, due to the higher operating temperature range, more aggressive strategies can be used that are less likely to cause problems, potentially saving time and money.
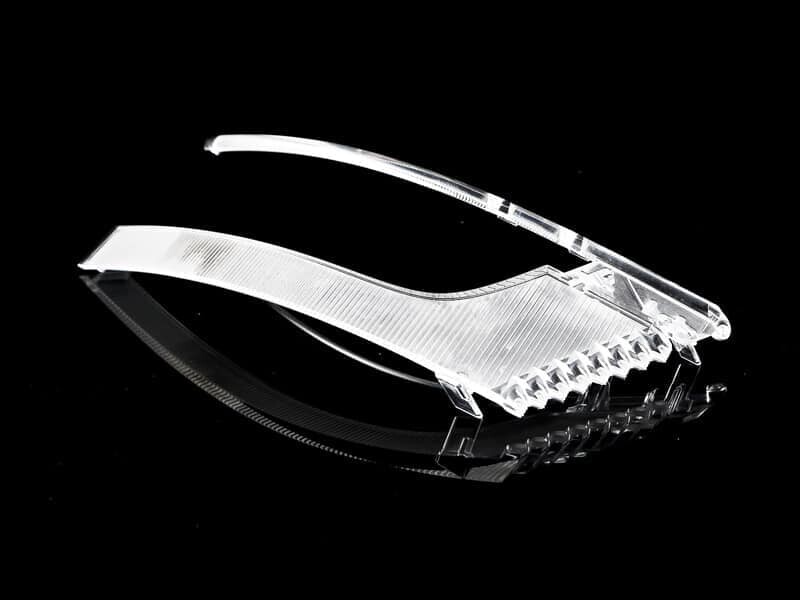

Acrylic and Polycarbonate Applications
Both acrylic and polycarbonate are lightweight, processable and have unique properties that make them suitable for a range of applications across industries.
Acrylic is a popular material in the automotive, construction and aerospace industries and is commonly used in items such as drying boxes, lenses, radiation shields and desiccators. Plus, its clarity, strength, and high impact resistance make it an excellent replacement for glass, and you can find it commonly used in greenhouses, aquariums, terrariums, security barriers, and more.
Polycarbonate, like acrylic, is popular in the automotive, aerospace and construction industries, but its heat resistance and strong dimensional stability make it very popular in the medical industry, where CNC polycarbonate parts can withstand limited autoclave and radiation sterilization. Among its more common applications, polycarbonate is commonly used in point-of-purchase retail displays, face shields, construction, clear manifolds, bulletproof windows, and more.
Advantages and disadvantages of using CNC acrylic to make parts
Acrylic has a range of positive properties, including:
Clarity: Acrylic allows up to 92% of light to pass through, making it more transparent than some grades of glass and most other thermoplastics. It can also be tinted without sacrificing transparency, although more opaque acrylic parts can also be made. What’s more, when formulated with UV stabilizers, it has better resistance to UV radiation and works in the temperature range of 40-80°C.
Strength: Acrylic is stronger and more impact resistant than glass. Most grades of acrylic are four to eight times stronger than glass.
Environmental Resistance: Acrylic is naturally resistant to scratches, weathering and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
Chemical Resistance: Acrylic is resistant to many chemicals, including alkalis, detergents, cleaners and dilute mineral acids.
Hygroscopicity: Acrylic has low moisture absorption, which allows it to retain its size when used outdoors.
Compatibility with coatings: Acrylic parts can be coated with antistatic, hardcoat or antiglare layers to improve their surface quality, prolong their service life and ensure that they meet specific requirements.
Affordable: Despite its strength, durability, and clarity, acrylic is relatively inexpensive to manufacture and process. In comparison, polycarbonate is about 35 – 40% more expensive.
Color: Acrylic is available in a variety of colors.
Disadvantages of acrylic
CNC machining acrylic is not without its drawbacks. As mentioned, acrylic is more prone to cracking and chipping than polycarbonate, and is slightly more difficult to process, as it loses structural integrity and begins to melt at temperatures above 160°C. When designing acrylic parts for CNC machining, you need to keep in mind the relatively low melting point, as it makes the material easier to deform during manufacturing. To avoid the risk of melting and achieve a high-quality surface finish, it is critical to use the proper feed rate and pass depth. Also, to reduce chatter and achieve high-quality cuts, acrylic parts should be machined with cutters that have short flute lengths and depths of cut that are approximately half the diameter of the drill.
The intended use of your product will also determine whether acrylic is the best choice for your CNC project. For example, the very high biocompatibility of acrylic makes it a good choice for bone implants, dentures, or other skin-contact applications; likewise, its resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and scratches makes it ideal for outdoor applications parts used. On the other hand, acrylic may not be the best choice for food containers that are exposed to high temperatures, such as dishwashers or microwave ovens, because acrylic parts only retain their dimensions up to 149°F (65°C), where At one point they start to soften.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Polycarbonate Manufacturing Parts
Advantages of using polycarbonate include:
Clarity: Polycarbonate is a naturally transparent thermoplastic with 88 % light transmission and can transmit light as effectively as glass, making it ideal for lenses, lighting and bulletproof glass. Like acrylic, polycarbonate can be colored without sacrificing clarity.
Variety: There are several polycarbonate formulations on the market, including glass-filled and FDA-compliant variants, so you’ll be able to find one that meets your CNC project’s needs.
Strength and Impact Resistance: Polycarbonate has approximately 200 times the tensile strength of glass and is highly impact resistant. As such, it is often used in bulletproof glass and protective gear.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Stability: Polycarbonate retains its dimensions under most conditions and has a low shrinkage of 0.6 – 0.9%.
Environmental Resistance: Polycarbonate is naturally resistant to UV radiation and can withstand varying humidity levels and fluctuating temperatures, making it an excellent material for outdoor applications and eyewear.
Chemical Resistance: Polycarbonate is resistant to a wide variety of chemicals, including dilute acids, oils, waxes, aliphatic hydrocarbons, alcohols and greases.
Hygroscopicity: Polycarbonate is slightly less hygroscopic than acrylic.
Compatibility with coatings: Like acrylic, polycarbonate components can be coated with antistatic, hardcoat and antiglare coatings. Polycarbonate is also UV and anti-fog compatible.
High Machinability: Since polycarbonate is very durable and heat resistant, it is easier to machine than acrylics.
While polycarbonate offers many advantages, there are also some disadvantages to using polycarbonate in CNC machining projects, including high cost and tendency to dent. Since polycarbonate scratches easily, finishing is more likely to be required, which is further complicated by the fact that only certain finishing processes, such as vapor polishing and coating, are suitable for polycarbonate parts. In addition, PC has average weather resistance, but not UV resistance.
Also, it’s worth noting that polycarbonate parts are also prone to dents or voids in thicker sections. To prevent this, it’s best to break up thicker components into smaller, thinner parts that can be assembled later.
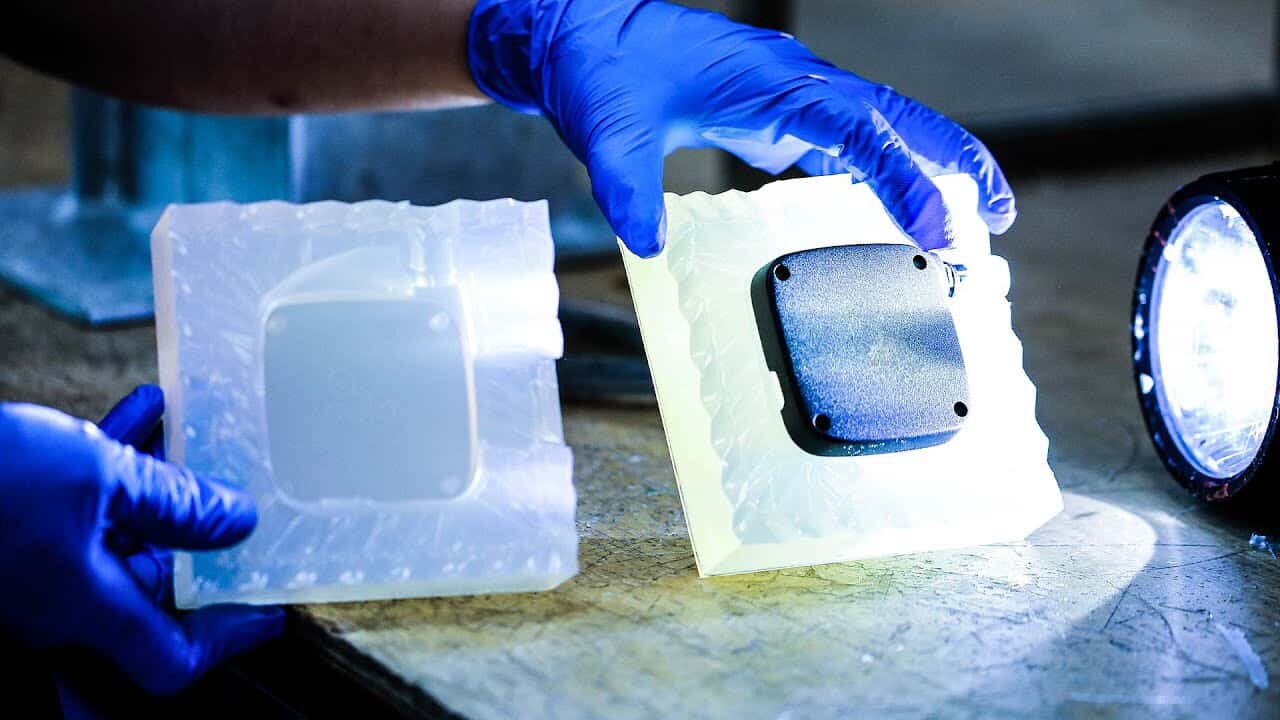
Acrylic and polycarbonate finishing options
There are a variety of finishing options available for acrylic and polycarbonate, some of which can help prepare parts for end-use applications in appearance and aesthetics, and even improve clarity:
Post-machined surface treatment: The standard and most economical surface treatment, “post-machined” or “post-milled” means no additional post-processing of the part. The machined parts have a tight dimensional finish and may represent a faster and more affordable manufacturing option. In some cases, machined parts may have small but visible surface tool marks, blemishes or scratches.
Grit Blasting: Grit blasting is an economical surface preparation method that creates a uniform appearance, tends to leave a dull or satin finish, and is effective in removing tool marks and surface imperfections.
Vapor Polishing: This finishing option uses solvent vapor to transform matte or opaque surfaces into smooth, high-gloss, or optically clear surfaces. Vapor polishing is often used on parts where rough surfaces are unacceptable or where clarity is critical.
The machined surface of acrylic and polycarbonate parts is usually translucent if sufficient care is taken during cutting, but can become nearly opaque if the material is melted. If melting occurs, surface opacity can be addressed with post-processing options such as vapor polishing. However, it is worth noting that the CNC-machined surface of acrylic and polycarbonate parts will not be optically clear, although it is possible to achieve optical clarity if diamond tools are used, but this must be specifically requested during the quoting process because It affects optical clarity. Significantly increased costs.
CNC Machinability of Acrylic and Polycarbonate
Special care should be taken with the design of CNC machined acrylics because of the greater potential for stress cracking. With this in mind, sharp cutting tools are recommended to avoid melting the acrylic or causing cracks; although carbide knives are much less expensive, diamond knives produce the best surface finish. It is also necessary to use a relatively fast feed rate to keep the acrylic from melting, but keep in mind that too fast a feed rate can result in extremely high cutting pressure and breakage.
While polycarbonate is generally better for CNC machining due to its rigidity, toughness, durability, and higher melting point, the downside is that polycarbonate is not as transparent as acrylic. However, if you need to create special-purpose parts such as protective gear, fuse boxes, or large, tough components, transparency may not be an issue. On the other hand, if you’re designing a product where transparency is a top priority, CNC machining acrylic may be worth it.
Get high-quality PC and PMMA parts with AN-Prototype
AN-Prototype is a reliable plastic CNC machining service provider of high quality, high precision PC and PMMA parts. The knowledge of our expert engineers and mechanics enables us to provide quality parts made from engineering plastics such as acrylic and polycarbonate.
Choosing the right material for your fabrication project can be the difference between success and failure. While we’ve explored the pros and cons of acrylic and polycarbonate, it’s worth remembering that they’re not your only options. Many CNC machining materials may be compatible with your part’s design and intended application, and selecting the right material can be a complex process.
Fortunately, manufacturing partners like AN-Prototype can reduce the complexity and solve the challenges faced by some materials. In addition to helping you decide whether acrylic, polycarbonate, or another material is best for your part, our team can provide you with the tools and expertise you need to ensure production runs as smoothly and cost-effectively as possible.
We also offer comprehensive machining capabilities, including CNC machining, 3D printing, vacuum casting, rapid tooling, and more. All of these help us meet your unique requirements, no matter how tight tolerances and surface finishes may be. Contact us today and let us handle your prototyping and part production with shorter lead times and competitive prices.
Conclusion
Compared to acrylic, CNC machined polycarbonate offers unique properties required for different applications, making these materials an ideal replacement for glass. This article compares the differences in material properties, applications, processing and surface treatment options. However, determining the perfect material for your product will depend on your needs.